Plutonium-241
Encyclopedia
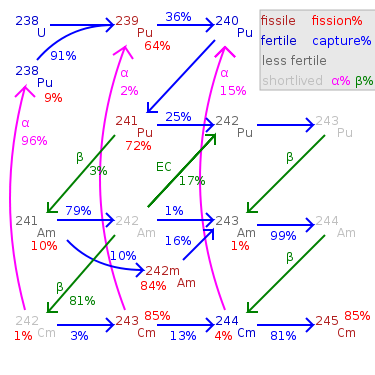
Isotopes of plutonium
Plutonium is an artificial element, except for trace quantities of primordial 244Pu, and thus a standard atomic mass cannot be given. Like all artificial elements, it has no stable isotopes. It was synthesized long before being found in nature, the first isotope synthesized being 238Pu in 1940....
of plutonium
Plutonium
Plutonium is a transuranic radioactive chemical element with the chemical symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, forming a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation...
formed when plutonium-240
Plutonium-240
Plutonium-240 is an isotope of the metal plutonium formed when plutonium-239 captures a neutron. About 62% to 73% of the time when Pu-239 captures a neutron it undergoes fission; the rest of the time it forms Pu-240. The longer a nuclear fuel element remains in a nuclear reactor the greater the...
captures a neutron
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic hadron particle which has the symbol or , no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton. With the exception of hydrogen, nuclei of atoms consist of protons and neutrons, which are therefore collectively referred to as nucleons. The number of...
. Like Pu-239 but unlike 240Pu, 241Pu is fissile
Fissile
In nuclear engineering, a fissile material is one that is capable of sustaining a chain reaction of nuclear fission. By definition, fissile materials can sustain a chain reaction with neutrons of any energy. The predominant neutron energy may be typified by either slow neutrons or fast neutrons...
, with a neutron absorption cross section
Neutron cross-section
In nuclear and particle physics, the concept of a neutron cross section is used to express the likelihood of interaction between an incident neutron and a target nucleus. In conjunction with the neutron flux, it enables the calculation of the reaction rate, for example to derive the thermal power...
about 1/3 greater than 239Pu, and a similar probability of fissioning on neutron absorption, around 73%. In the non-fission case, neutron capture produces plutonium-242
Plutonium-242
Pu-242 is one of the isotopes of plutonium, the second longest-lived, with a half-life of 373,300 years.242Pu's halflife is about 15 times as long as Pu-239's halflife; therefore it is 1/15 as radioactive and not one of the larger contributors to nuclear waste radioactivity.242Pu's gamma ray...
. In general, isotopes with an odd number of neutrons are both more likely to absorb a neutron, and more likely to fission on neutron absorption, than isotopes with an even number of neutrons.
Decay to americium
241Pu has a half-lifeHalf-life
Half-life, abbreviated t½, is the period of time it takes for the amount of a substance undergoing decay to decrease by half. The name was originally used to describe a characteristic of unstable atoms , but it may apply to any quantity which follows a set-rate decay.The original term, dating to...
of 14 years, corresponding to a decay of about 5% of Pu-241 nuclei over a one-year period. The longer spent nuclear fuel
Spent nuclear fuel
Spent nuclear fuel, occasionally called used nuclear fuel, is nuclear fuel that has been irradiated in a nuclear reactor...
waits before reprocessing
Nuclear reprocessing
Nuclear reprocessing technology was developed to chemically separate and recover fissionable plutonium from irradiated nuclear fuel. Reprocessing serves multiple purposes, whose relative importance has changed over time. Originally reprocessing was used solely to extract plutonium for producing...
, the more 241Pu decays to americium-241, which is nonfissile (although fissionable by fast neutrons) and an alpha
Alpha decay
Alpha decay is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle and thereby transforms into an atom with a mass number 4 less and atomic number 2 less...
emitter with a halflife of 432 years
which is a major contributor to the radioactivity of nuclear waste on a scale of hundreds or thousands of years.
