Power scaling
Encyclopedia
Power scaling of a laser
is increasing its output power without changing the geometry, shape, or principle of operation. Power scalability is considered an important advantage in a laser design.
Usually, power scaling requires a more powerful pump
source, stronger cooling, and an increase in size. It may also require reduction of the background loss in the laser resonator and, in particular, in the gain medium.
is used to increase the power of the beam while preserving its main properties. The master oscillator has no need to be powerful, and has no need to operate at high efficiency because the efficiency is determined mainly by the power amplifier. The combination of several laser amplifiers seeded by a common master oscillator is essential concept of the
High Power Laser Energy Research Facility.
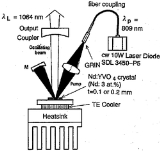
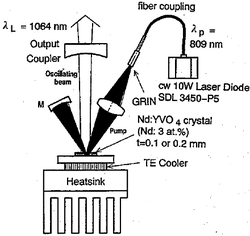 One type of solid-state laser
One type of solid-state laser
designed for good power scaling is the disk laser
(or "active mirror"). Such lasers are believed to be scalable to a power of several kilowatts
from a single active element in continuous-wave operation.
Perhaps, the expectations for power scalability of disk lasers is a little bit exaggerated:
some of publications in favor of disk laser just repeat each other; compare, for example
and
these articles differ with only titles.
Amplified spontaneous emission
, overheating and round-trip loss seem to be the most important processes that limit the power of disk laser
s. For future power scaling, the reduction of the
round-trip loss and/or combining of several active elements is required.
s are another type of solid-state laser with good power scaling. The power scaling of fiber lasers is limited by Raman scattering
and Brillouin scattering
, and by the fact that such lasers cannot be very long. The limited length of the double-clad fiber
s limits the usable power of the multi-mode
pump, because the pump is not absorbed efficiently in the fiber's active core. Optimization of the shape of the cladding can extend the limit of power scaling.
.
The pump in such a laser is delivered from side of a disk, made of coiled fiber with doped core.
Several such disks (with a coolant between them) can be combined into a stack.
The power scaling is limited by the ability to dissipate the heat. Usually, the thermal conductivity of materials designed for efficient laser action, is small compared to that of materials optimal for the heat transfer (metals, diamonds).
For the efficient drain of heat from a compact device, the active medium should be a narrow slab; in order to give advantage to the amplification of light at wanted direction over the ASE
, the energy and head would be withdrawn in orthogonal directions, as it is shown in figure. At low background loss (typically, at the level of 0.01 or 0.001)
the heat and the light can be withdrawn in the opposite directions, allowing active elements of wide aperture. In this case,
combining of several active elements is used for the power scaling.
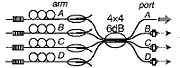 Scalability can also be achieved by combining separate laser beams. Completely independent beams cannot usually be combined to produce a beam with higher radiance
Scalability can also be achieved by combining separate laser beams. Completely independent beams cannot usually be combined to produce a beam with higher radiance
than each beam has alone. Beams can only be combined if they are coherent
with each other. Such beams can be combined actively or passively.
In the passive combining (or coherent addition
) of lasers, only the few mode
s common to all of the combined lasers can be above the lasing threshold
. Efficient passive combining of eight lasers has been reported. Further power scaling requires exponential growth
of the gain bandwidth
and/or length of the individual lasers.
Active combining implies the real-time measurement of the phase
of individual lasers' output, and quick adjustment to keep them all in phase. Such adjustment can be done by adaptive optics
, which is effective for suppression of phase noise at acoustic frequencies
. Faster schemes based on all-optical switching are being researched.
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
is increasing its output power without changing the geometry, shape, or principle of operation. Power scalability is considered an important advantage in a laser design.
Usually, power scaling requires a more powerful pump
Laser pumping
Laser pumping is the act of energy transfer from an external source into the gain medium of a laser. The energy is absorbed in the medium, producing excited states in its atoms. When the number of particles in one excited state exceeds the number of particles in the ground state or a less-excited...
source, stronger cooling, and an increase in size. It may also require reduction of the background loss in the laser resonator and, in particular, in the gain medium.
MOPA
The most popular way of achieving power scalability is the "MOPA" (Master Oscillator Power Amplifier) approach. The master oscillator produces a highly coherent beam, and an optical amplifierOptical amplifier
An optical amplifier is a device that amplifies an optical signal directly, without the need to first convert it to an electrical signal. An optical amplifier may be thought of as a laser without an optical cavity, or one in which feedback from the cavity is suppressed...
is used to increase the power of the beam while preserving its main properties. The master oscillator has no need to be powerful, and has no need to operate at high efficiency because the efficiency is determined mainly by the power amplifier. The combination of several laser amplifiers seeded by a common master oscillator is essential concept of the
High Power Laser Energy Research Facility.
Disk lasers

Solid-state laser
A solid-state laser is a laser that uses a gain medium that is a solid, rather than a liquid such as in dye lasers or a gas as in gas lasers. Semiconductor-based lasers are also in the solid state, but are generally considered as a separate class from solid-state lasers .-Solid-state...
designed for good power scaling is the disk laser
Disk laser
A disk laser or active mirror is a type of solid-state laser characterized by a heat sink and laser output that are realized on opposite sides of a thin layer of active gain medium...
(or "active mirror"). Such lasers are believed to be scalable to a power of several kilowatts
from a single active element in continuous-wave operation.
Perhaps, the expectations for power scalability of disk lasers is a little bit exaggerated:
some of publications in favor of disk laser just repeat each other; compare, for example
and
these articles differ with only titles.
Amplified spontaneous emission
Amplified spontaneous emission
Amplified spontaneous emission or superluminescence is light, produced by spontaneous emission, that has been optically amplified by the process of stimulated emission in a gain medium. It is inherent in the field of random lasers....
