
Portuguese-Brazilian
Encyclopedia
Portuguese Brazilians are Brazil
ian citizens whose ancestry originates wholly or partly in Portugal
. Most of the Portuguese
arrived throughout the centuries to Brazil, sought economic opportunities. Although present since the onset of colonization
, Portuguese people began migrating to Brazil in larger numbers and without state support, in the 18th century.
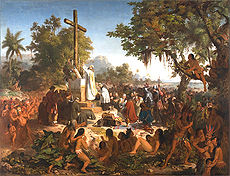


and Diogo Álvares Correia
. At the time the Portuguese Crown was focused on securing its highly lucrative Portuguese Empire
in Asia, and so did little to protect the newly discovered lands in the Americas from foreign interlopers. As a result, many pirates, mainly French, began dealing in pau brasil
with the Amerindians. This situation worried Portugal, which in the 1530s started to encourage the colonization of Brazil, principally for defensive reasons. The towns of Cananéia
(1531), São Vicente
(1532), Porto Seguro
(1534) and Iguape
(1538) date from that period.
By the mid-16th century, Portuguese colonists were already settling in significant numbers, mainly along the coastal regions of Brazil. Numerous cities were established, including Salvador
(1549), São Paulo
(1554) and Rio de Janeiro
(1565). While most Portuguese (and predominantly male) settlers came willingly, some were forced exiles or degredados. Such convicts were sentenced for a variety of crimes according to the Ordenações do Reino, which included common theft, attempted murder and adultery.
During the 17th century, most Portuguese settlers in Brazil, who throughout the entire colonial period tended to originate from Northern Portugal, moved to the northeastern part of the country to establish the first sugar plantations. Some of the new arrivals were New Christians, that is, descendants of Portuguese Jews who had been induced to convert to Catholicism and remained in Portugal, yet were often targeted by the Inquisition (established in 1536) under the accusation of being crypto-Jews. The number of Portuguese Jews and New Christians who settled in colonial Brazil is unknown, but it is estimated that they represented 14% of the White population in Pernambuco
during the 16th century. Between 1579 and 1620, 32% of the owners of cane sugar mill
s (engenho
s) in Pernambuco were of Jewish extraction. Portuguese colonists of Jewish origin settled in Brazil during all colonial period, including during the mass migration of the 18th century, when 300,000 Portuguese went to the mining areas of Minas Gerais
and other regions. Unlike other Portuguese who tended to arrive alone, the Jews used to bring their wives and entire families to Brazil, with a high proportion of endogamy
, as New Christians tended to marry among themselves. They were also likely to mix with Amerindians and Black slaves. Some colonists of Jewish origin were accused of following Judaism and condemned by the Inquisition
, usually being expelled from Brazil and arrested or killed in Portugal. Others were able to hide their Jewish origin and mingled within the Brazilian population, influencing the ethnic and cultural composition of the country.
were discovered in the region of Minas Gerais
, which then led to the arrival of not only Portuguese, but also of native-born Brazilians. Regarding the former, most were peasants from the Minho region in Portugal. In the beginning, Portugal stimulated the immigration of minhotos to Brazil. After some time, however, the number of departures was so great that the Portuguese Crown had to establish barriers to further immigration. Most of these Portuguese involved in the goldrush ended up settling in Minas Gerais and in the Center-West region of Brazil, where they founded dozens of cities such as Ouro Preto
, Congonhas
, Mariana, São João del Rei
, Tiradentes, Goiás
, etc.
In the words of Simão Ferreira Machado, in Triunfo Eucarístico, published in Lisbon in 1734, "half of Portugal was transplanted" to Brazil at that time.
Official estimates - and most estimates made so far - place the number of Portuguese migrants to Colonial Brazil during the gold rush of the XVIII century at 600,000. Though not usually studied, this represented one of the largest movements of European populations to their colonies to the Americas during the colonial times. According to historian Leslie Bethell
, "In 1700 Portugal had a population of about two million people." During the eighteenth century hundreds of thousands left for the Portuguese Colony of Brazil
, despite efforts by the crown to place severe restrictions on emigration.
Between 1748 and 1756, 7,817 settlers from the Azores Islands arrived in Santa Catarina
, located in the Southern Region
of Brazil. Several hundred couples of Azoreans also settled in Rio Grande do Sul
. The majority of those colonists, composed of small farmers and fishermen, settled along the litoral of those two states and founded the cities of Florianópolis
and Porto Alegre
. Unlike previous trends, in the south entire Portuguese families came to seek a better life for themselves, not just men. During this period, the number of Portuguese women in Brazil increased, which resulted in a larger white population
. This was especially true in Southern Brazil.
A significant immigration of very rich Portuguese to Brazil occurred in 1808, when Queen Maria I of Portugal
and her son and regent, the future João VI of Portugal, fleeing from Napoleon's invading armies, relocated to the Portuguese Colony of Brazil with 15,000 members of the royal family, nobles and government, and established themselves in Rio de Janeiro. After the Portuguese military had successfully repelled Napoleon's invasion, King João VI returned to Europe on 26 April 1821, leaving his elder son Prince Pedro de Alcântara as regent to rule Brazil. The Portuguese government attempted to turn Brazil into a colony once again, thus depriving it of its achievements since 1808. The Brazilians refused to yield and Prince Pedro stood by them declaring the country's independence from Portugal on 7 September 1822. On 12 October 1822, Pedro was declared the first Emperor of Brazil and crowned Dom Pedro I on 1 December 1822.. Thousands of ordinary Portuguese
settler
s left for Brazil after independence.
and Rio de Janeiro
, working mainly as small traders or shopkeepers.
They and their descendants were quick to organize themselves and establish mutual aid societies (such as the Casas de Portugal), hospitals (e.g. Beneficência Portuguesa de São Paulo, Beneficência Portuguesa de Porto Alegre
, Hospital Português de Salvador
, Real Hospital Português do Recife
, etc.), libraries (e.g. Real Gabinete Português de Leitura in Rio de Janeiro and in Salvador), newspapers (e.g. Jornal Mundo Lusíada), magazines (e.g. Revista Atlântico) and even sports club
s with football team
s, including two regular contenders of the Brazilian Série A: the Club de Regatas Vasco da Gama
in Rio de Janeiro and the the Associação Portuguesa de Desportos
in São Paulo. Other clubs inlclude Associação Atlética Portuguesa
in Rio de Janeiro, the Associação Atlética Portuguesa Santista
in Santos
, the Associação Portuguesa Londrinense
in Londrina
, and the Tuna Luso Brasileira
in Belém
.
established legislation that hindered the settlement of immigrants in Brazil. WWII reduced immigration from Europe to Brazil; after it, immigration grew again, but, with the completion of demographic transition
in Europe, European emigration gradually dwindled. As this process in Portugal came later than elsewhere in Europe, Portuguese emigration diminished slowly; but it was also gradually redirected to North America and other European countries, particularly France.
However, between 1945 and 1963, during Salazar
's dictatorship (Estado Novo), thousands of Portuguese
citizens still emigrated to Brazil. Due to the independence of Portuguese overseas provinces after the Carnation Revolution
in 1974, a new wave of Portuguese immigrants arrived in Brazil until the late 1970s as refugees. This wave included Portuguese immigrants, including political refugees, who had previously been members of the Portuguese Estado Novo regime's elite, with a reputed background in politics, academics and business in the days of the old regime (António Champalimaud and Marcello Caetano are just a few of its most prominent examples).
Economic reasons, with others of social, religious and political nature, are the main cause for the large Portuguese
diaspora
in Brazil. The country received the majority of Portuguese immigrants in the world.
After Portugal's recovery from the effects of Salazarist dictatorship of the Estado Novo, the Portuguese Colonial war
, and the turmoil of the Carnation Revolution
, in the 1980s and 1990s with the growth of the Portuguese economy and a deeper European integration
, very few Portuguese immigrants
went to Brazil. In the 1990s and 2000s, Portuguese emigrants mainly went to the European Union, followed by Canada, the U.S.A., Venezuela and South Africa.
 The typical Portuguese immigrant in Brazil was a single man. As an example, in the records of the community of Inhaúma, in the countryside of the state of Rio de Janeiro, from 1807 to 1841, the Portuguese-born population comprised approximately 15% of the population, of whom 90% were males. Inhaúma was not unique: this trend had lasted since the beginning of colonization. In 1872, the Consul general of Rio de Janeiro reported: (...)49,610 (Portuguese) arrivals in the past ten years by sailing ships, major, male, 35,740 and, female, 4,280; of these, 13,240 married and 22,500 unmarried; minor, 9,590, as a family, 920(...)
The typical Portuguese immigrant in Brazil was a single man. As an example, in the records of the community of Inhaúma, in the countryside of the state of Rio de Janeiro, from 1807 to 1841, the Portuguese-born population comprised approximately 15% of the population, of whom 90% were males. Inhaúma was not unique: this trend had lasted since the beginning of colonization. In 1872, the Consul general of Rio de Janeiro reported: (...)49,610 (Portuguese) arrivals in the past ten years by sailing ships, major, male, 35,740 and, female, 4,280; of these, 13,240 married and 22,500 unmarried; minor, 9,590, as a family, 920(...)
