
Principle of indifference
Encyclopedia
The principle of indifference (also called principle of insufficient reason) is a rule for assigning epistemic probabilities.
Suppose that there are n > 1 mutually exclusive
and collectively exhaustive
possibilities.
The principle of indifference states that if the n possibilities are indistinguishable except for their names,
then each possibility should be assigned a probability equal to 1/n.
In Bayesian probability
, this is the simplest non-informative prior.
The principle of indifference is meaningless under the frequency interpretation of probability
, in which probabilities are relative frequencies rather than degrees of belief in uncertain propositions, conditional upon a state of information.
s, dice
, and cards.
In a macroscopic
system, at least,
it must be assumed that the physical laws which govern the system are not known well enough to predict the outcome.
As observed some centuries ago by John Arbuthnot
(in the preface of Of the Laws of Chance, 1692),
Given enough time and money,
there is no fundamental reason to suppose that suitably precise measurements could not be made,
which would enable the prediction of the outcome of coins, dice, and cards with high accuracy: Persi Diaconis
's work with coin-flipping
machines is a practical example of this.
coin has two sides, arbitrarily labeled heads and tails.
Assuming that the coin must land on one side or the other,
the outcomes of a coin toss are mutually exclusive, exhaustive, and interchangeable.
According to the principle of indifference, we assign each of the possible outcomes a probability of 1/2.
It is implicit in this analysis that the forces acting on the coin are not known with any precision.
If the momentum imparted to the coin as it is launched were known with sufficient accuracy,
the flight of the coin could be predicted according to the laws of mechanics.
Thus the uncertainty in the outcome of a coin toss is derived (for the most part) from the uncertainty with respect to initial conditions.
This point is discussed at greater length in the article on coin flipping.
There is also a third possible outcome: the coin could land on its edge.
However,
the principle of indifference doesn't say anything about this outcome, as the labels head, tail, and edge are not interchangeable.
One could argue, though, that head and tail remain interchangeable, and therefore Pr(head) and Pr(tail) are equal, and both are equal to 1/2 (1 - Pr(edge)).
die
has n faces, arbitrarily labeled from 1 to n.
Ordinary cubical dice have n = 6 faces,
although symmetric dice with different numbers of faces can be constructed;
see dice
.
We assume that the die must land on one face or another,
and there are no other possible outcomes.
Applying the principle of indifference, we assign each of the possible outcomes a probability of 1/n.
As with coins,
it is assumed that the initial conditions of throwing the dice are not known
with enough precision to predict the outcome according to the laws of mechanics.
Dice are typically thrown so as to bounce on a table or other surface.
This interaction makes prediction of the outcome much more difficult.
This example, more than the others, shows the difficulty of actually applying the principle of indifference in real situations. What we really mean by the phrase "arbitrarily ordered" is simply that we don't have any information that would lead us to favor a particular card. In actual practice, this is rarely the case: a new deck of cards is certainly not in arbitrary order, and neither is a deck immediately after a hand of cards. In practice, we therefore shuffle the cards; this does not destroy the information we have, but instead (hopefully) renders our information practically unusable, although it is still usable in principle. In fact, some expert blackjack players can track aces through the deck; for them, the condition for applying the principle of indifference is not satisfied.
In this example, mutually contradictory estimates of the length, surface area, and volume of the cube arise because we have assumed three mutually contradictory distributions for these parameters: a uniform distribution
for any one of the variables implies a non-uniform distribution for the other two. (The same paradox arises if we make it discrete: the side is either exactly 3 cm, 4 cm, or 5 cm, mutatis mutandis.) In general, the principle of indifference does not indicate which variable (e.g. in this case, length, surface area, or volume) is to have a uniform epistemic probability distribution.
