Position sensitive device
Encyclopedia
A Position Sensitive Device and/or Position Sensitive Detector (PSD) is an optical position sensor (OPS), that can measure a position of a light spot in one or two-dimensions on a sensor surface.
 The technical term PSD was first used in a 1957 publication by J.T. Wallmark for lateral photoelectric effect
The technical term PSD was first used in a 1957 publication by J.T. Wallmark for lateral photoelectric effect
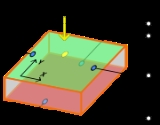
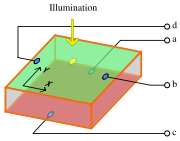
used for local measurements. On a laminar semiconductor, a so-called PIN diode
is exposed to a tiny spot of light. This exposure causes a change in local resistance and thus electron flow in four electrodes. From the currents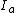 ,
, 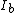 ,
, 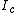 and
and 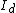 in the electrodes, the location of the light spot is computed using the following equations.
in the electrodes, the location of the light spot is computed using the following equations.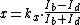
and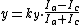
The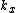 and
and 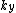 are simple scaling factors, which permit transformation into coordinates.
are simple scaling factors, which permit transformation into coordinates.
An advantage of this process is the continuous measurement of the light spot position with measuring rates up to over 100 kHz. The dependence of local measurement on form and size of the light spot as well as the nonlinear connection are a disadvantage that can be partly compensated by special electrode shapes.
or CMOS
cameras. The sensor is partitioned into individual pixels whose exposure value can be read out sequentially. The position of the light spot can be computed with the methods of photogrammetry
directly from the brightness distribution.
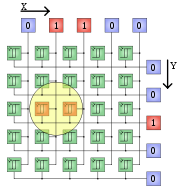 For faster applications, matrix sensors with parallel processing were developed. Both line by line and in columns, the density of light of each pixel is compared with a global threshold value. The results of comparison become lines and columns with logical OR links. From all columns and all lines the one element that is brighter than a given threshold value is the average value of the coordinates computed of the light spot.
For faster applications, matrix sensors with parallel processing were developed. Both line by line and in columns, the density of light of each pixel is compared with a global threshold value. The results of comparison become lines and columns with logical OR links. From all columns and all lines the one element that is brighter than a given threshold value is the average value of the coordinates computed of the light spot.
Principles
PSDs can be divided into two classes which work according to different principles: In the first class, the sensors have an isotropic sensor surface that has a raster-like structure that supplies continuous position data. The second class has discrete sensors on the sensor surface that supply local discrete data.Isotropic Sensors

Photoelectric effect
In the photoelectric effect, electrons are emitted from matter as a consequence of their absorption of energy from electromagnetic radiation of very short wavelength, such as visible or ultraviolet light. Electrons emitted in this manner may be referred to as photoelectrons...
used for local measurements. On a laminar semiconductor, a so-called PIN diode
PIN diode
A PIN diode is a diode with a wide, lightly doped 'near' intrinsic semiconductor region between a p-type semiconductor and an n-type semiconductor region. The p-type and n-type regions are typically heavily doped because they are used for ohmic contacts....
is exposed to a tiny spot of light. This exposure causes a change in local resistance and thus electron flow in four electrodes. From the currents
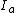 ,
, 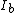 ,
, 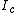 and
and 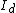 in the electrodes, the location of the light spot is computed using the following equations.
in the electrodes, the location of the light spot is computed using the following equations.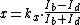
and
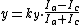
The
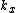 and
and 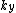 are simple scaling factors, which permit transformation into coordinates.
are simple scaling factors, which permit transformation into coordinates.An advantage of this process is the continuous measurement of the light spot position with measuring rates up to over 100 kHz. The dependence of local measurement on form and size of the light spot as well as the nonlinear connection are a disadvantage that can be partly compensated by special electrode shapes.
Serial Processing
The most common sensor applications with a sampling rate of less than 1000 Hz are CCDCharge-coupled device
A charge-coupled device is a device for the movement of electrical charge, usually from within the device to an area where the charge can be manipulated, for example conversion into a digital value. This is achieved by "shifting" the signals between stages within the device one at a time...
or CMOS
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits...
cameras. The sensor is partitioned into individual pixels whose exposure value can be read out sequentially. The position of the light spot can be computed with the methods of photogrammetry
Photogrammetry
Photogrammetry is the practice of determining the geometric properties of objects from photographic images. Photogrammetry is as old as modern photography and can be dated to the mid-nineteenth century....
directly from the brightness distribution.
Parallel Processing

External links
See also
- PhotodiodePhotodiodeA photodiode is a type of photodetector capable of converting light into either current or voltage, depending upon the mode of operation.The common, traditional solar cell used to generateelectric solar power is a large area photodiode....
- PIN diodePIN diodeA PIN diode is a diode with a wide, lightly doped 'near' intrinsic semiconductor region between a p-type semiconductor and an n-type semiconductor region. The p-type and n-type regions are typically heavily doped because they are used for ohmic contacts....
- Photoelectric effectPhotoelectric effectIn the photoelectric effect, electrons are emitted from matter as a consequence of their absorption of energy from electromagnetic radiation of very short wavelength, such as visible or ultraviolet light. Electrons emitted in this manner may be referred to as photoelectrons...