Although these data are not complete — they do not include who arrived as passengers of small ships or illegally — we clearly see that females made up only 1/8 of total Portuguese immigration. In Bahia
, as of 1872, the situation was even clearer: of a total of 1,498 Portuguese, only 64 were women (about 4.2%).
The disparity between the number of men and women among the Portuguese immigrants in Brazil really started to change in the early 20th century, when the largest numbers of Portuguese immigrated to Brazil. In the records of the Port of Santos
, between 1908 and 1936, Portuguese female immigrants accounted for 32.1% of the Portuguese who entered Brazil, compared to less than 10% before 1872. This figure was similar to the entries of women of other nationalities, such as Italians (35.3% of women), Spaniards (40.6%) and Japanese (43.8%) and higher than the figures found among "Turks" (actually Arabs, 26.7%) and Austrians
(27.3%). However, the majority still immigrated alone to Brazil (53%). Only the "Turks" (62.5%) arrived as unaccompanied immigrants in a higher percentage than the Portuguese. In comparison, only 5.1% of the Japanese immigrants arrived alone to Brazil. The Japanese kept a strong familiar connection when they immigrated to Brazil, with the largest numbers of family members, comprising 5.3 people, followed by Spaniards, with similar figures. The families of Italian origin included lower number of members, at 4.1. The Portuguese, among all immigrants, had the smallest number of people when they immigrated as families: 3.6. About 23% of the Portuguese who disembarked at the Port of Santos were under 12 years old. This figure shows that, for the first time in Brazil's history, large numbers of Portuguese families were settling in Brazil.
The Portuguese also had one of highest illiteracy rates among immigrants arriving to Brazil during the early 20th century: 57.5% of them were illiterate. Only the Spaniards had a higher percentage of illiteracy: 72%. (In comparison, only 13.2% of the German immigrants to Brazil were illiterate.) The waves of Portuguese immigration to Brazil due to both the Carnation Revolution
in 1974 and the European sovereign debt crisis, included large numbers of highly qualified and experienced professionals and businessmen.
Records of the Portuguese immigrants to Brazil in the early 20th century reveal that they had the lowest levels of intermarriage with Brazilians among all European immigrants. Male Portuguese immigrants mainly married Portuguese female immigrants. Of the 22,030 Portuguese men and women who married in Rio de Janeiro from 1907 to 1916, 51% of men married Portuguese women. (Meanwhile 50% of the Italian
men married Italian women and only 47% of Spanish
men married women from their country.) Endogamy
was even higher among the female Portuguese immigrants: 84% of Portuguese women in Rio married Portuguese men, compared to 64% of Italian and 52% of Spanish women who married men from their own countries. The high level of endogamy found among the more recent Portuguese immigrants in Brazil is surprising because of many reasons. In the early 20th century, most of the Portuguese immigrants in Rio were men (a ratio of 320 men to 100 women, compared to the proportion of 266 men to 100 women among all European immigrants). The Portuguese men had fewer female compatriots with whom they could marry than the other foreign men. Despite this, more Portuguese men married compatriots than the other immigrants. Despite the cultural and linguistic similarity between Brazilians and Portuguese, the high rates of endogamy of Portuguese immigrants may be attributed to the prejudice
that Brazilians had toward Portuguese immigrants, who were usually very poor. Due to this poverty, many of the criminals in Rio de Janeiro were Portuguese immigrants: of the men convicted of crimes there during the four years from 1915 to 1918, 32% were Portuguese (although Portuguese immigrants made up only 15% of the male population of Rio de Janeiro in 1920): 47% of counterfeit
ers, 43% of arsonists and 23% of convicted murderers were Portuguese. Exactly half of the 220 individuals convicted of manslaughter
were Portuguese and 54% of the 1,024 individuals who were serving sentences in prison for assault were also from Portugal. Over time, endogamy became less frequent among Portuguese immigrants, even though they remained as the European group that least married Brazilians in Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo records. Only the Japanese immigrants had higher levels of endogamy in Brazil.
The more recent immigrant groups of Portuguese in Brazil keep a close relation with Portugal and the Portuguese culture mainly through the Casa de Portugal. Several events also take place to maintain cultural interchange between Portuguese and Brazilian students, and between the Portugal and the Portuguese community in Brazil. There are many Portuguese associations "Associações Portuguesas" in Brazil. Other institutions preserve the cultural heritage of the Portuguese community like the "Real Gabinete" and the Liceu Literário.
Today, news online like "Mundo Lusíada" keeps Portuguese immigrants informed about the many cultural events of the Portuguese community in Brazil. A recent analysis suggests that the more recent Portuguese immigrants (from 1900 onwards) had "low rates of intermarriage with native Brazilians and other immigrants".
's influence and contribution has been systematically erased from the Brazilian culture. Tomás Antônio Gonzaga
, Padre António Vieira
, Carmen Miranda are some of the Portuguese who are presented as Brazilians. The Brazilian culture
is in large part derived from the Portuguese culture
and the similarities between both cultures and the relatively easy integration
of immigrants in Brazil
, make it nearly impossible for some to keep a separate Portuguese identity.
In the late 1990s and the 2000s, some Portuguese
pensioners have been moving to Brazil, mainly to the northeast, attracted by the tropical weather and the beach
es.
The Portuguese crisis in 2010 and 2011 led to higher immigration of Portuguese citizens to Brazil. In the first six months of 2011, with the economic crisis in Portugal a record number of 328,826 Portuguese citizens made their situation regular in Brazil. This wave of Portuguese immigration to Brazil included large numbers of highly qualified and experienced professionals.
", Brazilians of different "races" may have Portuguese ancestry: Whites
, Blacks
, Amerindians
and people of mixed race
.
There are no reliable figures for how many Brazilians descend from the Portuguese. This is mainly because the Portuguese presence in Brazil is very old, making it almost impossible to find correct numbers even though most Brazilians have Portuguese ancestry.
In 1872, there were 3.7 million Whites
in Brazil (the vast majority of them of Portuguese ancestry), 4.1 million mixed-race
people (mostly of Portuguese-Amerindian-African ancestry) and 1.9 million Blacks (some of whom probably had some degree of Portuguese ancestry). These numbers give the percentage of 80% of people with total or partial Portuguese ancestry in Brazil in the 1870s. At that time, the Portuguese were the only Europeans to settle Brazil in large numbers, since other groups (notably Italians) only started arriving in large numbers after 1875.
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, a new large wave of immigrants from Portugal arrived. From 1881 to 1991, over 1.5 million Portuguese immigrated to Brazil. In 1906, for example, there were 133,393 Portuguese-born people living in Rio de Janeiro, comprising 16% of the city's population. Rio is still today considered the largest "Portuguese city" outside of Portugal itself.
Genetic studies also confirm the strong proportion of Portuguese genetic ancestry in Brazilians. According to one study, at least half of the Brazilian population's Y Chromosome
comes from Portugal. Black Brazilians have an average of 48% non-African genes; most of them may have Portuguese ancestors.
. However, the following list only those who can actually be considered "Portuguese Brazilian" (i.e. either born in Portugal or who have close Portuguese ancestry, 1st or 2nd generation
).


Brazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
ian citizens whose ancestry originates wholly or partly in Portugal
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
. Most of the Portuguese
Portuguese people
The Portuguese are a nation and ethnic group native to the country of Portugal, in the west of the Iberian peninsula of south-west Europe. Their language is Portuguese, and Roman Catholicism is the predominant religion....
arrived throughout the centuries to Brazil, sought economic opportunities. Although present since the onset of colonization
Portuguese colonization of the Americas
Portugal was the leading country in the European exploration of the world in the 15th century. The Treaty of Tordesillas divided the Earth, outside Europe, in 1494 into Spanish and Portuguese global territorial hemispheres for exclusive conquest and colonization...
, Portuguese people began migrating to Brazil in larger numbers and without state support, in the 18th century.
History
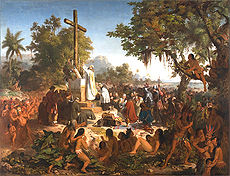


Early Settlement and Colonization (1500-1700)
Some of the earliest colonists for whom we have written records are João RamalhoJoão Ramalho
João Ramalho is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. The population in 2004 is 4,245 and the area is 417.18 km². The elevation is 551 m....
and Diogo Álvares Correia
Caramuru
Diogo Álvares Correia , called Caramuru by the Tupinambá, was a Portuguese settler born in Viana do Castelo. He departed for Brazil in 1509, and his ship wrecked in the coast of Bahia, Diogo Álvares found himself among the Tupinamba Indians...
. At the time the Portuguese Crown was focused on securing its highly lucrative Portuguese Empire
Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire , also known as the Portuguese Overseas Empire or the Portuguese Colonial Empire , was the first global empire in history...
in Asia, and so did little to protect the newly discovered lands in the Americas from foreign interlopers. As a result, many pirates, mainly French, began dealing in pau brasil
Pau Brasil
Pau Brasil is a town and municipality in the state of Bahia in the North-East region of Brazil.-References:...
with the Amerindians. This situation worried Portugal, which in the 1530s started to encourage the colonization of Brazil, principally for defensive reasons. The towns of Cananéia
Cananéia
Cananéia is the southernmost city in the state of São Paulo, Brazil, near to where the Tordesilhas Line passed. The population in 2008 was 12,377 and the area is 1,242.010 km². The elevation is 8 m. The city of Cananéia is host to the Dr. João de Paiva Carvalho research base belonging to the...
