Post-traumatic seizure
Encyclopedia
Post-traumatic seizures are seizure
s that result from traumatic brain injury
(TBI), brain damage
caused by physical trauma
. PTS may be a risk factor for post-traumatic epilepsy
(PTE), but a person who has a seizure or seizures due to traumatic brain injury does not necessarily have PTE, which is a form of epilepsy
, a chronic condition in which seizures occur repeatedly. However, "PTS" and "PTE" may be used interchangeably in medical literature.
Seizures are usually an indication of a more severe TBI. Seizures that occur shortly after a person suffers a brain injury may further damage the already vulnerable brain. They may reduce the amount of oxygen available to the brain, cause excitatory neurotransmitter
s to be released in excess, increase the brain's metabolic
need, and raise the pressure within the intracranial space
, further contributing to damage. Thus, people who suffer severe head trauma are given anticonvulsant
medications as a precaution against seizures.
Around 5–7% of people hospitalized with TBI have at least one seizure. PTS are more likely to occur in more severe injuries, and certain types of injuries increase the risk further. The risk that a person will suffer PTS becomes progressively lower as time passes after the injury. However, TBI survivors may still be at risk over 15 years after the injury. Children and older adults are at a higher risk for PTS.
into early and late seizures, those occurring within the first week of injury and those occurring after a week, respectively. Though the seven day cutoff for early seizures is used widely, it is arbitrary; seizures occurring after the first week but within the first month of injury may share characteristics with early seizures. Some studies use a 30 day cutoff for early seizures instead. Later it became accepted to further divide seizures into immediate PTS, seizures occurring within 24 hours of injury; early PTS, with seizures between a day and a week after trauma; and late PTS, seizures more than one week after trauma. Some consider late PTS to be synonymous with post-traumatic epilepsy
.
Early PTS occur at least once in about 4 or 5% of people hospitalized with TBI, and late PTS occur at some point in 5% of them. Of the seizures that occur within the first week of trauma, about half occur within the first 24 hours. In children, early seizures are more likely to occur within an hour and a day of injury than in adults. Of the seizures that occur within the first four weeks of head trauma, about 10% occur after the first week. Late seizures occur at the highest rate in the first few weeks after injury. About 40% of late seizures start within six months of injury, and 50% start within a year.
Especially in children and people with severe TBI, the life-threatening condition of persistent seizure called status epilepticus
is a risk in early seizures; 10 to 20% of PTS develop into the condition. In one study, 22% of children under 5 years old developed status seizures, while 11% of the whole TBI population studied did. Status seizures early after a TBI may heighten the chances that a person will suffer unprovoked seizures later.
Immediate and early seizures are thought to be a direct reaction to the injury, while late seizures are believed to result from damage to the cerebral cortex
by mechanisms such as excitotoxicity
and iron from blood. Immediate seizures occurring within two seconds of injury probably occur because the force from the injury stimulates brain tissue that has a low threshold for seizures when stimulated. Early PTS are considered to be provoked seizures, because they result from the direct effects of the head trauma and are thus not considered to be actual epilepsy, while late seizures are thought to indicate permanent changes in the brain's structure and to imply epilepsy. Early seizures can be caused by factors such as cerebral edema
, intracranial hemorrhage
, cerebral contusion or laceration
. Factors that may result in seizures that occur within two weeks of an insult include the presence of blood within the brain; alterations in the blood brain barrier; excessive release of excitatory neurotransmitters such as glutamate; damage to tissues caused by free radicals; and changes in the way cells produce energy. Late seizures are thought to be the result of epileptogenesis
, in which neural network
s are restructured in a way that increases the likelihood that they will become excited, leading to seizures.