Americium
Americium
Americium is a synthetic element that has the symbol Am and atomic number 95. This transuranic element of the actinide series is located in the periodic table below the lanthanide element europium, and thus by analogy was named after another continent, America.Americium was first produced in 1944...
has lower valence
Valence (chemistry)
In chemistry, valence, also known as valency or valence number, is a measure of the number of bonds formed by an atom of a given element. "Valence" can be defined as the number of valence bonds...
and lower electronegativity
Electronegativity
Electronegativity, symbol χ , is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom or a functional group to attract electrons towards itself. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance that its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus...
than plutonium, neptunium
Neptunium
Neptunium is a chemical element with the symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element and belongs to the actinide series. Its most stable isotope, 237Np, is a by-product of nuclear reactors and plutonium production and it can be used as a...
or uranium
Uranium
Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons...
, so in most nuclear reprocessing
Nuclear reprocessing
Nuclear reprocessing technology was developed to chemically separate and recover fissionable plutonium from irradiated nuclear fuel. Reprocessing serves multiple purposes, whose relative importance has changed over time. Originally reprocessing was used solely to extract plutonium for producing...
, Am tends to fractionate not with U, Np, Pu but with the alkaline fission products: lanthanides, strontium
Strontium
Strontium is a chemical element with the symbol Sr and the atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, strontium is a soft silver-white or yellowish metallic element that is highly reactive chemically. The metal turns yellow when exposed to air. It occurs naturally in the minerals celestine and...
, caesium
Caesium
Caesium or cesium is the chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-gold alkali metal with a melting point of 28 °C , which makes it one of only five elemental metals that are liquid at room temperature...
, barium
Barium
Barium is a chemical element with the symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in Group 2, a soft silvery metallic alkaline earth metal. Barium is never found in nature in its pure form due to its reactivity with air. Its oxide is historically known as baryta but it reacts with...
, yttrium
Yttrium
Yttrium is a chemical element with symbol Y and atomic number 39. It is a silvery-metallic transition metal chemically similar to the lanthanides and it has often been classified as a "rare earth element". Yttrium is almost always found combined with the lanthanides in rare earth minerals and is...
, and is therefore not recycled into nuclear fuel
Nuclear fuel
Nuclear fuel is a material that can be 'consumed' by fission or fusion to derive nuclear energy. Nuclear fuels are the most dense sources of energy available...
unless special efforts are made.
In a thermal reactor
Thermal reactor
A thermal reactor is a nuclear reactor that uses slow or thermal neutrons. Most power reactors are of this type. These type of reactors use a neutron moderator to slow neutrons until they approach the average kinetic energy of the surrounding particles, that is, to reduce the speed of the neutrons...
, 241Am captures a neutron to become americium
Americium
Americium is a synthetic element that has the symbol Am and atomic number 95. This transuranic element of the actinide series is located in the periodic table below the lanthanide element europium, and thus by analogy was named after another continent, America.Americium was first produced in 1944...
-242, which quickly becomes curium
Curium
Curium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This radioactive transuranic element of the actinide series was named after Marie Skłodowska-Curie and her husband Pierre Curie. Curium was first intentionally produced and identified in summer 1944 by the group of...
-242 (or, 17.3% of the time, 242Pu) via beta decay
Beta decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay is a type of radioactive decay in which a beta particle is emitted from an atom. There are two types of beta decay: beta minus and beta plus. In the case of beta decay that produces an electron emission, it is referred to as beta minus , while in the case of a...
. Both Cm-242 and Pu-242 are much less likely to absorb a neutron, and even less likely to fission; however, 242Cm is short-lived (halflife 160 days) and almost always undergoes alpha decay
Alpha decay
Alpha decay is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle and thereby transforms into an atom with a mass number 4 less and atomic number 2 less...
to Pu-238 rather than capturing another neutron. In short, Am-241 needs to absorb two neutron
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic hadron particle which has the symbol or , no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton. With the exception of hydrogen, nuclei of atoms consist of protons and neutrons, which are therefore collectively referred to as nucleons. The number of...
s before again becoming a fissile
Fissile
In nuclear engineering, a fissile material is one that is capable of sustaining a chain reaction of nuclear fission. By definition, fissile materials can sustain a chain reaction with neutrons of any energy. The predominant neutron energy may be typified by either slow neutrons or fast neutrons...
isotope.