(1531), São Vicente
São Vicente, São Paulo
São Vicente is a coastal city of southern São Paulo, Brazil. Its estimated population in 2006 was 329,370 inhabitants.It was the first Portuguese permanent settlement in the Americas and the first capital of the Captaincy of São Vicente, now the state of São Paulo...
(1532), Porto Seguro
Porto Seguro
Porto Seguro is a municipality in the Brazilian state of Bahia. It is the site where the Portuguese explorer Pedro Álvares Cabral first set foot on Brazilian soil on April 22, 1500...
(1534) and Iguape
Iguape
Iguape is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. The population in 2004 was 28,367 and the area is 1,985.4 km², making it the largest city by area in São Paulo state. The elevation is 3 m...
(1538) date from that period.
By the mid-16th century, Portuguese colonists were already settling in significant numbers, mainly along the coastal regions of Brazil. Numerous cities were established, including Salvador
Salvador, Bahia
Salvador is the largest city on the northeast coast of Brazil and the capital of the Northeastern Brazilian state of Bahia. Salvador is also known as Brazil's capital of happiness due to its easygoing population and countless popular outdoor parties, including its street carnival. The first...
(1549), São Paulo
São Paulo
São Paulo is the largest city in Brazil, the largest city in the southern hemisphere and South America, and the world's seventh largest city by population. The metropolis is anchor to the São Paulo metropolitan area, ranked as the second-most populous metropolitan area in the Americas and among...
(1554) and Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro , commonly referred to simply as Rio, is the capital city of the State of Rio de Janeiro, the second largest city of Brazil, and the third largest metropolitan area and agglomeration in South America, boasting approximately 6.3 million people within the city proper, making it the 6th...
(1565). While most Portuguese (and predominantly male) settlers came willingly, some were forced exiles or degredados. Such convicts were sentenced for a variety of crimes according to the Ordenações do Reino, which included common theft, attempted murder and adultery.
During the 17th century, most Portuguese settlers in Brazil, who throughout the entire colonial period tended to originate from Northern Portugal, moved to the northeastern part of the country to establish the first sugar plantations. Some of the new arrivals were New Christians, that is, descendants of Portuguese Jews who had been induced to convert to Catholicism and remained in Portugal, yet were often targeted by the Inquisition (established in 1536) under the accusation of being crypto-Jews. The number of Portuguese Jews and New Christians who settled in colonial Brazil is unknown, but it is estimated that they represented 14% of the White population in Pernambuco
Pernambuco
Pernambuco is a state of Brazil, located in the Northeast region of the country. To the north are the states of Paraíba and Ceará, to the west is Piauí, to the south are Alagoas and Bahia, and to the east is the Atlantic Ocean. There are about of beaches, some of the most beautiful in the...
during the 16th century. Between 1579 and 1620, 32% of the owners of cane sugar mill
Cane sugar mill
A cane sugar mill is a factory that processes sugar cane to produce raw or white sugar.- Processing :Traditionally, sugarcane processing requires two stages. Mills extract raw sugar from freshly harvested cane, and sometimes bleach it to make "mill white" sugar for local consumption...
s (engenho
Engenho
Engenho is a colonial-era Portuguese term for a cane sugar mill and the associated facilities. The word engenho usually only referred to the mill, but it could also describe the area as a whole including land, a mill, the people who farmed and who had a knowledge of sugar production, and a crop of...
s) in Pernambuco were of Jewish extraction. Portuguese colonists of Jewish origin settled in Brazil during all colonial period, including during the mass migration of the 18th century, when 300,000 Portuguese went to the mining areas of Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais is one of the 26 states of Brazil, of which it is the second most populous, the third richest, and the fourth largest in area. Minas Gerais is the Brazilian state with the largest number of Presidents of Brazil, the current one, Dilma Rousseff, being one of them. The capital is the...
and other regions. Unlike other Portuguese who tended to arrive alone, the Jews used to bring their wives and entire families to Brazil, with a high proportion of endogamy
Endogamy
Endogamy is the practice of marrying within a specific ethnic group, class, or social group, rejecting others on such basis as being unsuitable for marriage or other close personal relationships. A Greek Orthodox Christian endogamist, for example, would require that a marriage be only with another...
, as New Christians tended to marry among themselves. They were also likely to mix with Amerindians and Black slaves. Some colonists of Jewish origin were accused of following Judaism and condemned by the Inquisition
Inquisition
The Inquisition, Inquisitio Haereticae Pravitatis , was the "fight against heretics" by several institutions within the justice-system of the Roman Catholic Church. It started in the 12th century, with the introduction of torture in the persecution of heresy...
, usually being expelled from Brazil and arrested or killed in Portugal. Others were able to hide their Jewish origin and mingled within the Brazilian population, influencing the ethnic and cultural composition of the country.
Growing Portuguese immigrants (1700-1822)
In the 18th century, immigration to Brazil from Portugal increased dramatically. Many gold and diamond minesMining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the earth, from an ore body, vein or seam. The term also includes the removal of soil. Materials recovered by mining include base metals, precious metals, iron, uranium, coal, diamonds, limestone, oil shale, rock...
were discovered in the region of Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais is one of the 26 states of Brazil, of which it is the second most populous, the third richest, and the fourth largest in area. Minas Gerais is the Brazilian state with the largest number of Presidents of Brazil, the current one, Dilma Rousseff, being one of them. The capital is the...
, which then led to the arrival of not only Portuguese, but also of native-born Brazilians. Regarding the former, most were peasants from the Minho region in Portugal. In the beginning, Portugal stimulated the immigration of minhotos to Brazil. After some time, however, the number of departures was so great that the Portuguese Crown had to establish barriers to further immigration. Most of these Portuguese involved in the goldrush ended up settling in Minas Gerais and in the Center-West region of Brazil, where they founded dozens of cities such as Ouro Preto
Ouro Preto
-History:Founded at the end of the 17th century, Ouro Preto was originally called Vila Rica, or "rich village," the focal point of the gold rush and Brazil's golden age in the 18th century under Portuguese rule....
, Congonhas
Congonhas
Congonhas is a historical Brazilian city located in the state of Minas Gerais. It is situated south from Belo Horizonte, the capital of state of Minas Gerais, by the highway BR-040...
, Mariana, São João del Rei
São João del Rei
São João del-Rei also spelled São João del Rey or São João del Rei is a historical city in the state of Minas Gerais, Brazil.Population: 40,600 inhabitants....
, Tiradentes, Goiás
Goiás
Goiás is a state of Brazil, located in the central part of the country. The name Goiás comes from the name of an indigenous community...
, etc.
In the words of Simão Ferreira Machado, in Triunfo Eucarístico, published in Lisbon in 1734, "half of Portugal was transplanted" to Brazil at that time.
Official estimates - and most estimates made so far - place the number of Portuguese migrants to Colonial Brazil during the gold rush of the XVIII century at 600,000. Though not usually studied, this represented one of the largest movements of European populations to their colonies to the Americas during the colonial times. According to historian Leslie Bethell
Leslie Bethell
Leslie Michael Bethell is an English historian, university professor, and Brazilianist who specializes in the study of 19th and 20th Century Latin America, emphasizing on Brazil in particular. He received both his Bachelor of Arts and Doctorate in History at the University of London...
, "In 1700 Portugal had a population of about two million people." During the eighteenth century hundreds of thousands left for the Portuguese Colony of Brazil
Colonial Brazil
In the history of Brazil, Colonial Brazil, officially the Viceroyalty of Brazil comprises the period from 1500, with the arrival of the Portuguese, until 1815, when Brazil was elevated to kingdom alongside Portugal as the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves.During the over 300 years...
, despite efforts by the crown to place severe restrictions on emigration.
Between 1748 and 1756, 7,817 settlers from the Azores Islands arrived in Santa Catarina
Santa Catarina (state)
Santa Catarina is a state in southern Brazil with one of the highest standards of living in Latin America. Its capital is Florianópolis, which mostly lies on the Santa Catarina Island. Neighbouring states are Rio Grande do Sul to the south and Paraná to the north. It is bounded on the east by...
, located in the Southern Region
Southern Region, Brazil
The South Region of Brazil is one of the five regions of Brazil. It includes the states of Paraná, Santa Catarina and Rio Grande do Sul and covers 576,409.6 km ², being the smallest portion of the country...
of Brazil. Several hundred couples of Azoreans also settled in Rio Grande do Sul
Rio Grande do Sul
Rio Grande do Sul is the southernmost state in Brazil, and the state with the fifth highest Human Development Index in the country. In this state is located the southernmost city in the country, Chuí, on the border with Uruguay. In the region of Bento Gonçalves and Caxias do Sul, the largest wine...
. The majority of those colonists, composed of small farmers and fishermen, settled along the litoral of those two states and founded the cities of Florianópolis
Florianópolis
-Climate:Florianópolis experiences a warm humid subtropical climate, falling just short of a true tropical climate. The seasons of the year are distinct, with a well-defined summer and winter, and characteristic weather for autumn and spring. Frost is infrequent, but occurs occasionally in the winter...
and Porto Alegre
Porto Alegre
Porto Alegre is the tenth most populous municipality in Brazil, with 1,409,939 inhabitants, and the centre of Brazil's fourth largest metropolitan area . It is also the capital city of the southernmost Brazilian state of Rio Grande do Sul. The city is the southernmost capital city of a Brazilian...