, excessive release of excitatory neurotransmitter
s, increased metabolic demands, and increased pressure within the intracranial space. Medications used to prevent seizures include valproate, phenytoin
, and phenobarbital
. It is recommended that treatment with anti-seizure medication be initiated as soon as possible after TBI. Prevention of early seizures differs from that of late seizures, because the aim of the former is to prevent damage caused by the seizures, whereas the aim of the latter is to prevent epileptogenesis. Strong evidence from clinical trials suggests that antiepileptic drugs given within a day of injury prevent seizures within the first week of injury, but not after. For example, a 2003 review of medical literature found phenytoin to be preventative of early, but probably not late PTS. In children, anticonvulsants may be ineffective for both early and late seizures. For unknown reasons, prophylactic use of antiepileptic drugs over a long period is associated with an increased risk for seizures. For these reasons, antiepileptic drugs are widely recommended for a short time after head trauma to prevent immediate and early, but not late, seizures. No treatment is widely accepted to prevent the development of epilepsy. However, medications may be given to repress more seizures if late seizures do occur.
. Neurological examination
s and tests to measure levels of serum electrolyte
s are performed.
Not all seizures that occur after trauma are PTS; they may be due to a seizure disorder that already existed, which may even have caused the trauma. In addition, post-traumatic seizures are not to be confused with concussive convulsions, which may immediately follow a concussion but which are not actually seizures and are not a predictive factor for epilepsy.
Neuroimaging
is used to guide treatment. Often, MRI
is performed in any patient with PTS, but the less sensitive but more easily accessed CT scan may also be used.
Seizures that result from TBI are often difficult to treat. Antiepileptic drugs that may be given intravenously
shortly after injury include phenytoin, sodium valproate
, carbamazepine
, and phenobarbital. Antiepileptic drugs do not prevent all seizures in all people, but phenytoin and sodium valproate usually stop seizures that are in progress.
Studies have reported that 25–40% of PTS patients go into remission; later studies conducted after the development of more effective seizure medications reported higher overall remission rates. In one quarter of people with seizures from a head trauma, medication controls them well. However, a subset of patients have seizures despite aggressive antiepileptic drug therapy. The likelihood that PTS will go into remission is lower for people who have frequent seizures in the first year after injury.
 Research has found that the incidence of PTS varies widely based on the population studied; it may be as low as 4.4% or as high as 53%. Of all TBI patients who are hospitalized, 5 to 7% have PTS. PTS occur in about 3.1% of traumatic brain injuries, but the severity of injury affects the likelihood of occurrence.
Research has found that the incidence of PTS varies widely based on the population studied; it may be as low as 4.4% or as high as 53%. Of all TBI patients who are hospitalized, 5 to 7% have PTS. PTS occur in about 3.1% of traumatic brain injuries, but the severity of injury affects the likelihood of occurrence.
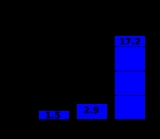
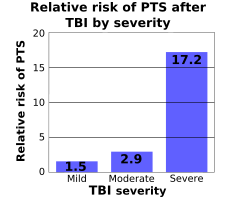
The most important factor in whether a person will develop early and late seizures is the extent of the damage to the brain. More severe brain injury also confers a risk for developing PTS for a longer time after the event. One study found that the probability that seizures will occur within 5 years of injury is in 0.5% of mild traumatic brain injuries (defined as no skull fracture
and less than 30 minutes of post-traumatic amnesia
, abbreviated PTA, or loss of consciousness, abbreviated LOC); 1.2% of moderate injuries (skull fracture or PTA or LOC lasting between 30 minutes and 24 hours); and 10.0% of severe injuries (cerebral contusion, intracranial hematoma, or LOC or PTA for over 24 hours). Another study found that the risk of seizures 5 years after TBI is 1.5% in mild (defined as PTA or LOC for less than 30 minutes), 2.9% in moderate (LOC lasting between 30 minutes and 1 day), and 17.2% in severe TBI (cerebral contusion, subdural hematoma, or LOC for over a day; image at right).
Immediate seizures have an incidence of 1 to 4%, that of early seizures is 4 to 25%, and that of late seizures is 9 to 42%.