Another classic example of this kind of misuse is Bertrand's paradox
. Edwin T. Jaynes introduced the principle of transformation groups
, which can yield an epistemic probability distribution for this problem. This generalises the principle of indifference, by saying that one is indifferent between equivalent problems rather than indifference between propositions. This still reduces to the "ordinary" principle of indifference when one considers a "permutation" of the labels as generating equivalent problems (i.e. using the permutation transformation group). To apply this to the above box example, we have three problems, with no reason to think one problem is "our problem" more than any other - we are indifferent between each. If we have no reason to favour one over the other, then our prior probabilities must be related by the rule for changing variables in continuous distributions. Let L be the length, and V be the volume. Then we must have
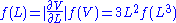
Which has a general solution: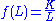 Where K is an arbitrary constant, determined by the range of L, in this case equal to:
Where K is an arbitrary constant, determined by the range of L, in this case equal to:
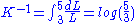
To put this "to the test", we ask for the probability that the length is less than 4. This has probability of:
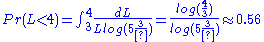 .
.
For the volume, this should be equal to the probability that the volume is less than 43 = 64. The pdf of the volume is
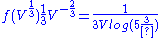 .
.
And then probability of volume less than 64 is
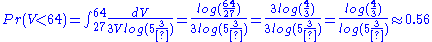 .
.
Thus we have achieve invariance with respect to volume and length. You can also show the same invariance with respect to surface area being less than 6(42) = 96. However, note that this probability assignment is not necessarily a "correct" one. For the exact distribution of lengths, volume, or surface area will depend on how the "experiment" is conducted. This probability assignment is very similar to the maximum entropy one, in that the frequency distribution corresponding to the above probability distribution is the most likely to be seen. So, if one was to go to N people individually and simply say "make me a box somewhere between 3 and 5 cm, or a volume between 27 and 125 cm, or a surface area between 54 and 150 cm", then unless there is a systematic influence on how they make the boxes (e.g. they form a group, and choose one particular method of making boxes), about 56% of the boxes will be less than 4 cm - and it will get very close to this amount very quickly. So, for large N, any deviation from this basically indicates the makers of the boxes were "systematic" in how the boxes were made.
The fundamental hypothesis of statistical physics
, that any two microstates of a system with the same total energy are equally probable at equilibrium
, is in a sense an example of the principle of indifference. However, when the microstates are described by continuous variables (such as positions and momenta), an additional physical basis is needed in order to explain under which parameterization the probability density will be uniform. Liouville's theorem
justifies the use of canonically conjugate variables, such as positions and their conjugate momenta.
These earlier writers, Laplace in particular, naively generalized the principle of indifference to the case of continuous parameters, giving the so-called "uniform prior probability distribution", a function which is constant over all real numbers. He used this function to express a complete lack of knowledge as to the value of a parameter.
The principle of insufficient reason was its first name, given to it by later writers, possibly as a play on Leibniz
's principle of sufficient reason
. These later writers (George Boole
, John Venn
, and others) objected to the use of the uniform prior for two reasons. The first reason is that the constant function is not normalizable, and thus is not a proper probability distribution. The second reason is its inapplicability to continuous variables, as described above. (However, these paradoxical issues can be resolved. In the first case, a constant, or any more general finite polynomial, is normalizable within any finite range: the range [0,1] is all that matters here. Alternatively, modify the function to be zero outside that range. See uniform distribution
. In the second case, there is no ambiguity provided the problem is "well-posed", so that no unwarranted assumptions can be made, or have to be made, thereby fixing the appropriate prior probability density function
or prior moment generating function (with variables fixed appropriately) to be used for the probability itself. See the Bertrand paradox (probability) for an analogous case.)
The "Principle of insufficient reason" was renamed the "Principle of Indifference" by the economist , who was careful to note that it applies only when there is no knowledge indicating unequal probabilities.
Attempts to put the notion on firmer philosophical
ground have generally begun with the concept of equipossibility and progressed from it to equiprobability.
The principle of indifference can be given a deeper logical justification by noting that equivalent states of knowledge should be assigned equivalent epistemic probabilities. This argument was propounded by E.T. Jaynes: it leads to two generalizations, namely the principle of transformation groups
as in the Jeffreys prior
, and the principle of maximum entropy
.