. Unlike previous trends, in the south entire Portuguese families came to seek a better life for themselves, not just men. During this period, the number of Portuguese women in Brazil increased, which resulted in a larger white population
White Brazilian
White Brazilians make up 48.4% of Brazil's population, or around 92 million people, according to the IBGE's 2008 PNAD . Whites are present in the entire territory of Brazil, although the main concentrations are found in the South and Southeastern parts of the country...
. This was especially true in Southern Brazil.
A significant immigration of very rich Portuguese to Brazil occurred in 1808, when Queen Maria I of Portugal
Maria I of Portugal
Maria I was Queen regnant of Portugal and the Algarves from 1777 until her death. Known as Maria the Pious , or Maria the Mad , she was the first undisputed Queen regnant of Portugal...
and her son and regent, the future João VI of Portugal, fleeing from Napoleon's invading armies, relocated to the Portuguese Colony of Brazil with 15,000 members of the royal family, nobles and government, and established themselves in Rio de Janeiro. After the Portuguese military had successfully repelled Napoleon's invasion, King João VI returned to Europe on 26 April 1821, leaving his elder son Prince Pedro de Alcântara as regent to rule Brazil. The Portuguese government attempted to turn Brazil into a colony once again, thus depriving it of its achievements since 1808. The Brazilians refused to yield and Prince Pedro stood by them declaring the country's independence from Portugal on 7 September 1822. On 12 October 1822, Pedro was declared the first Emperor of Brazil and crowned Dom Pedro I on 1 December 1822.. Thousands of ordinary Portuguese
Portuguese people
The Portuguese are a nation and ethnic group native to the country of Portugal, in the west of the Iberian peninsula of south-west Europe. Their language is Portuguese, and Roman Catholicism is the predominant religion....
settler
Settler
A settler is a person who has migrated to an area and established permanent residence there, often to colonize the area. Settlers are generally people who take up residence on land and cultivate it, as opposed to nomads...
s left for Brazil after independence.
Portuguese immigration to Brazil (1822-1960)
A few years after independence from Portugal in 1822, Portuguese people would start arriving in Brazil as immigrants, and the Portuguese population in Brazil actually increased. Most of them were peasants from the rural areas of Portugal. The majority settled in urban centers, mainly in São PauloSão Paulo
São Paulo is the largest city in Brazil, the largest city in the southern hemisphere and South America, and the world's seventh largest city by population. The metropolis is anchor to the São Paulo metropolitan area, ranked as the second-most populous metropolitan area in the Americas and among...
and Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro , commonly referred to simply as Rio, is the capital city of the State of Rio de Janeiro, the second largest city of Brazil, and the third largest metropolitan area and agglomeration in South America, boasting approximately 6.3 million people within the city proper, making it the 6th...
, working mainly as small traders or shopkeepers.
They and their descendants were quick to organize themselves and establish mutual aid societies (such as the Casas de Portugal), hospitals (e.g. Beneficência Portuguesa de São Paulo, Beneficência Portuguesa de Porto Alegre
Porto Alegre
Porto Alegre is the tenth most populous municipality in Brazil, with 1,409,939 inhabitants, and the centre of Brazil's fourth largest metropolitan area . It is also the capital city of the southernmost Brazilian state of Rio Grande do Sul. The city is the southernmost capital city of a Brazilian...
, Hospital Português de Salvador
Salvador, Bahia
Salvador is the largest city on the northeast coast of Brazil and the capital of the Northeastern Brazilian state of Bahia. Salvador is also known as Brazil's capital of happiness due to its easygoing population and countless popular outdoor parties, including its street carnival. The first...
, Real Hospital Português do Recife
Recife
Recife is the fifth-largest metropolitan area in Brazil with 4,136,506 inhabitants, the largest metropolitan area of the North/Northeast Regions, the 5th-largest metropolitan influence area in Brazil, and the capital and largest city of the state of Pernambuco. The population of the city proper...
, etc.), libraries (e.g. Real Gabinete Português de Leitura in Rio de Janeiro and in Salvador), newspapers (e.g. Jornal Mundo Lusíada), magazines (e.g. Revista Atlântico) and even sports club
Sports club
A sports club or sport club, sometimes athletics club or sports association is a club for the purpose of playing one or more sports...
s with football team
Football team
A football team is the collective name given to a group of players selected together in the various team sports known as football.Such teams could be selected to play in an against an opposing team, to represent a football club, group, state or nation, an All-star team or even selected as a...
s, including two regular contenders of the Brazilian Série A: the Club de Regatas Vasco da Gama
Club de Regatas Vasco da Gama
Club de Regatas Vasco da Gama |Rowing Club]]), usually known as Vasco da Gama or simply Vasco, is a famous and traditional Brazilian multisports club from Rio de Janeiro in Brazil, founded on August 21, 1898...
in Rio de Janeiro and the the Associação Portuguesa de Desportos
Associação Portuguesa de Desportos
Associação Portuguesa de Desportos, usually called Portuguesa or Lusa, is a sports club, and a Brazilian football team from São Paulo in São Paulo state, founded on August 14, 1920 by the Portuguese population of the city.-History:...
in São Paulo. Other clubs inlclude Associação Atlética Portuguesa
Associação Atlética Portuguesa (RJ)
Associação Atlética Portuguesa, or Portuguesa as they are usually called, is a traditional Brazilian football team from Rio de Janeiro in Rio de Janeiro, founded on December 17, 1924.-History:...
in Rio de Janeiro, the Associação Atlética Portuguesa Santista
Associação Atlética Portuguesa Santista
Associação Atlética Portuguesa, usually known as Portuguesa Santista, is a Brazilian football team from Santos in São Paulo state, founded on November 20, 1917 by the Portuguese population of the city....
in Santos
Santos (São Paulo)
-Sister cities: Shimonoseki, Japan Nagasaki, Japan Funchal, Portugal Trieste, Italy Coimbra, Portugal Ansião, Portugal Arouca, Portugal Ushuaia, Argentina Havana, Cuba Taizhou. China Ningbo. China Constanţa, Romania Ulsan, South Korea Colón, Panama* Cadiz, Spain...
, the Associação Portuguesa Londrinense
Associação Portuguesa Londrinense
Associação Portuguesa Londrinense, usually known simply as Portuguesa Londrinense, is a Brazilian football team from the city of Londrina, Paraná state, founded on May 14, 1950.-History:...
in Londrina
Londrina
Londrina is a city located in the northern region of the state of Paraná, Brazil, and is 369 km away from the capital, Curitiba. Londrina was originally founded by British settlers. The city exerts great influence on Paraná and Brazil's south region...
, and the Tuna Luso Brasileira
Tuna Luso Brasileira
Tuna Luso Brasileira, or Tuna Luso as they are usually called, is a Brazilian football team from Belém in Pará, founded on January 1, 1903. The club won the Campeonato Brasileiro Série B in 1985, the Campeonato Brasileiro Série C in 1992, and has also won the state championship ten...
in Belém
Belém
Belém is a Brazilian city, the capital and largest city of state of Pará, in the country's north region. It is the entrance gate to the Amazon with a busy port, airport and bus/coach station...
.
Dwindling Portuguese immigration (1960-2009)
In the 1930s, the Brazilian President Getúlio VargasGetúlio Vargas
Getúlio Dornelles Vargas served as President of Brazil, first as dictator, from 1930 to 1945, and in a democratically elected term from 1951 until his suicide in 1954. Vargas led Brazil for 18 years, the most for any President, and second in Brazilian history to Emperor Pedro II...
established legislation that hindered the settlement of immigrants in Brazil. WWII reduced immigration from Europe to Brazil; after it, immigration grew again, but, with the completion of demographic transition
Demographic transition
The demographic transition model is the transition from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates as a country develops from a pre-industrial to an industrialized economic system. The theory is based on an interpretation of demographic history developed in 1929 by the American...
in Europe, European emigration gradually dwindled. As this process in Portugal came later than elsewhere in Europe, Portuguese emigration diminished slowly; but it was also gradually redirected to North America and other European countries, particularly France.
However, between 1945 and 1963, during Salazar
António de Oliveira Salazar
António de Oliveira Salazar, GColIH, GCTE, GCSE served as the Prime Minister of Portugal from 1932 to 1968. He also served as acting President of the Republic briefly in 1951. He founded and led the Estado Novo , the authoritarian, right-wing government that presided over and controlled Portugal...
's dictatorship (Estado Novo), thousands of Portuguese
Portuguese people
The Portuguese are a nation and ethnic group native to the country of Portugal, in the west of the Iberian peninsula of south-west Europe. Their language is Portuguese, and Roman Catholicism is the predominant religion....
citizens still emigrated to Brazil. Due to the independence of Portuguese overseas provinces after the Carnation Revolution
Carnation Revolution
The Carnation Revolution , also referred to as the 25 de Abril , was a military coup started on 25 April 1974, in Lisbon, Portugal, coupled with an unanticipated and extensive campaign of civil resistance...
in 1974, a new wave of Portuguese immigrants arrived in Brazil until the late 1970s as refugees. This wave included Portuguese immigrants, including political refugees, who had previously been members of the Portuguese Estado Novo regime's elite, with a reputed background in politics, academics and business in the days of the old regime (António Champalimaud and Marcello Caetano are just a few of its most prominent examples).
