Pous
Encyclopedia
The pous was a unit of length used through much of the Iron Age
in Europe
and the Ancient Near East
.
A pous is a Greek foot. One stadion is always 600 podes,
though the length of the pous varies like the Mesopotamian units, where the cubit or ku was divided into four different digits,
a thumb
, palms, and various hands, fists, spans and quarters. The Greek pous also has long, median and short forms.
(daktylos or finger) which are multiplied as shown. Generally the sexagesimal or decimal multiples have Mesopotamian origins while the septenary multiples have Egyptian origins.
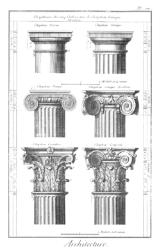
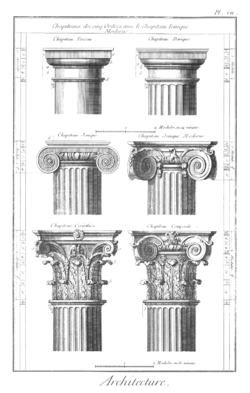
Greek measures of short median and long podes can be thought of as based on body measures. Stecchini and others propose the Greek podes are different sizes because they are divided into different numbers of different sized daktylos to facilitate different calculations. The most obvious place to observe the relative difference is in the Greek orders of architecture whose canon of proportions is based on column diameters.
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the archaeological period generally occurring after the Bronze Age, marked by the prevalent use of iron. The early period of the age is characterized by the widespread use of iron or steel. The adoption of such material coincided with other changes in society, including differing...
in Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
and the Ancient Near East
Ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was the home of early civilizations within a region roughly corresponding to the modern Middle East: Mesopotamia , ancient Egypt, ancient Iran The ancient Near East was the home of early civilizations within a region roughly corresponding to the modern Middle East: Mesopotamia...
.
A pous is a Greek foot. One stadion is always 600 podes,
though the length of the pous varies like the Mesopotamian units, where the cubit or ku was divided into four different digits,
a thumb
Thumb
The thumb is the first digit of the hand. When a person is standing in the medical anatomical position , the thumb is the lateral-most digit...
, palms, and various hands, fists, spans and quarters. The Greek pous also has long, median and short forms.

Comparative analysis
A pous is divided into digitsDigit (unit)
The digit or finger is an ancient and obsolete non-SI unit of measurement of length. It was originally based on the breadth of a human finger...
(daktylos or finger) which are multiplied as shown. Generally the sexagesimal or decimal multiples have Mesopotamian origins while the septenary multiples have Egyptian origins.
Greek measures of short median and long podes can be thought of as based on body measures. Stecchini and others propose the Greek podes are different sizes because they are divided into different numbers of different sized daktylos to facilitate different calculations. The most obvious place to observe the relative difference is in the Greek orders of architecture whose canon of proportions is based on column diameters.
| Unit | no. of daktylos | each daktylo (mm) | total (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Doric order Doric order The Doric order was one of the three orders or organizational systems of ancient Greek or classical architecture; the other two canonical orders were the Ionic and the Corinthian.-History:... pous (foot) |
18 | 18 | 324 mm |
| 1 Luwian pous (foot) | 17 | 19 | 323 mm |
| 1 Attic Attica Attica is a historical region of Greece, containing Athens, the current capital of Greece. The historical region is centered on the Attic peninsula, which projects into the Aegean Sea... pous (foot) |
16 | 19.275 | 308.4 mm |
| 1 Minoan pous (foot) | 16 | 19 | 304 mm |
| 1 Egypt Egypt Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world... ian bd (foot) |
16 | 18.75 | 300 mm |
| 1 Ionian Order Ionic order The Ionic order forms one of the three orders or organizational systems of classical architecture, the other two canonic orders being the Doric and the Corinthian... pous (foot) |
16 | 18.5 | 296 mm |
| 1 Roman Roman Empire The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean.... pes (foot) |
16 | 18.5 | 296 mm |
| 1 Athenian Athens Athens , is the capital and largest city of Greece. Athens dominates the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, as its recorded history spans around 3,400 years. Classical Athens was a powerful city-state... pous (foot) |
15 | 21 | 315 mm |
| 1 Phoenicia Phoenicia Phoenicia , was an ancient civilization in Canaan which covered most of the western, coastal part of the Fertile Crescent. Several major Phoenician cities were built on the coastline of the Mediterranean. It was an enterprising maritime trading culture that spread across the Mediterranean from 1550... n (Pele) pous (foot) |
15 | 20 | 300 mm |

