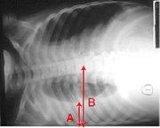
Pleural effusion
Overview
Pleural fluid is secreted by the visceral layer of the pleura and reabsorbed by the parietal layer of the pleura.
Four types of fluids can accumulate in the pleural space:
- Serous fluidSerous fluidIn physiology, the term serous fluid is used for various bodily fluids that are typically pale yellow and transparent, and of a benign nature, that fill the inside of body cavities. Serous fluid originates from serous glands, with secretions enriched with proteins and water. Serous fluid may also...
(hydrothoraxHydrothoraxA hydrothorax is a condition that results from serous fluid accumulating in the pleural cavity. This specific condition can be related to cirrhosis with ascites in which ascitic fluid leaks into the pleural cavity...
) - BloodBloodBlood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
(haemothorax) - ChyleChyleChyle is a milky bodily fluid consisting of lymph and emulsified fats, or free fatty acids . It is formed in the small intestine during digestion of fatty foods, and taken up by lymph vessels specifically known as lacteals...
(chylothoraxChylothoraxA chylothorax is a type of pleural effusion. It results from lymphatic fluid accumulating in the pleural cavity.-Causes:...
) - PusPusPus is a viscous exudate, typically whitish-yellow, yellow, or yellow-brown, formed at the site of inflammatory during infection. An accumulation of pus in an enclosed tissue space is known as an abscess, whereas a visible collection of pus within or beneath the epidermis is known as a pustule or...
(pyothorax or empyemaEmpyemaPleural empyema is an accumulation of pus in the pleural cavity. Most pleural empyemas arise from an infection within the lung , often associated with parapneumonic effusions. There are three stages: exudative, fibrinopurulent and organizing. In the exudative stage, the pus accumulates...
)
Pleural effusion is usually diagnosed on the basis of medical history
Medical history
The medical history or anamnesis of a patient is information gained by a physician by asking specific questions, either of the patient or of other people who know the person and can give suitable information , with the aim of obtaining information useful in formulating a diagnosis and providing...
and physical exam, and confirmed by chest x-ray
Chest X-ray
In medicine, a chest radiograph, commonly called a chest X-ray , is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures...
.