Economic reasons, with others of social, religious and political nature, are the main cause for the large Portuguese
Portuguese people
The Portuguese are a nation and ethnic group native to the country of Portugal, in the west of the Iberian peninsula of south-west Europe. Their language is Portuguese, and Roman Catholicism is the predominant religion....
diaspora
Diaspora
A diaspora is "the movement, migration, or scattering of people away from an established or ancestral homeland" or "people dispersed by whatever cause to more than one location", or "people settled far from their ancestral homelands".The word has come to refer to historical mass-dispersions of...
in Brazil. The country received the majority of Portuguese immigrants in the world.
After Portugal's recovery from the effects of Salazarist dictatorship of the Estado Novo, the Portuguese Colonial war
Portuguese Colonial War
The Portuguese Colonial War , also known in Portugal as the Overseas War or in the former colonies as the War of liberation , was fought between Portugal's military and the emerging nationalist movements in Portugal's African colonies between 1961 and 1974, when the Portuguese regime was...
, and the turmoil of the Carnation Revolution
Carnation Revolution
The Carnation Revolution , also referred to as the 25 de Abril , was a military coup started on 25 April 1974, in Lisbon, Portugal, coupled with an unanticipated and extensive campaign of civil resistance...
, in the 1980s and 1990s with the growth of the Portuguese economy and a deeper European integration
European integration
European integration is the process of industrial, political, legal, economic integration of states wholly or partially in Europe...
, very few Portuguese immigrants
Immigration to Brazil
Immigration to Brazil is the movement to Brazil of foreign persons to reside permanently. It should not be confused with the colonisation of the country by the Portuguese, or with the forcible bringing of people from Africa as slaves....
went to Brazil. In the 1990s and 2000s, Portuguese emigrants mainly went to the European Union, followed by Canada, the U.S.A., Venezuela and South Africa.
The Portuguese sovereign debt and Eurozone crisis (2009-present)
In the first six months of 2011, with the economic crisis in Portugal and several other European Union member states, including Spain, Italy, Ireland and Greece, a record number of 328,826 Portuguese citizens made their situation regular in Brazil. One of the reasons which explained this rise in Portuguese immigration to Brazil was the economic crisis in Portugal, where unemployment rate rose to over 12,5%. In that period, the Portuguese lead the numbers of foreigners making their situation regular in Brazil. This wave differentiates from the two previous waves by the higher education level of the new Portuguese emigrants, what represents an effective brain drain since large numbers of highly qualified and experienced professionals and businessmen left their country.Portuguese immigration in numbers
| Portuguese immigration to Brazil Source: Brazilian Institute for Geography and Statistics | |||||||||||||||
| 1500-1700 | 1701-1760 | 1808-1817 | 1827-1829 | 1837-1841 | 1856-1857 | 1881-1900 | 1901-1930 | 1931-1950 | 1951-1960 | 1961-1967 | 1981-1991 | ||||
| 100,000 | 600,000 | 24,000 | 2,004 | 629 | 16,108 | 316,204 | 754,147 | 148,699 | 235,635 | 54,767 | 4,605 | ||||
Characteristics of the immigrants

Although these data are not complete — they do not include who arrived as passengers of small ships or illegally — we clearly see that females made up only 1/8 of total Portuguese immigration. In Bahia
Bahia
Bahia is one of the 26 states of Brazil, and is located in the northeastern part of the country on the Atlantic coast. It is the fourth most populous Brazilian state after São Paulo, Minas Gerais and Rio de Janeiro, and the fifth-largest in size...
, as of 1872, the situation was even clearer: of a total of 1,498 Portuguese, only 64 were women (about 4.2%).
The disparity between the number of men and women among the Portuguese immigrants in Brazil really started to change in the early 20th century, when the largest numbers of Portuguese immigrated to Brazil. In the records of the Port of Santos
Port of Santos
The Port of Santos is located in the city of Santos, Brazil. As of 2006, it is the busiest container port in Latin America. It possesses a wide variety of cargo handling terminals - solid and liquid bulk, containers and general loads. It is Brazil's leading port in container traffic...
, between 1908 and 1936, Portuguese female immigrants accounted for 32.1% of the Portuguese who entered Brazil, compared to less than 10% before 1872. This figure was similar to the entries of women of other nationalities, such as Italians (35.3% of women), Spaniards (40.6%) and Japanese (43.8%) and higher than the figures found among "Turks" (actually Arabs, 26.7%) and Austrians
Austrians
Austrians are a nation and ethnic group, consisting of the population of the Republic of Austria and its historical predecessor states who share a common Austrian culture and Austrian descent....
(27.3%). However, the majority still immigrated alone to Brazil (53%). Only the "Turks" (62.5%) arrived as unaccompanied immigrants in a higher percentage than the Portuguese. In comparison, only 5.1% of the Japanese immigrants arrived alone to Brazil. The Japanese kept a strong familiar connection when they immigrated to Brazil, with the largest numbers of family members, comprising 5.3 people, followed by Spaniards, with similar figures. The families of Italian origin included lower number of members, at 4.1. The Portuguese, among all immigrants, had the smallest number of people when they immigrated as families: 3.6. About 23% of the Portuguese who disembarked at the Port of Santos were under 12 years old. This figure shows that, for the first time in Brazil's history, large numbers of Portuguese families were settling in Brazil.
The Portuguese also had one of highest illiteracy rates among immigrants arriving to Brazil during the early 20th century: 57.5% of them were illiterate. Only the Spaniards had a higher percentage of illiteracy: 72%. (In comparison, only 13.2% of the German immigrants to Brazil were illiterate.) The waves of Portuguese immigration to Brazil due to both the Carnation Revolution
Carnation Revolution
The Carnation Revolution , also referred to as the 25 de Abril , was a military coup started on 25 April 1974, in Lisbon, Portugal, coupled with an unanticipated and extensive campaign of civil resistance...
in 1974 and the European sovereign debt crisis, included large numbers of highly qualified and experienced professionals and businessmen.
| Portuguese emigration at the end XIX century to Brazil http://www.revistasusp.sibi.usp.br/scielo.php?pid=S0034-83091991000100004&script=sci_arttext#nt20 | |
|---|---|
| Region | Percentage |
| Beira Litoral Beira Litoral Province Beira Litoral is a former province of Portugal, formally instituted in an administrative reform of 1936. The territory corresponds mainly to the Douro Province from the 19th century... |
25% |
| Beira Alta | 22,6% |
| Douro Litoral Douro Litoral Douro Litoral is a historical province of Portugal. It is centered on the city of Porto, now the capital of the Norte Region. Other important cities in the province are Vila Nova de Gaia, Matosinhos, Maia, Póvoa de Varzim, and the historically important Penafiel, Amarante, Feira, Vila do Conde.The... |
17% |
| Trás-os-Montes Trás-os-Montes (region) Trás-os-Montes was one of the 13 regions of continental Portugal identified by geographer Amorim Girão, in a study published between 1927 and 1930.Together with Alto Douro it formed Trás-os-Montes e Alto Douro Province.- See also :... |
14,5% |
| Estremadura Estremadura Estremadura may refer to:* Estremadura Province * Estremadura Province * Lisboa VR, a Portuguese wine region called Estremadura until 2009... to the North of Tejo River (included the city of Lisbon Lisbon Lisbon is the capital city and largest city of Portugal with a population of 545,245 within its administrative limits on a land area of . The urban area of Lisbon extends beyond the administrative city limits with a population of 3 million on an area of , making it the 9th most populous urban... ) |
6,3% |
| Baixo Tejo or the part of Estremadura to the South of Tejo River | 0,6% |
| Beira Baixa | 0,5% |
| Ribatejo Ribatejo The Ribatejo is the most central of the traditional provinces of Portugal, with no coastline or border with Spain. The region is crossed by the Tagus River... |
0,5% |
| Algarve | 0,4% |
| Alto Alentejo Alto Alentejo Province Alto Alentejo was a Portuguese province. It was abolished with the Constitution of 1976.The area is now covered by Alto Alentejo Subregion and Alentejo Central Subregion.-Municipalities:*Alandroal Municipality*Alter do Chão Municipality... |
0,1% |
Intermarriage with other ethnic groups
| Marriages of Portuguese immigrants in Rio de Janeiro (1907–1916) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Nationalities of the grooms and brides | Number of marriages | ||
| Portuguese man and Portuguese woman | 6,964 | ||
| Portuguese man and Brazilian woman | 6,176 | ||
| Portuguese man and Spanish woman | 357 | ||
| Portuguese man and Italian woman | 156 | ||
| Portuguese man and another foreign woman | 100 | ||
| Total of marriages | 13,753 | ||
Records of the Portuguese immigrants to Brazil in the early 20th century reveal that they had the lowest levels of intermarriage with Brazilians among all European immigrants. Male Portuguese immigrants mainly married Portuguese female immigrants. Of the 22,030 Portuguese men and women who married in Rio de Janeiro from 1907 to 1916, 51% of men married Portuguese women. (Meanwhile 50% of the Italian
Italian Brazilian
-Italian immigration to Brazil:The Italian government claims there are 25 million Brazilians of Italian descent, which would be the largest population of Italian background outside of Italy itself. There are no actual surveys, or even verifiable calculations supporting such claims. According to...
