
Potential density
Encyclopedia
The potential density of a fluid parcel at pressure
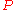 is the density
is the density
that the parcel would acquire if adiabatically
brought to a reference pressure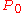 , often 1 bar
, often 1 bar
(100 kPa). Whereas density changes with changing pressure, potential density of a fluid parcel is conserved
as the pressure experienced by the parcel changes (provided no mixing with other parcels or net heat flux occurs). The concept is used in oceanography
http://oceanworld.tamu.edu/resources/ocng_textbook/contents.html and (to a lesser extent) atmospheric science.
Potential density is a dynamically important property: for static stability potential density must decrease upward. If it doesn't, a fluid parcel displaced upward finds itself lighter than its neighbors, and continues to move upward; similarly, a fluid parcel displaced downward would be heavier than its neighbors. This is true even if the density of the fluid decreases upward. In stable conditions (potential density decreasing upward) motion along surfaces of constant potential density (isopycnal
s) is energetically favored over flow across these surfaces (diapycnal flow), so most of the motion within a 3-D geophysical fluid takes place along these 2-D surfaces.
In oceanography, the symbol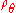 is used to denote potential density, with the reference pressure
is used to denote potential density, with the reference pressure 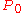 taken to be the pressure at the ocean surface. The corresponding potential density anomaly is denoted by
taken to be the pressure at the ocean surface. The corresponding potential density anomaly is denoted by 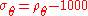 kg
kg
/m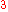 . Because the compressibility of seawater
. Because the compressibility of seawater
varies with salinity
and temperature
, the reference pressure must chosen to be near the actual pressure to keep the definition of potential density dynamically meaningful. Reference pressures are often chosen as a whole multiple of 100 bar; for water near a pressure of 400 bar (40 MPa), say, the reference pressure 400 bar would be used, and the potential density anomaly symbol would be written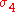 .
.
Potential density adjusts for the effect of compression in two ways:
A parcel's density may be calculated from an equation of state
: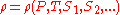
where is temperature,
is temperature, 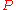 is pressure and
is pressure and 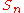 are other tracer
are other tracer
s that affect density (e.g. salinity
of seawater
). The potential density would then be calculated as: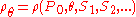
where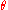 is the potential temperature of the fluid parcel for the same reference pressure
is the potential temperature of the fluid parcel for the same reference pressure 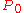 .
.
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
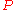 is the density
is the densityDensity
The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
that the parcel would acquire if adiabatically
Adiabatic process
In thermodynamics, an adiabatic process or an isocaloric process is a thermodynamic process in which the net heat transfer to or from the working fluid is zero. Such a process can occur if the container of the system has thermally-insulated walls or the process happens in an extremely short time,...
brought to a reference pressure
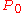 , often 1 bar
, often 1 barBar (unit)
The bar is a unit of pressure equal to 100 kilopascals, and roughly equal to the atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level. Other units derived from the bar are the megabar , kilobar , decibar , centibar , and millibar...
(100 kPa). Whereas density changes with changing pressure, potential density of a fluid parcel is conserved
Conservation law
In physics, a conservation law states that a particular measurable property of an isolated physical system does not change as the system evolves....
as the pressure experienced by the parcel changes (provided no mixing with other parcels or net heat flux occurs). The concept is used in oceanography
Oceanography
Oceanography , also called oceanology or marine science, is the branch of Earth science that studies the ocean...
http://oceanworld.tamu.edu/resources/ocng_textbook/contents.html and (to a lesser extent) atmospheric science.
Potential density is a dynamically important property: for static stability potential density must decrease upward. If it doesn't, a fluid parcel displaced upward finds itself lighter than its neighbors, and continues to move upward; similarly, a fluid parcel displaced downward would be heavier than its neighbors. This is true even if the density of the fluid decreases upward. In stable conditions (potential density decreasing upward) motion along surfaces of constant potential density (isopycnal
Isopycnal
An isopycnal is a surface of constant potential density of water. In the ocean, as the depth increases, so too does the density. Varying degrees of salinity and temperature act to modify the density of water, and the denser water always lies below the less dense water. Because of the action of...
s) is energetically favored over flow across these surfaces (diapycnal flow), so most of the motion within a 3-D geophysical fluid takes place along these 2-D surfaces.
In oceanography, the symbol
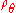 is used to denote potential density, with the reference pressure
is used to denote potential density, with the reference pressure 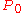 taken to be the pressure at the ocean surface. The corresponding potential density anomaly is denoted by
taken to be the pressure at the ocean surface. The corresponding potential density anomaly is denoted by 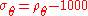 kg
kgKilogram
The kilogram or kilogramme , also known as the kilo, is the base unit of mass in the International System of Units and is defined as being equal to the mass of the International Prototype Kilogram , which is almost exactly equal to the mass of one liter of water...
/m
 . Because the compressibility of seawater
. Because the compressibility of seawaterSeawater
Seawater is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% . This means that every kilogram of seawater has approximately of dissolved salts . The average density of seawater at the ocean surface is 1.025 g/ml...
varies with salinity
Salinity
Salinity is the saltiness or dissolved salt content of a body of water. It is a general term used to describe the levels of different salts such as sodium chloride, magnesium and calcium sulfates, and bicarbonates...
and temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
, the reference pressure must chosen to be near the actual pressure to keep the definition of potential density dynamically meaningful. Reference pressures are often chosen as a whole multiple of 100 bar; for water near a pressure of 400 bar (40 MPa), say, the reference pressure 400 bar would be used, and the potential density anomaly symbol would be written
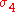 .
.Potential density adjusts for the effect of compression in two ways:
- The effect of a parcel's change in volume due to a change in pressure (as pressure increases, volume decreases).
- The effect of the parcel's change in temperature due to adiabatic change in pressure (as pressure increases, temperature increases).
A parcel's density may be calculated from an equation of state
Equation of state
In physics and thermodynamics, an equation of state is a relation between state variables. More specifically, an equation of state is a thermodynamic equation describing the state of matter under a given set of physical conditions...
:
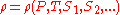
where
 is temperature,
is temperature, 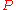 is pressure and
is pressure and 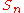 are other tracer
are other tracerTracer
Tracer may refer to:* Histochemical tracer, a substance used for tracing purposes in histochemistry, the study of the composition of cells and tissues...
s that affect density (e.g. salinity
Salinity
Salinity is the saltiness or dissolved salt content of a body of water. It is a general term used to describe the levels of different salts such as sodium chloride, magnesium and calcium sulfates, and bicarbonates...
of seawater
Seawater
Seawater is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% . This means that every kilogram of seawater has approximately of dissolved salts . The average density of seawater at the ocean surface is 1.025 g/ml...
). The potential density would then be calculated as:
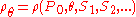
where
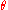 is the potential temperature of the fluid parcel for the same reference pressure
is the potential temperature of the fluid parcel for the same reference pressure 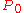 .
.