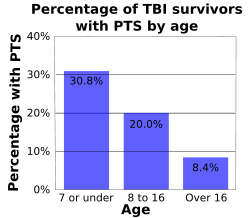
Age influences the risk for PTS. As age increases, risk of early and late seizures decreases; one study found that early PTS occurred in 30.8% of children age 7 or under, 20% of children between ages 8 and 16, and 8.4% of people who were over 16 at the time they were injured (graph at right). Early seizures occur up to twice as frequently in brain injured children as they do in their adult counterparts. In one study, children under five with trivial brain injuries (those with no LOC, no PTA, no depressed skull fracture, and no hemorrhage) suffered an early seizure 17% of the time, while people over age 5 did so only 2% of the time. Children under age five also have seizures within one hour of injury more often than adults do. One study found the incidence of early seizures to be highest among infants younger than one year and particularly high among those who suffered perinatal injury. However, adults are at higher risk than children are for late seizures. People over age 65 are also at greater risk for developing PTS after an injury, with a PTS risk that is 2.5 times higher than that of their younger counterparts.
before the injury also at higher risk for developing seizures.
Occurrence of seizures varies widely even among people with similar injuries. It is not known whether genetics play a role in PTS risk. Studies have had conflicting results with regard to the question of whether people with PTS are more likely to have family members with seizures, which would suggest a genetic role in PTS. Most studies have found that epilepsy in family members does not significantly increase the risk of PTS. People with the ApoE-ε4 allele may also be at higher risk for late PTS.
Risks for late PTS include hydrocephalus
, reduced blood flow to the temporal lobe
s of the brain, brain contusions, subdural hematoma
s, a torn dura mater
, and focal neurological deficits. PTA that lasts for longer than 24 hours after the injury is a risk factor for both early and late PTS. Up to 86% of people who have one late post-traumatic seizure have another within two years.
Seizure
An epileptic seizure, occasionally referred to as a fit, is defined as a transient symptom of "abnormal excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain". The outward effect can be as dramatic as a wild thrashing movement or as mild as a brief loss of awareness...
s that result from traumatic brain injury
Traumatic brain injury
Traumatic brain injury , also known as intracranial injury, occurs when an external force traumatically injures the brain. TBI can be classified based on severity, mechanism , or other features...
(TBI), brain damage
Brain damage
"Brain damage" or "brain injury" is the destruction or degeneration of brain cells. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors...
caused by physical trauma
Physical trauma
Trauma refers to "a body wound or shock produced by sudden physical injury, as from violence or accident." It can also be described as "a physical wound or injury, such as a fracture or blow." Major trauma can result in secondary complications such as circulatory shock, respiratory failure and death...
. PTS may be a risk factor for post-traumatic epilepsy
Post-traumatic epilepsy
Post-traumatic epilepsy is a form of epilepsy that results from brain damage caused by physical trauma to the brain . A person with PTE suffers repeated post-traumatic seizures more than a week after the initial injury...
(PTE), but a person who has a seizure or seizures due to traumatic brain injury does not necessarily have PTE, which is a form of epilepsy
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a common chronic neurological disorder characterized by seizures. These seizures are transient signs and/or symptoms of abnormal, excessive or hypersynchronous neuronal activity in the brain.About 50 million people worldwide have epilepsy, and nearly two out of every three new cases...
, a chronic condition in which seizures occur repeatedly. However, "PTS" and "PTE" may be used interchangeably in medical literature.
Seizures are usually an indication of a more severe TBI. Seizures that occur shortly after a person suffers a brain injury may further damage the already vulnerable brain. They may reduce the amount of oxygen available to the brain, cause excitatory neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to...
s to be released in excess, increase the brain's metabolic
Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
need, and raise the pressure within the intracranial space
Intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure is the pressure inside the skull and thus in the brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid . The body has various mechanisms by which it keeps the ICP stable, with CSF pressures varying by about 1 mmHg in normal adults through shifts in production and absorption of CSF...
, further contributing to damage. Thus, people who suffer severe head trauma are given anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsant
The anticonvulsants are a diverse group of pharmaceuticals used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of bipolar disorder, since many seem to act as mood stabilizers, and in the treatment of neuropathic pain. The goal of an...
medications as a precaution against seizures.
