Cytolysis
Encyclopedia
Lysis
Lysis refers to the breaking down of a cell, often by viral, enzymic, or osmotic mechanisms that compromise its integrity. A fluid containing the contents of lysed cells is called a "lysate"....
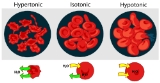
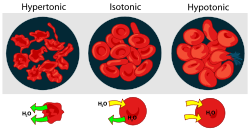
, occurs when a cell bursts due to an osmotic imbalance
Osmosis
Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration, aiming to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides...
that has caused excess water to move into the cell. It occurs in a hypotonic environment, where water diffuse
Diffusion
Molecular diffusion, often called simply diffusion, is the thermal motion of all particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size of the particles...
s into the cell and causes its volume to increase. If the volume of water exceeds the cell membrane
Cell membrane
The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. It basically protects the cell...
's capacity then the cell will burst. The cell will only burst if the cell is an animal cell and it will only expand if it is a plant cell.
In Plants
Cytolysis does not occur in plant cellPlant cell
Plant cells are eukaryotic cells that differ in several key respects from the cells of other eukaryotic organisms. Their distinctive features include:...
s because plant cells have a strong bond that is lacking in the animal cell wall, which can result in the bursting of the cell wall
Cell wall
The cell wall is the tough, usually flexible but sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to...
that contains the osmotic pressure, or turgor pressure
Turgor pressure
Turgor Pressure or turgidity is the main pressure of the cell contents against the cell wall in plant cells and bacteria cells, determined by the water content of the vacuole, resulting from osmotic pressure, i.e...
, which would normally cause cytolysis not to occur. Contrary to organisms without a cell wall, plant cells must be in a hypotonic environment in order to have this turgor pressure, which provides the cells more structural support, preventing the plant from wilting. In a hypertonic environment, plasmolysis
Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis is the process in plant cells where the cytoplasm pulls away from the cell wall due to the loss of water through osmosis. The reverse process, cytolysis, can occur if the cell is in a hypotonic solution resulting in a higher external osmotic pressure and a net flow of water into the cell...
occurs, which is nearly the complete opposite of cytolysis: Instead of expanding, the cytoplasm of the plant cell retracts from the cell wall, causing the plant to wilt.
In Mammals
Osmotic lysis is often one result of a strokeStroke
A stroke, previously known medically as a cerebrovascular accident , is the rapidly developing loss of brain function due to disturbance in the blood supply to the brain. This can be due to ischemia caused by blockage , or a hemorrhage...
, because improper nutrient perfusion and waste removal alter cell metabolism
Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
. Such malfunction results in an inflow of extracellular fluid
Extracellular fluid
Extracellular fluid usually denotes all body fluid outside of cells. The remainder is called intracellular fluid.In some animals, including mammals, the extracellular fluid can be divided into two major subcompartments, interstitial fluid and blood plasma...
into the cells.
In Bacteria
Osmotic lysis would be expected to occur when bacterial cells are treated with a hypotonic solution with added lysozymeLysozyme
Lysozyme, also known as muramidase or N-acetylmuramide glycanhydrolase, are glycoside hydrolases, enzymes that damage bacterial cell walls by catalyzing hydrolysis of 1,4-beta-linkages between N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in a peptidoglycan and between...
.
Prevention
Different cells and organisms have adapted different ways of preventing cytolysis from occurring. For example, the parameciumParamecium
Paramecium is a group of unicellular ciliate protozoa, which are commonly studied as a representative of the ciliate group, and range from about 0.05 to 0.35 mm in length. Simple cilia cover the body, which allow the cell to move with a synchronous motion at speeds of approximately 12 body...
uses a contractile vacuole
Contractile vacuole
A contractile vacuole is a sub-cellular structure involved in osmoregulation. It is found predominantly in protists and in unicellular algae. It was previously known as pulsatile or pulsating vacuole....
, which rapidly pumps out excessive water to prevent the build-up of water and the otherwise subsequent lysis.
Other organisms pump solutes out of their cytosol
Cytosol
The cytosol or intracellular fluid is the liquid found inside cells, that is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into compartments....
, which brings the solute concentration
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
closer to that of their environment and slows down the process of water's diffusion into the cell, preventing cytolysis. If the cell can pump out enough solutes so that an isotonic environment can be achieved, there will be no net movement of water.
See also
- Cell disruptionCell disruptionCell disruption is a method or process for releasing biological molecules from inside a cell.- Choice of disruption method:The production of biologically-interesting molecules using cloning and culturing methods allows the study and manufacture of relevant molecules.Except for excreted molecules,...
- LysisLysisLysis refers to the breaking down of a cell, often by viral, enzymic, or osmotic mechanisms that compromise its integrity. A fluid containing the contents of lysed cells is called a "lysate"....
- Osmotic pressureOsmotic pressureOsmotic pressure is the pressure which needs to be applied to a solution to prevent the inward flow of water across a semipermeable membrane....
- PlasmolysisPlasmolysisPlasmolysis is the process in plant cells where the cytoplasm pulls away from the cell wall due to the loss of water through osmosis. The reverse process, cytolysis, can occur if the cell is in a hypotonic solution resulting in a higher external osmotic pressure and a net flow of water into the cell...
- CrenationCrenationCrenation is the contraction of a cell after exposure to a hypertonic solution, due to the loss of water through osmosis. The word is from the Latin "crenatus" meaning scalloped or notched, and is named for the scalloped-edged shape the cells take on when crenated.Crenation occurs because in a...
- Water intoxicationWater intoxicationWater intoxication, also known as water poisoning, is a potentially fatal disturbance in brain functions that results when the normal balance of electrolytes in the body is pushed outside of safe limits by over-consumption of water....