men married Italian women and only 47% of Spanish
Spanish immigration to Brazil
Spanish emigration peaked in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and it was concentrated to Argentina and Cuba. Between 1882 and 1930, 3,297,312 Spaniards emigrated, of whom 1,594,622 went to Argentina and 1,118,960 went to Cuba...
men married women from their country.) Endogamy
Endogamy
Endogamy is the practice of marrying within a specific ethnic group, class, or social group, rejecting others on such basis as being unsuitable for marriage or other close personal relationships. A Greek Orthodox Christian endogamist, for example, would require that a marriage be only with another...
was even higher among the female Portuguese immigrants: 84% of Portuguese women in Rio married Portuguese men, compared to 64% of Italian and 52% of Spanish women who married men from their own countries. The high level of endogamy found among the more recent Portuguese immigrants in Brazil is surprising because of many reasons. In the early 20th century, most of the Portuguese immigrants in Rio were men (a ratio of 320 men to 100 women, compared to the proportion of 266 men to 100 women among all European immigrants). The Portuguese men had fewer female compatriots with whom they could marry than the other foreign men. Despite this, more Portuguese men married compatriots than the other immigrants. Despite the cultural and linguistic similarity between Brazilians and Portuguese, the high rates of endogamy of Portuguese immigrants may be attributed to the prejudice
Prejudice
Prejudice is making a judgment or assumption about someone or something before having enough knowledge to be able to do so with guaranteed accuracy, or "judging a book by its cover"...
that Brazilians had toward Portuguese immigrants, who were usually very poor. Due to this poverty, many of the criminals in Rio de Janeiro were Portuguese immigrants: of the men convicted of crimes there during the four years from 1915 to 1918, 32% were Portuguese (although Portuguese immigrants made up only 15% of the male population of Rio de Janeiro in 1920): 47% of counterfeit
Counterfeit
To counterfeit means to illegally imitate something. Counterfeit products are often produced with the intent to take advantage of the superior value of the imitated product...
ers, 43% of arsonists and 23% of convicted murderers were Portuguese. Exactly half of the 220 individuals convicted of manslaughter
Manslaughter
Manslaughter is a legal term for the killing of a human being, in a manner considered by law as less culpable than murder. The distinction between murder and manslaughter is said to have first been made by the Ancient Athenian lawmaker Dracon in the 7th century BC.The law generally differentiates...
were Portuguese and 54% of the 1,024 individuals who were serving sentences in prison for assault were also from Portugal. Over time, endogamy became less frequent among Portuguese immigrants, even though they remained as the European group that least married Brazilians in Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo records. Only the Japanese immigrants had higher levels of endogamy in Brazil.
| Brazilians who were born to a foreign-born father (1940 Census) | |
|---|---|
| Main places of birth of the father | Number of children |
| Italy | 1,260,931 |
| Portugal | 735,929 |
| Spain | 340,479 |
| Germany | 159,809 |
| Syria- Lebanon- Palestine- Iraq - Middle-Eastern | 107,074 |
| Japan-Korea | 104,355 |
| Brazilians who were born to a foreign-born mother (1940 Census) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Main places of birth of the mother | Number of female immigrants over 12 years old who had children | Number of children |
| Italy | 130,273 | 1,069,862 |
| Portugal | 99,197 | 524,940 |
| Spain | 66,354 | 436,305 |
| Japan | 35,640 | 171,790 |
| Germany | 22,232 | 98,653 |
Portuguese-Brazilian identity
Brazil was colonized by Portugal, and both countries share Portugese, Roman Catholicism, and many traditions. After independence, the elite of Brazil, although of Portuguese descent, tried to diminish the influence of the Portuguese culture in the new country and to establish a specifically Brazilian culture..The more recent immigrant groups of Portuguese in Brazil keep a close relation with Portugal and the Portuguese culture mainly through the Casa de Portugal. Several events also take place to maintain cultural interchange between Portuguese and Brazilian students, and between the Portugal and the Portuguese community in Brazil. There are many Portuguese associations "Associações Portuguesas" in Brazil. Other institutions preserve the cultural heritage of the Portuguese community like the "Real Gabinete" and the Liceu Literário.
Today, news online like "Mundo Lusíada" keeps Portuguese immigrants informed about the many cultural events of the Portuguese community in Brazil. A recent analysis suggests that the more recent Portuguese immigrants (from 1900 onwards) had "low rates of intermarriage with native Brazilians and other immigrants".
Identity merge
Many Portuguese who had a significant importance in Brazilian culture are known in Brazil as Brazilian. In this way, much of the Portuguese peoplePortuguese people
The Portuguese are a nation and ethnic group native to the country of Portugal, in the west of the Iberian peninsula of south-west Europe. Their language is Portuguese, and Roman Catholicism is the predominant religion....
's influence and contribution has been systematically erased from the Brazilian culture. Tomás Antônio Gonzaga
Tomás Antônio Gonzaga
Tomás Antônio Gonzaga was a Portuguese poet. One of the most famous Neoclassic Brazilian writers, he was also the ouvidor and the ombudsman of the city of Ouro Preto , as well as the desembargador of the appeal court in Bahia...
, Padre António Vieira
António Vieira
Father António Vieira was a Portuguese Jesuit and writer, the "prince" of Catholic pulpit-orators of his time.-Life:Vieira was born in Lisbon to Cristóvão Vieira Ravasco, the son of a mulatto woman, and Maria de Azevedo. Accompanying his parents to Brazil in 1614, he received his education at the...
, Carmen Miranda are some of the Portuguese who are presented as Brazilians. The Brazilian culture
Culture of Brazil
The culture of Brazil presents a very diverse nature reflecting an ethnic and cultural mixing occurred in the colonial period involving mostly Native Americans, Portuguese and Africans...
is in large part derived from the Portuguese culture
Culture of Portugal
The culture of Portugal is the result of a complex flow of different civilizations during the past Millennia. From prehistoric cultures, to its Pre-Roman civilizations , passing through its contacts with the Phoenician-Carthaginian world, the Roman period , the...
and the similarities between both cultures and the relatively easy integration
Social integration
Social integration, in sociology and other social sciences, is the movement of minority groups such as ethnic minorities, refugees and underprivileged sections of a society into the mainstream of societies...
of immigrants in Brazil
Immigration to Brazil
Immigration to Brazil is the movement to Brazil of foreign persons to reside permanently. It should not be confused with the colonisation of the country by the Portuguese, or with the forcible bringing of people from Africa as slaves....
, make it nearly impossible for some to keep a separate Portuguese identity.
The Portuguese in contemporary Brazil
Portuguese people are the largest immigrant community in Brazil. In the 2000 census, there were 213,203 Portuguese immigrants in Brazil.In the late 1990s and the 2000s, some Portuguese
Portuguese people
The Portuguese are a nation and ethnic group native to the country of Portugal, in the west of the Iberian peninsula of south-west Europe. Their language is Portuguese, and Roman Catholicism is the predominant religion....
pensioners have been moving to Brazil, mainly to the northeast, attracted by the tropical weather and the beach
Beach
A beach is a geological landform along the shoreline of an ocean, sea, lake or river. It usually consists of loose particles which are often composed of rock, such as sand, gravel, shingle, pebbles or cobblestones...
es.
The Portuguese crisis in 2010 and 2011 led to higher immigration of Portuguese citizens to Brazil. In the first six months of 2011, with the economic crisis in Portugal a record number of 328,826 Portuguese citizens made their situation regular in Brazil. This wave of Portuguese immigration to Brazil included large numbers of highly qualified and experienced professionals.
How many Brazilians have Portuguese ancestry?
Most Brazilians have some degree of Portuguese ancestry: some descend from colonial settlers, while others have recent immigrant Portuguese origin, dating back to anywhere between the mid-19th and mid-20th centuries. Due to "miscegenationMiscegenation
Miscegenation is the mixing of different racial groups through marriage, cohabitation, sexual relations, and procreation....
", Brazilians of different "races" may have Portuguese ancestry: Whites
White Brazilian
White Brazilians make up 48.4% of Brazil's population, or around 92 million people, according to the IBGE's 2008 PNAD . Whites are present in the entire territory of Brazil, although the main concentrations are found in the South and Southeastern parts of the country...
, Blacks
Afro-Brazilian
In Brazil, the term "preto" is one of the five categories used by the Brazilian Census, along with "branco" , "pardo" , "amarelo" and "indígena"...
, Amerindians
Indigenous peoples in Brazil
The Indigenous peoples in Brazil comprise a large number of distinct ethnic groups who inhabited the country prior to the European invasion around 1500...
and people of mixed race
Mixed-race Brazilian
Brazilian censuses do not use a "multiracial" category. Instead, the censuses use skin colour categories, with a Pardo one, that may include people of varied "mixed racial" ancestry, but probably also accounts for non-mixed acculturated Amerindians...
.
There are no reliable figures for how many Brazilians descend from the Portuguese. This is mainly because the Portuguese presence in Brazil is very old, making it almost impossible to find correct numbers even though most Brazilians have Portuguese ancestry.