Around 5–7% of people hospitalized with TBI have at least one seizure. PTS are more likely to occur in more severe injuries, and certain types of injuries increase the risk further. The risk that a person will suffer PTS becomes progressively lower as time passes after the injury. However, TBI survivors may still be at risk over 15 years after the injury. Children and older adults are at a higher risk for PTS.
Classification
In the mid 1970s, PTS was first classified by Bryan JennettBryan Jennett
Bryan Jennett was a pioneering Professor of Neurosurgery who established Glasgow as a world centre in the speciality and made major advances in the care and management of patients...
into early and late seizures, those occurring within the first week of injury and those occurring after a week, respectively. Though the seven day cutoff for early seizures is used widely, it is arbitrary; seizures occurring after the first week but within the first month of injury may share characteristics with early seizures. Some studies use a 30 day cutoff for early seizures instead. Later it became accepted to further divide seizures into immediate PTS, seizures occurring within 24 hours of injury; early PTS, with seizures between a day and a week after trauma; and late PTS, seizures more than one week after trauma. Some consider late PTS to be synonymous with post-traumatic epilepsy
Post-traumatic epilepsy
Post-traumatic epilepsy is a form of epilepsy that results from brain damage caused by physical trauma to the brain . A person with PTE suffers repeated post-traumatic seizures more than a week after the initial injury...
.
Early PTS occur at least once in about 4 or 5% of people hospitalized with TBI, and late PTS occur at some point in 5% of them. Of the seizures that occur within the first week of trauma, about half occur within the first 24 hours. In children, early seizures are more likely to occur within an hour and a day of injury than in adults. Of the seizures that occur within the first four weeks of head trauma, about 10% occur after the first week. Late seizures occur at the highest rate in the first few weeks after injury. About 40% of late seizures start within six months of injury, and 50% start within a year.
Especially in children and people with severe TBI, the life-threatening condition of persistent seizure called status epilepticus
Status epilepticus
Status epilepticus is a life-threatening condition in which the brain is in a state of persistent seizure. Definitions vary, but traditionally it is defined as one continuous unremitting seizure lasting longer than 5 minutes, or recurrent seizures without regaining consciousness between seizures...
is a risk in early seizures; 10 to 20% of PTS develop into the condition. In one study, 22% of children under 5 years old developed status seizures, while 11% of the whole TBI population studied did. Status seizures early after a TBI may heighten the chances that a person will suffer unprovoked seizures later.
Pathophysiology
It is not completely understood what physiological mechanisms cause seizures after injury, but early seizures are thought to have different underlying processes than late ones.Immediate and early seizures are thought to be a direct reaction to the injury, while late seizures are believed to result from damage to the cerebral cortex
Cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex is a sheet of neural tissue that is outermost to the cerebrum of the mammalian brain. It plays a key role in memory, attention, perceptual awareness, thought, language, and consciousness. It is constituted of up to six horizontal layers, each of which has a different...
by mechanisms such as excitotoxicity
Excitotoxicity
Excitotoxicity is the pathological process by which nerve cells are damaged and killed by excessive stimulation by neurotransmitters such as glutamate and similar substances. This occurs when receptors for the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate such as the NMDA receptor and AMPA receptor are...
and iron from blood. Immediate seizures occurring within two seconds of injury probably occur because the force from the injury stimulates brain tissue that has a low threshold for seizures when stimulated. Early PTS are considered to be provoked seizures, because they result from the direct effects of the head trauma and are thus not considered to be actual epilepsy, while late seizures are thought to indicate permanent changes in the brain's structure and to imply epilepsy. Early seizures can be caused by factors such as cerebral edema
Cerebral edema
Cerebral edema or cerebral œdema is an excess accumulation of water in the intracellular or extracellular spaces of the brain.-Vasogenic:Due to a breakdown of tight endothelial junctions which make up the blood-brain barrier...
, intracranial hemorrhage
Intracranial hemorrhage
An intracranial hemorrhage is a hemorrhage, or bleeding, within the skull.-Causes:Intracranial bleeding occurs when a blood vessel within the skull is ruptured or leaks. It can result from physical trauma or nontraumatic causes such as a ruptured aneurysm...