, overheating and round-trip loss seem to be the most important processes that limit the power of disk laser
Disk laser
A disk laser or active mirror is a type of solid-state laser characterized by a heat sink and laser output that are realized on opposite sides of a thin layer of active gain medium...
s. For future power scaling, the reduction of the
round-trip loss and/or combining of several active elements is required.
Fiber lasers
Fiber laserFiber laser
A fiber laser or fibre laser is a laser in which the active gain medium is an optical fiber doped with rare-earth elements such as erbium, ytterbium, neodymium, dysprosium, praseodymium, and thulium. They are related to doped fiber amplifiers, which provide light amplification without lasing...
s are another type of solid-state laser with good power scaling. The power scaling of fiber lasers is limited by Raman scattering
Raman scattering
Raman scattering or the Raman effect is the inelastic scattering of a photon. It was discovered by Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman and Kariamanickam Srinivasa Krishnan in liquids, and by Grigory Landsberg and Leonid Mandelstam in crystals....
and Brillouin scattering
Brillouin scattering
Brillouin scattering, named after Léon Brillouin, occurs when light in a medium interacts with time dependent optical density variations and changes its energy and path. The density variations may be due to acoustic modes, such as phonons, magnetic modes, such as magnons, or temperature gradients...
, and by the fact that such lasers cannot be very long. The limited length of the double-clad fiber
Double-clad fiber
Double-clad fiber is a class of optical fiber with a structure consisting of three layers of optical material instead of the usual two. The inner-most layer is called the core. It is surrounded by the inner cladding, which is surrounded by the outer cladding...
s limits the usable power of the multi-mode
Transverse mode
A transverse mode of a beam of electromagnetic radiation is a particular electromagnetic field pattern of radiation measured in a plane perpendicular to the propagation direction of the beam...
pump, because the pump is not absorbed efficiently in the fiber's active core. Optimization of the shape of the cladding can extend the limit of power scaling.
Fiber disk lasers
The limit of power scaling of fiber lasers can be extended with lateral delivery of the pump. This is realized in so-called fiber disk lasers.
The pump in such a laser is delivered from side of a disk, made of coiled fiber with doped core.
Several such disks (with a coolant between them) can be combined into a stack.
Problem of heat sink
.]]The power scaling is limited by the ability to dissipate the heat. Usually, the thermal conductivity of materials designed for efficient laser action, is small compared to that of materials optimal for the heat transfer (metals, diamonds).
For the efficient drain of heat from a compact device, the active medium should be a narrow slab; in order to give advantage to the amplification of light at wanted direction over the ASE
Amplified spontaneous emission
Amplified spontaneous emission or superluminescence is light, produced by spontaneous emission, that has been optically amplified by the process of stimulated emission in a gain medium. It is inherent in the field of random lasers....
, the energy and head would be withdrawn in orthogonal directions, as it is shown in figure. At low background loss (typically, at the level of 0.01 or 0.001)
the heat and the light can be withdrawn in the opposite directions, allowing active elements of wide aperture. In this case,
combining of several active elements is used for the power scaling.
Coherent addition and combining beams

Radiance
Radiance and spectral radiance are radiometric measures that describe the amount of radiation such as light or radiant heat that passes through or is emitted from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle in a specified direction. They are used to characterize both emission from...
than each beam has alone. Beams can only be combined if they are coherent
Coherence (physics)
In physics, coherence is a property of waves that enables stationary interference. More generally, coherence describes all properties of the correlation between physical quantities of a wave....
with each other. Such beams can be combined actively or passively.
In the passive combining (or coherent addition
Coherent addition
Coherent addition of lasersis one of methods of the power scaling. It allows a to increase the output power and brightness of single-transversal mode laser.Usually, the term coherent addition applies to fiber lasers...
) of lasers, only the few mode
Normal mode
A normal mode of an oscillating system is a pattern of motion in which all parts of the system move sinusoidally with the same frequency and with a fixed phase relation. The frequencies of the normal modes of a system are known as its natural frequencies or resonant frequencies...
s common to all of the combined lasers can be above the lasing threshold
Lasing threshold
The lasing threshold is the lowest excitation level at which a laser's output is dominated by stimulated emission rather than by spontaneous emission. Below the threshold, the laser's output power rises slowly with increasing excitation. Above threshold, the slope of power vs. excitation is orders...
. Efficient passive combining of eight lasers has been reported. Further power scaling requires exponential growth
Exponential growth
Exponential growth occurs when the growth rate of a mathematical function is proportional to the function's current value...
of the gain bandwidth
Gain-bandwidth product
The gain–bandwidth product for an amplifier is the product of the amplifier's bandwidth, and the gain at which the bandwidth is measured....
and/or length of the individual lasers.
Active combining implies the real-time measurement of the phase
Phase (waves)
Phase in waves is the fraction of a wave cycle which has elapsed relative to an arbitrary point.-Formula:The phase of an oscillation or wave refers to a sinusoidal function such as the following:...
of individual lasers' output, and quick adjustment to keep them all in phase. Such adjustment can be done by adaptive optics
Adaptive optics
Adaptive optics is a technology used to improve the performance of optical systems by reducing the effect of wavefront distortions. It is used in astronomical telescopes and laser communication systems to remove the effects of atmospheric distortion, and in retinal imaging systems to reduce the...
, which is effective for suppression of phase noise at acoustic frequencies
Sound
Sound is a mechanical wave that is an oscillation of pressure transmitted through a solid, liquid, or gas, composed of frequencies within the range of hearing and of a level sufficiently strong to be heard, or the sensation stimulated in organs of hearing by such vibrations.-Propagation of...
. Faster schemes based on all-optical switching are being researched.

