
Prandtl number
Encyclopedia
The Prandtl number 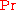 is a dimensionless number; the ratio of momentum diffusivity (kinematic viscosity) to thermal diffusivity
is a dimensionless number; the ratio of momentum diffusivity (kinematic viscosity) to thermal diffusivity
. It is named after the German physicist Ludwig Prandtl.
It is defined as: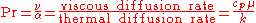
where:
Note that whereas the Reynolds number and Grashof number are subscripted with a length scale variable, Prandtl number contains no such length scale in its definition and is dependent only on the fluid and the fluid state. As such, Prandtl number is often found in property tables alongside other properties such as viscosity
and thermal conductivity
.
Typical values for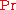 are:
are:
(Low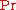 - conductive transfer strong)
- conductive transfer strong)
(High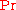 - convective transfer strong)
- convective transfer strong)
For mercury, heat conduction
is very effective compared to convection
: thermal diffusivity is dominant.
For engine oil, convection is very effective in transferring energy
from an area, compared to pure conduction: momentum diffusivity is dominant.
In heat transfer problems, the Prandtl number controls the relative thickness of the momentum and thermal boundary layers. When Pr is small, it means that the heat diffuses very quickly compared to the velocity (momentum). This means that for liquid metals the thickness of the thermal boundary layer is much bigger than the velocity boundary layer.
The mass transfer analog of the Prandtl number is the Schmidt number
.
 is a dimensionless number; the ratio of momentum diffusivity (kinematic viscosity) to thermal diffusivity
is a dimensionless number; the ratio of momentum diffusivity (kinematic viscosity) to thermal diffusivityThermal diffusivity
In heat transfer analysis, thermal diffusivity is the thermal conductivity divided by density and specific heat capacity at constant pressure. It has the SI unit of m²/s...
. It is named after the German physicist Ludwig Prandtl.
It is defined as:
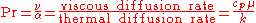
where:
-
 : kinematic viscosity,
: kinematic viscosity,  , (SISiSi, si, or SI may refer to :- Measurement, mathematics and science :* International System of Units , the modern international standard version of the metric system...
, (SISiSi, si, or SI may refer to :- Measurement, mathematics and science :* International System of Units , the modern international standard version of the metric system...
units : m2/s) -
 : thermal diffusivityThermal diffusivityIn heat transfer analysis, thermal diffusivity is the thermal conductivity divided by density and specific heat capacity at constant pressure. It has the SI unit of m²/s...
: thermal diffusivityThermal diffusivityIn heat transfer analysis, thermal diffusivity is the thermal conductivity divided by density and specific heat capacity at constant pressure. It has the SI unit of m²/s...
, , (SI units : m2/s)
, (SI units : m2/s) -
 : dynamic viscosity, (SI units : Pa s = (N s)/m2)
: dynamic viscosity, (SI units : Pa s = (N s)/m2) -
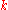 : thermal conductivityThermal conductivityIn physics, thermal conductivity, k, is the property of a material's ability to conduct heat. It appears primarily in Fourier's Law for heat conduction....
: thermal conductivityThermal conductivityIn physics, thermal conductivity, k, is the property of a material's ability to conduct heat. It appears primarily in Fourier's Law for heat conduction....
, (SI units : W/(m K) ) -
 : specific heat, (SI units : J/(kg K) )
: specific heat, (SI units : J/(kg K) ) -
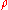 : densityDensityThe mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
: densityDensityThe mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
, (SI units : kg/m3 ).
Note that whereas the Reynolds number and Grashof number are subscripted with a length scale variable, Prandtl number contains no such length scale in its definition and is dependent only on the fluid and the fluid state. As such, Prandtl number is often found in property tables alongside other properties such as viscosity
Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
and thermal conductivity
Thermal conductivity
In physics, thermal conductivity, k, is the property of a material's ability to conduct heat. It appears primarily in Fourier's Law for heat conduction....
.
Typical values for
 are:
are:(Low
 - conductive transfer strong)
- conductive transfer strong)
- around 0.015 for mercuryMercury (element)Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver or hydrargyrum...
- around 0.16-0.7 for mixtures of noble gasNoble gasThe noble gases are a group of chemical elements with very similar properties: under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases, with very low chemical reactivity...
es or noble gases with hydrogenHydrogenHydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly... - around 0.7-0.8 for air and many other gasGasGas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
es, - between 4 and 5 for R-12 refrigerantDichlorodifluoromethaneDichlorodifluoromethane , is a colorless gas, and usually sold under the brand name Freon-12, is a chlorofluorocarbon halomethane , used as a refrigerant and aerosol spray propellant. Complying with the Montreal Protocol, its manufacture was banned in the United States along with many other...
- around 7 for waterWaterWater is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
(At 20 degrees Celsius) - between 100 and 40,000 for engine oil
- around 1 for EarthEarthEarth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
's mantleMantle (geology)The mantle is a part of a terrestrial planet or other rocky body large enough to have differentiation by density. The interior of the Earth, similar to the other terrestrial planets, is chemically divided into layers. The mantle is a highly viscous layer between the crust and the outer core....
.
(High
 - convective transfer strong)
- convective transfer strong)For mercury, heat conduction
Heat conduction
In heat transfer, conduction is a mode of transfer of energy within and between bodies of matter, due to a temperature gradient. Conduction means collisional and diffusive transfer of kinetic energy of particles of ponderable matter . Conduction takes place in all forms of ponderable matter, viz....
is very effective compared to convection
Convection
Convection is the movement of molecules within fluids and rheids. It cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids....
: thermal diffusivity is dominant.
For engine oil, convection is very effective in transferring energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
from an area, compared to pure conduction: momentum diffusivity is dominant.
In heat transfer problems, the Prandtl number controls the relative thickness of the momentum and thermal boundary layers. When Pr is small, it means that the heat diffuses very quickly compared to the velocity (momentum). This means that for liquid metals the thickness of the thermal boundary layer is much bigger than the velocity boundary layer.
The mass transfer analog of the Prandtl number is the Schmidt number
Schmidt number
Schmidt number is a dimensionless number defined as the ratio of momentum diffusivity and mass diffusivity, and is used to characterize fluid flows in which there are simultaneous momentum and mass diffusion convection processes...
.