, cerebral contusion or laceration
Cerebral contusion
Cerebral contusion, Latin contusio cerebri, a form of traumatic brain injury, is a bruise of the brain tissue. Like bruises in other tissues, cerebral contusion can be associated with multiple microhemorrhages, small blood vessel leaks into brain tissue. Contusion occurs in 20–30% of severe head...
. Factors that may result in seizures that occur within two weeks of an insult include the presence of blood within the brain; alterations in the blood brain barrier; excessive release of excitatory neurotransmitters such as glutamate; damage to tissues caused by free radicals; and changes in the way cells produce energy. Late seizures are thought to be the result of epileptogenesis
Epileptogenesis
Epileptogenesis is a process by which a normal brain develops epilepsy, a chronic condition in which seizures occur. The process, which is gradual, occurs in symptomatic epilepsy, in which seizures are caused by an identifiable lesion in the brain. It results from acute brain insults such as...
, in which neural network
Neural network
The term neural network was traditionally used to refer to a network or circuit of biological neurons. The modern usage of the term often refers to artificial neural networks, which are composed of artificial neurons or nodes...
s are restructured in a way that increases the likelihood that they will become excited, leading to seizures.
Prevention
Shortly after TBI, people are given anticonvulsant medication, because seizures that occur early after trauma can increase brain damage through hypoxiaHypoxia (medical)
Hypoxia, or hypoxiation, is a pathological condition in which the body as a whole or a region of the body is deprived of adequate oxygen supply. Variations in arterial oxygen concentrations can be part of the normal physiology, for example, during strenuous physical exercise...
, excessive release of excitatory neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to...
s, increased metabolic demands, and increased pressure within the intracranial space. Medications used to prevent seizures include valproate, phenytoin
Phenytoin
Phenytoin sodium is a commonly used antiepileptic. Phenytoin acts to suppress the abnormal brain activity seen in seizure by reducing electrical conductance among brain cells by stabilizing the inactive state of voltage-gated sodium channels...
, and phenobarbital
Phenobarbital
Phenobarbital or phenobarbitone is a barbiturate, first marketed as Luminal by Friedr. Bayer et comp. It is the most widely used anticonvulsant worldwide, and the oldest still commonly used. It also has sedative and hypnotic properties but, as with other barbiturates, has been superseded by the...
. It is recommended that treatment with anti-seizure medication be initiated as soon as possible after TBI. Prevention of early seizures differs from that of late seizures, because the aim of the former is to prevent damage caused by the seizures, whereas the aim of the latter is to prevent epileptogenesis. Strong evidence from clinical trials suggests that antiepileptic drugs given within a day of injury prevent seizures within the first week of injury, but not after. For example, a 2003 review of medical literature found phenytoin to be preventative of early, but probably not late PTS. In children, anticonvulsants may be ineffective for both early and late seizures. For unknown reasons, prophylactic use of antiepileptic drugs over a long period is associated with an increased risk for seizures. For these reasons, antiepileptic drugs are widely recommended for a short time after head trauma to prevent immediate and early, but not late, seizures. No treatment is widely accepted to prevent the development of epilepsy. However, medications may be given to repress more seizures if late seizures do occur.
Assessment and treatment
Medical personnel aim to determine whether a seizure is caused by a change in the patient's biochemistry, such as hyponatremiaHyponatremia
Hyponatremia is an electrolyte disturbance in which the sodium concentration in the serum is lower than normal. In the vast majority of cases, hyponatremia occurs as a result of excess body water diluting the serum sodium and is not due to sodium deficiency. Sodium is the dominant extracellular...
. Neurological examination
Neurological examination
A neurological examination is the assessment of sensory neuron and motor responses, especially reflexes, to determine whether the nervous system is impaired...
s and tests to measure levels of serum electrolyte
Electrolyte
In chemistry, an electrolyte is any substance containing free ions that make the substance electrically conductive. The most typical electrolyte is an ionic solution, but molten electrolytes and solid electrolytes are also possible....
s are performed.