In 1872, there were 3.7 million Whites
White Brazilian
White Brazilians make up 48.4% of Brazil's population, or around 92 million people, according to the IBGE's 2008 PNAD . Whites are present in the entire territory of Brazil, although the main concentrations are found in the South and Southeastern parts of the country...
in Brazil (the vast majority of them of Portuguese ancestry), 4.1 million mixed-race
Mixed-race Brazilian
Brazilian censuses do not use a "multiracial" category. Instead, the censuses use skin colour categories, with a Pardo one, that may include people of varied "mixed racial" ancestry, but probably also accounts for non-mixed acculturated Amerindians...
people (mostly of Portuguese-Amerindian-African ancestry) and 1.9 million Blacks (some of whom probably had some degree of Portuguese ancestry). These numbers give the percentage of 80% of people with total or partial Portuguese ancestry in Brazil in the 1870s. At that time, the Portuguese were the only Europeans to settle Brazil in large numbers, since other groups (notably Italians) only started arriving in large numbers after 1875.
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, a new large wave of immigrants from Portugal arrived. From 1881 to 1991, over 1.5 million Portuguese immigrated to Brazil. In 1906, for example, there were 133,393 Portuguese-born people living in Rio de Janeiro, comprising 16% of the city's population. Rio is still today considered the largest "Portuguese city" outside of Portugal itself.
| Group | Population | Percentage of the City http://books.google.com.br/books?id=ObM0dMga1cMC&pg=PA11&dq=japoneses+rio+janeiro&hl=pt-BR&ei=UY4DTuPNLtO3tgfhxcT4DQ&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=3&ved=0CDUQ6AEwAjgU#v=onepage&q=portugueses&f=false |
|---|---|---|
| Portuguese immigrants | 106,461 | 20,36% |
| Brazilians who were born to a Portuguese father or mother | 161,203 | 30,84% |
| Portuguese immigrants and descendents | 267,664 | 51,2% |
Genetic studies also confirm the strong proportion of Portuguese genetic ancestry in Brazilians. According to one study, at least half of the Brazilian population's Y Chromosome
Y chromosome
The Y chromosome is one of the two sex-determining chromosomes in most mammals, including humans. In mammals, it contains the gene SRY, which triggers testis development if present. The human Y chromosome is composed of about 60 million base pairs...
comes from Portugal. Black Brazilians have an average of 48% non-African genes; most of them may have Portuguese ancestors.
Some notable Portuguese Brazilians
Most notable Brazilians are at least partially of Portuguese descentPortuguese people
The Portuguese are a nation and ethnic group native to the country of Portugal, in the west of the Iberian peninsula of south-west Europe. Their language is Portuguese, and Roman Catholicism is the predominant religion....
. However, the following list only those who can actually be considered "Portuguese Brazilian" (i.e. either born in Portugal or who have close Portuguese ancestry, 1st or 2nd generation
Generation
Generation , also known as procreation in biological sciences, is the act of producing offspring....
).
Business
- Abílio dos Santos Diniz (chairman and former owner of Grupo Pão de Açúcar; Portuguese parents);
- Albino Souza CruzAlbino Souza CruzAlbino Sousa Cruz was a Brazilian businessman, founder of Souza Cruz, later the subsidiary of British American Tobacco in Brazil....
(founder - 1903 - and chairman - up to 1962 - of Souza Cruz, tobacco corporation); - Antônio Ermírio de MoraesAntônio Ermírio de MoraesAntônio Ermírio de Moraes is a Brazilian businessman who is the chairman of the Votorantim Group; one of the country's largest companies, specialized in metals, paper, cement and frozen orange juice...
(businessman, chairman of Grupo Votorantim; Portuguese grandfather); - Irineu Evangelista de SousaIrineu Evangelista de SousaIrineu Evangelista de Sousa, the Viscount of Mauá was a Brazilian entrepreneur, industrialist, banker and politician. He was called the Rothschild of the South American continent by the New York Times in 1871. He received the titles of baron and visconde com grandeza of Mauá...
(Barão de Mauá) (industrialist; Azorean-Portuguese grandparents)
Literature
- Aluísio AzevedoAluísio AzevedoAluísio Tancredo Gonçalves de Azevedo was a Brazilian novelist, caricaturist, diplomat, playwright and short story writer. Initially a Romantic writer, he would later adhere to the Naturalist movement...
(writer; Portuguese ancestry - Brazilian-born); - Antônio Gonçalves DiasAntônio Gonçalves DiasAntônio Gonçalves Dias was a Brazilian Romantic poet, playwright and linguist. He is famous for writing the poem "Canção do exílio", arguably the most well-known poem of the Brazilian literature, and many other nationalist and patriotic poems that would later give him the title of national poet of...
(poet; Portuguese father); - Padre António VieiraAntónio VieiraFather António Vieira was a Portuguese Jesuit and writer, the "prince" of Catholic pulpit-orators of his time.-Life:Vieira was born in Lisbon to Cristóvão Vieira Ravasco, the son of a mulatto woman, and Maria de Azevedo. Accompanying his parents to Brazil in 1614, he received his education at the...
(writer; Portuguese-born); - Augusto BoalAugusto BoalAugusto Boal was a Brazilian theatre director, writer and politician. He was the founder of Theatre of the Oppressed, a theatrical form originally used in radical popular education movements...
(playwright and essayist; Portuguese parents); - Basílio da GamaBasílio da GamaJosé Basílio da Gama was a Brazilian-born Portuguese poet and member of the Society of Jesus, famous for the epic poem O Uraguai...
(poet and writer; Portuguese father); - Casimiro de AbreuCasimiro de AbreuCasimiro José Marques de Abreu was a Brazilian poet, novelist and playwright, adept of the "Ultra-Romanticism" movement...
(writer; Portuguese father); - Cecília MeirelesCecília MeirelesCecília Benevides de Carvalho Meireles was a Brazilian writer and educator, known principally as a poet. She is a canonical name of Brazilian Modernism, one of the great female poets in the Portuguese language, and is widely considered the best poetess from Brazil, though she combatted the word...
(writer; Portuguese grandparents); - Cláudio Manuel da CostaCláudio Manuel da CostaCláudio Manuel da Costa was a Brazilian poet and musician, considered to be the introducer of the Neoclassicism in Brazil...
(writer; Portuguese father); - Coelho NetoCoelho NetoHenrique Maximiano Coelho Neto was a Brazilian writer and politician...
(writer; Portuguese father); - Euclides da CunhaEuclides da CunhaEuclides da Cunha was a Brazilian writer, sociologist and engineer. His most important work is Os Sertões , a non-fictional account of the military expeditions promoted by the Brazilian government against the rebellious village of Canudos, known as the War of Canudos...
(writer; grandparents); - Gregório de Matos (colonial poet; Portuguese father);
- João Ubaldo RibeiroJoão Ubaldo RibeiroJoão Ubaldo Ribeiro is a Brazilian author born in Itaparica, Bahia on January 23, 1941. In the English speaking world his An Invincible Memory has been highly praised...
(writer; Portuguese paternal grandfather); - Machado de Assis (writer, Portuguese mother);
- Manuel Antônio de AlmeidaManuel Antônio de AlmeidaManuel Antônio de Almeida was a Brazilian writer, medician and teacher. He is famous for the book Memoirs of a Police Sergeant, written under the pen name Um Brasileiro...
(writer; Portuguese parents); - Rubem FonsecaRubem FonsecaRubem Fonseca is a Brazilian writer.He was born in Juiz de Fora, in the state of Minas Gerais, but he has lived most of his life in Rio de Janeiro. In 1952, he started his career as a low-level cop and, later became a police commissioner, one of the highest ranks in the civil police of Brazil...
(writer; Portuguese parents); - Tomás Antônio GonzagaTomás Antônio GonzagaTomás Antônio Gonzaga was a Portuguese poet. One of the most famous Neoclassic Brazilian writers, he was also the ouvidor and the ombudsman of the city of Ouro Preto , as well as the desembargador of the appeal court in Bahia...
(poet and involved in the Inconfidência MineiraInconfidência MineiraThe Inconfidência Mineira of 1789 was an unsuccessful Brazilian independence movement.It was a result of the confluence of external and internal causes...
; Portuguese-born).
Music

- Arthur Napoleão dos SantosArthur Napoleão dos SantosArthur Napoleão dos Santos was a Brazilian composer, pianist, instrument dealer and music publisher.-Biography:...
(composer and pianist); - César Guerra-PeixeCésar Guerra-PeixeCésar Guerra-Peixe was a Brazilian violinist and composer.Guerra-Peixe was born in Petrópolis, son of Portuguese immigrants with gypsy origins. As a composer he wrote influenced by Hans-Joachim Koellreutter several works using straight twelve-tone technique, but switched in 1949 to adapt...
(composer and conductor; Portuguese father); - Marcos PortugalMarcos PortugalMarcos António da Fonseca Portugal was a Portuguese classical composer, who achieved great international fame for his operas in Italian....
(colonial composer; Portuguese-born);
Popular music
- Carmen MirandaCarmen MirandaCarmen Miranda, GCIH was a Portuguese-born Brazilian samba singer, Broadway actress and Hollywood film star popular in the 1940s and 1950s. She was, by some accounts, the highest-earning woman in the United States and noted for her signature fruit hat outfit she wore in the 1943 movie The Gang's...
(singer and Hollywood actress; Portuguese-born); - Daniela MercuryDaniela MercuryDaniela Mercury , is a Latin Grammy Award-winning Brazilian axé, samba-reggae and MPB singer, songwriter and record producer. Since her breakthrough, Mercury has become one of the best known Brazilian female singers, selling over 20 million albums worldwide...
(singer; Portuguese father); - Dóris MonteiroDóris MonteiroAdelina Doris Monteiro is a Brazilian singer and actress.In 1949, she was discovered as a singer on the program Carbon Paper by Renato Murce, radio National in Rio de Janeiro.- 1950s :...
(singer; Portuguese parents); - Fernanda AbreuFernanda Abreu-Biography:Fernanda was born and raised in a middle-class family of the South Zone, a neighborhood of Rio. Her first notable public appearance was the backing vocal of the band Blitz until 1986...
(singer and songwriter; Portuguese father); - Francisco de Morais Alves (singer; Portuguese parents);
- JoannaJoannaJoanna is a feminine given name deriving from Koine Greek Iōanna from Hebrew יוֹחָנָה meaning "God is gracious". Variants in English include Joan, Joann, Joanne, and Johanna...
(singer and songwriter; Portuguese father); - Nelson GonçalvesNelson GonçalvesNelson Gonçalves was a Brazilian singer and songwriter.Born Antônio Gonçalves Sobral in Santana do Livramento, Rio Grande do Sul, he was raised in São Paulo...
(singer; Portuguese parents); - Roberto LealRoberto LealRoberto Leal, stage name of António Joaquim Fernandes, is a Portuguese-Brazilian singer, born in Macedo de Cavaleiros municipality, Braganza district, in northeast Portugal. He has sold more than 17 million albums, and has received 30 golden records and 5 platinum records.In 1962 his family moved...
(singer; Portuguese-born).
Entertainment
- Amácio MazzaropiAmácio MazzaropiAmácio Mazzaropi was a Brazilian actor and filmmaker.- Filmography:* Sai da frente - * Nadando em dinheiro - * Candinho - * O gato da madame -...
(actor and film-maker; Portuguese mother); - Eugênia CâmaraEugênia CâmaraEugênia Câmara was a Portuguese actress, active in both Portugal and Brazil. As well as for her own artistic achievements, she is remembered for her affair with, and influence upon, the famous Brazilian poet Castro Alves.- References :...
(actress; Portuguese-born); - Fernanda MontenegroFernanda MontenegroFernanda Montenegro is a Brazilian stage, television and film actress, mostly recognized for her leading role in Central Station, which she was nominated for the Academy Award for Best Actress, becoming the first Brazilian actor to be nominated.She is commonly revered as one of Brazil's finest...
(Oscar-nominated actress; Portuguese grandparents); - Marília PêraMarília PêraMarília Pêra is an award-winning Brazilian actress.-Biography:Pêra was born to actors Manuel Pêra and Dinorah Marzullo. Her sister is also an accomplished actress Sandra Pêra...
(actress; Portuguese father); - Ruy GuerraRuy GuerraRuy Alexandre Guerra Coelho Pereira is a film director, screenwriter, film editor, and actor in Brazil. Guerra was born a Portuguese citizen in Lourenço Marques in Moçambique, when it was still a colony of Portugal....
(director; Portuguese-born); - Thiago LacerdaThiago LacerdaThiago Lacerda is a Brazilian actor of Portuguese origin.Thiago spent his childhood between Rio de Janeiro, where he was born, and Recreio, a mining town where his grandparents live. From the age of three to 16, he devoted himself to swimming, winning more than 170 medals...
(actor; Portuguese grandparents);

Fine arts
- Antônio Francisco Lisboa (Aleijadinho)AleijadinhoAleijadinho was a Colonial Brazil-born sculptor and architect, noted for his works on and in various churches of Brazil....
(colonial sculptor and architect; Portuguese father); - Artur BarrioArtur BarrioArtur Barrio is an artist who lives and works in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Much of his work consists of installation pieces that create interaction with the public. Barrio engages the viewer as participant in his art, often without their knowledge that it is art in which they are participating...
(sculptor and artist; Portuguese-born); - Joaquim TenreiroJoaquim TenreiroJoaquim Tenreiro was among the leading furniture designers and visual artists in midcentury Brazil. Born into a family of woodworkers and carpenters in Portugal, he emigrated to Rio de Janeiro and in the 1920s began working for the firm of Laubissh & Hirth...
(plastic artist and furniture designer, Portuguese-born); - Manoel da Costa AtaídeManoel da Costa AtaídeManoel da Costa Ataíde, better known as Mestre Ataíde , was a Brazilian painter, sculptor, gilder and teacher.He was an important artist of the baroque school in Minas Gerais and had a major influence on painting in the region, with many students and followers...
(colonial painter; Portuguese parents); - Victor MeirellesVictor MeirellesVictor Meirelles de Lima was a 19th century painter. He studied art in Paris but painted most of his works in and about his native Brazil. His religious and military paintings helped him become one of the most popular and celebrated Brazilian painters...
(painter; Azorean-Portuguese parents).
Government and politics
- Afonso Augusto Moreira PenaAfonso Augusto Moreira PenaAfonso Augusto Moreira Pena was a Brazilian politician, and president between 1906 and 1909. Before his political career, Pena was a lawyer, jurist and member of the Brazilian Supreme Court....
– 6th President of BrazilPresident of BrazilThe president of Brazil is both the head of state and head of government of the Federative Republic of Brazil. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the Brazilian Armed Forces... - Antônio Carlos MagalhãesAntônio Carlos MagalhãesAntônio Carlos Peixoto de Magalhães was a Brazilian politician. His paternal grandparents were Portuguese . He served as Governor of Bahia three times and represented Bahia in the Senate of Brazil three times...
– 37th, 39th, and 43rd Governor of Bahia - Artur da Costa e SilvaArtur da Costa e SilvaArtur da Costa e Silva was a Brazilian Army General, the second President of Brazil during the military regime set up by the 1964 coup d'état; he was born only a month before the coup that overthrow Dom Pedro II. He was married to Iolanda Barbosa Costa e Silva, the daughter of a soldier...
– 27th President of Brazil - Dom Pedro I – 1st Emperor of Brazil
- Dom Pedro IIPedro II of BrazilDom Pedro II , nicknamed "the Magnanimous", was the second and last ruler of the Empire of Brazil, reigning for over 58 years. Born in Rio de Janeiro, he was the seventh child of Emperor Dom Pedro I of Brazil and Empress Dona Maria Leopoldina and thus a member of the Brazilian branch of...
– 2nd Emperor of Brazil - Fernando Henrique CardosoFernando Henrique CardosoFernando Henrique Cardoso – also known by his initials FHC – was the 34th President of the Federative Republic of Brazil for two terms from January 1, 1995 to December 31, 2002. He is an accomplished sociologist, professor and politician...
– 34th President of Brazil - Francisco de Paula Rodrigues AlvesFrancisco de Paula Rodrigues AlvesFrancisco de Paula Rodrigues Alves, PC was a Brazilian politician who first served as governor of the State of São Paulo in 1887, and as Treasury minister in the 1890s. Rodrigues Alves was elected president of Brazil in 1902 and served until 1906....
– 5th President of Brazil - Getúlio VargasGetúlio VargasGetúlio Dornelles Vargas served as President of Brazil, first as dictator, from 1930 to 1945, and in a democratically elected term from 1951 until his suicide in 1954. Vargas led Brazil for 18 years, the most for any President, and second in Brazilian history to Emperor Pedro II...
– 14th, and 17th President of Brazil - José Gomes TemporãoJosé Gomes TemporãoJosé Gomes Temporão is a Brazilian public health physician and politician from the Brazilian Democratic Movement Party. He took office as Brazilian Minister of Health on March 16, 2007, during the second term of President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva's administration.-Biography:José Gomes Temporão...
– 41st Minister of Health of Brazil - João GoulartJoão GoulartJoão Belchior Marques Goulart was a Brazilian politician and the 24th President of Brazil until a military coup d'état deposed him on April 1, 1964. He is considered to have been the last left-wing President of the country until Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva took office in 2003.-Name:João Goulart is...
– 24nd President of Brazil - Mário CovasMário CovasMário Covas Júnior was a Brazilian politician.Covas studied engineering at the Polytechnic School of the University of São Paulo. He entered politics in his native city of Santos, in the state of São Paulo....
– 30th Governor of São Paulo
See also
- PortuguesePortuguese peopleThe Portuguese are a nation and ethnic group native to the country of Portugal, in the west of the Iberian peninsula of south-west Europe. Their language is Portuguese, and Roman Catholicism is the predominant religion....
- Geographic distribution of PortugueseGeographic distribution of PortuguesePortuguese is the official and first language of Angola, Brazil, Cape Verde, Guinea-Bissau, Mozambique, Portugal and São Tomé and Príncipe. It is also one of the official languages of East Timor , Macau and the Gabonese-Equatoguinean city of Cocobeach .Uruguay gave Portuguese an equal status to...
- Demography of Brazil
- White Brazilians
- White Latin AmericanWhite Latin AmericanWhite Latin Americans are the people of Latin America who are white in the racial classification systems used in individual Latin American countries. Persons who are classified as White in one Latin American country may be classified differently in another country...
- Brazilian people