Not all seizures that occur after trauma are PTS; they may be due to a seizure disorder that already existed, which may even have caused the trauma. In addition, post-traumatic seizures are not to be confused with concussive convulsions, which may immediately follow a concussion but which are not actually seizures and are not a predictive factor for epilepsy.
Neuroimaging
Neuroimaging
Neuroimaging includes the use of various techniques to either directly or indirectly image the structure, function/pharmacology of the brain...
is used to guide treatment. Often, MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging , nuclear magnetic resonance imaging , or magnetic resonance tomography is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize detailed internal structures...
is performed in any patient with PTS, but the less sensitive but more easily accessed CT scan may also be used.
Seizures that result from TBI are often difficult to treat. Antiepileptic drugs that may be given intravenously
Intravenous therapy
Intravenous therapy or IV therapy is the infusion of liquid substances directly into a vein. The word intravenous simply means "within a vein". Therapies administered intravenously are often called specialty pharmaceuticals...
shortly after injury include phenytoin, sodium valproate
Sodium valproate
Sodium valproate or valproate sodium is the sodium salt of valproic acid and is an anticonvulsant used in the treatment of epilepsy, anorexia nervosa, panic attack, anxiety disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder, migraine and bipolar disorder, as well as other psychiatric conditions requiring...
, carbamazepine
Carbamazepine
Carbamazepine is an anticonvulsant and mood-stabilizing drug used primarily in the treatment of epilepsy and bipolar disorder, as well as trigeminal neuralgia...
, and phenobarbital. Antiepileptic drugs do not prevent all seizures in all people, but phenytoin and sodium valproate usually stop seizures that are in progress.
Prognosis
PTS is associated with a generally good prognosis. It is unknown exactly how long after a TBI a person is at higher risk for seizures than the rest of the population, but estimates have suggested lengths of 10 to over 15 years. For most people with TBI, seizures do not occur after three months, and only 20–25% of people who suffer TBI have PTS more than two years after the injury. However, moderate and severe TBI still confer a high risk for PTS for up to five years after the injury.Studies have reported that 25–40% of PTS patients go into remission; later studies conducted after the development of more effective seizure medications reported higher overall remission rates. In one quarter of people with seizures from a head trauma, medication controls them well. However, a subset of patients have seizures despite aggressive antiepileptic drug therapy. The likelihood that PTS will go into remission is lower for people who have frequent seizures in the first year after injury.
Risk of developing PTE
It is not known whether PTS increase the likelihood of developing PTE. Early PTS, while not necessarily epileptic in nature, are associated with a higher risk of PTE. However, PTS do not indicate that development of epilepsy is certain to occur, and it is difficult to isolate PTS from severity of injury as a factor in PTE development. About 3% of patients with no early seizures develop late PTE; this number is 25% in those who do have early PTS, and the distinction is greater if other risk factors for developing PTE are excluded. Seizures that occur immediately after an insult are commonly believed not to confer an increased risk of recurring seizures, but evidence from at least one study has suggested that both immediate and early seizures may be risk factors for late seizures. Early seizures may be less of a predictor for PTE in children; while as many as a third of adults with early seizures develop PTE, the portion of children with early PTS who have late seizures is less than one fifth in children and may be as low as one tenth. The incidence of late seizures is about half that in adults with comparable injuries.Epidemiology


The most important factor in whether a person will develop early and late seizures is the extent of the damage to the brain. More severe brain injury also confers a risk for developing PTS for a longer time after the event. One study found that the probability that seizures will occur within 5 years of injury is in 0.5% of mild traumatic brain injuries (defined as no skull fracture
Skull fracture
A skull fracture is a break in one or more of the bones in the skull usually occurring as a result of blunt force trauma. If the force of the impact is excessive the bone may fracture at or near the site of the impact...
and less than 30 minutes of post-traumatic amnesia
Post-traumatic amnesia
Post-traumatic amnesia is a state of confusion that occurs immediately following a traumatic brain injury in which the injured person is disoriented and unable to remember events that occur after the injury. The person may be unable to state his or her name, where he or she is, and what time it...
, abbreviated PTA, or loss of consciousness, abbreviated LOC); 1.2% of moderate injuries (skull fracture or PTA or LOC lasting between 30 minutes and 24 hours); and 10.0% of severe injuries (cerebral contusion, intracranial hematoma, or LOC or PTA for over 24 hours). Another study found that the risk of seizures 5 years after TBI is 1.5% in mild (defined as PTA or LOC for less than 30 minutes), 2.9% in moderate (LOC lasting between 30 minutes and 1 day), and 17.2% in severe TBI (cerebral contusion, subdural hematoma, or LOC for over a day; image at right).
Immediate seizures have an incidence of 1 to 4%, that of early seizures is 4 to 25%, and that of late seizures is 9 to 42%.
Age influences the risk for PTS. As age increases, risk of early and late seizures decreases; one study found that early PTS occurred in 30.8% of children age 7 or under, 20% of children between ages 8 and 16, and 8.4% of people who were over 16 at the time they were injured (graph at right). Early seizures occur up to twice as frequently in brain injured children as they do in their adult counterparts. In one study, children under five with trivial brain injuries (those with no LOC, no PTA, no depressed skull fracture, and no hemorrhage) suffered an early seizure 17% of the time, while people over age 5 did so only 2% of the time. Children under age five also have seizures within one hour of injury more often than adults do. One study found the incidence of early seizures to be highest among infants younger than one year and particularly high among those who suffered perinatal injury. However, adults are at higher risk than children are for late seizures. People over age 65 are also at greater risk for developing PTS after an injury, with a PTS risk that is 2.5 times higher than that of their younger counterparts.
Risk factors
The chances that a person will suffer PTS are influenced by factors involving the injury and the person. The largest risks for PTS are having an altered level of consciousness for a protracted time after the injury, severe injuries with focal lesions, and fractures. The single largest risk for PTS is penetrating head trauma, which carries a 35 to 50% risk of seizures within 15 years. If a fragment of metal remains in within the skull after injury, the risk of both early and late PTS may be increased. Head trauma survivors who abused alcoholAlcohol abuse
Alcohol abuse, as described in the DSM-IV, is a psychiatric diagnosis describing the recurring use of alcoholic beverages despite negative consequences. Alcohol abuse eventually progresses to alcoholism, a condition in which an individual becomes dependent on alcoholic beverages in order to avoid...
before the injury also at higher risk for developing seizures.
Occurrence of seizures varies widely even among people with similar injuries. It is not known whether genetics play a role in PTS risk. Studies have had conflicting results with regard to the question of whether people with PTS are more likely to have family members with seizures, which would suggest a genetic role in PTS. Most studies have found that epilepsy in family members does not significantly increase the risk of PTS. People with the ApoE-ε4 allele may also be at higher risk for late PTS.
Risks for late PTS include hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus , also known as "water in the brain," is a medical condition in which there is an abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles, or cavities, of the brain. This may cause increased intracranial pressure inside the skull and progressive enlargement of the head,...
, reduced blood flow to the temporal lobe
Temporal lobe
The temporal lobe is a region of the cerebral cortex that is located beneath the Sylvian fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain....
s of the brain, brain contusions, subdural hematoma
Subdural hematoma
A subdural hematoma or subdural haematoma , also known as a subdural haemorrhage , is a type of haematoma, a form of traumatic brain injury. Blood gathers within the outermost meningeal layer, between the dura mater, which adheres to the skull, and the arachnoid mater, which envelops the brain...
s, a torn dura mater
Dura mater
The dura mater , or dura, is the outermost of the three layers of the meninges surrounding the brain and spinal cord. It is derived from Mesoderm. The other two meningeal layers are the pia mater and the arachnoid mater. The dura surrounds the brain and the spinal cord and is responsible for...
, and focal neurological deficits. PTA that lasts for longer than 24 hours after the injury is a risk factor for both early and late PTS. Up to 86% of people who have one late post-traumatic seizure have another within two years.