More generally, one speaks of non-informative priors.
Suppose that there are n > 1 mutually exclusive
Mutually exclusive
In layman's terms, two events are mutually exclusive if they cannot occur at the same time. An example is tossing a coin once, which can result in either heads or tails, but not both....
and collectively exhaustive
Collectively exhaustive
In probability theory, a set of events is jointly or collectively exhaustive if at least one of the events must occur. For example, when rolling a six-sided die, the outcomes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 are collectively exhaustive, because they encompass the entire range of possible outcomes.Another way...
possibilities.
The principle of indifference states that if the n possibilities are indistinguishable except for their names,
then each possibility should be assigned a probability equal to 1/n.
In Bayesian probability
Bayesian probability
Bayesian probability is one of the different interpretations of the concept of probability and belongs to the category of evidential probabilities. The Bayesian interpretation of probability can be seen as an extension of logic that enables reasoning with propositions, whose truth or falsity is...
, this is the simplest non-informative prior.
The principle of indifference is meaningless under the frequency interpretation of probability
Frequency probability
Frequency probability is the interpretation of probability that defines an event's probability as the limit of its relative frequency in a large number of trials. The development of the frequentist account was motivated by the problems and paradoxes of the previously dominant viewpoint, the...
, in which probabilities are relative frequencies rather than degrees of belief in uncertain propositions, conditional upon a state of information.
Examples
The textbook examples for the application of the principle of indifference are coinCoin
A coin is a piece of hard material that is standardized in weight, is produced in large quantities in order to facilitate trade, and primarily can be used as a legal tender token for commerce in the designated country, region, or territory....
s, dice
Dice
A die is a small throwable object with multiple resting positions, used for generating random numbers...
, and cards.
In a macroscopic
Macroscopic
The macroscopic scale is the length scale on which objects or processes are of a size which is measurable and observable by the naked eye.When applied to phenomena and abstract objects, the macroscopic scale describes existence in the world as we perceive it, often in contrast to experiences or...
system, at least,
it must be assumed that the physical laws which govern the system are not known well enough to predict the outcome.
As observed some centuries ago by John Arbuthnot
John Arbuthnot
John Arbuthnot, often known simply as Dr. Arbuthnot, , was a physician, satirist and polymath in London...
(in the preface of Of the Laws of Chance, 1692),
- It is impossible for a Die, with such determin'd force and direction, not to fall on such determin'd side, only I don't know the force and direction which makes it fall on such determin'd side, and therefore I call it Chance, which is nothing but the want of art....
Given enough time and money,
there is no fundamental reason to suppose that suitably precise measurements could not be made,
which would enable the prediction of the outcome of coins, dice, and cards with high accuracy: Persi Diaconis
Persi Diaconis
Persi Warren Diaconis is an American mathematician and former professional magician. He is the Mary V. Sunseri Professor of Statistics and Mathematics at Stanford University....
's work with coin-flipping
Coin flipping
Coin flipping or coin tossing or heads or tails is the practice of throwing a coin in the air to choose between two alternatives, sometimes to resolve a dispute between two parties...
machines is a practical example of this.
Coins
A symmetricSymmetry
Symmetry generally conveys two primary meanings. The first is an imprecise sense of harmonious or aesthetically pleasing proportionality and balance; such that it reflects beauty or perfection...
coin has two sides, arbitrarily labeled heads and tails.
Assuming that the coin must land on one side or the other,
the outcomes of a coin toss are mutually exclusive, exhaustive, and interchangeable.
According to the principle of indifference, we assign each of the possible outcomes a probability of 1/2.
It is implicit in this analysis that the forces acting on the coin are not known with any precision.
If the momentum imparted to the coin as it is launched were known with sufficient accuracy,
the flight of the coin could be predicted according to the laws of mechanics.
Thus the uncertainty in the outcome of a coin toss is derived (for the most part) from the uncertainty with respect to initial conditions.
This point is discussed at greater length in the article on coin flipping.
There is also a third possible outcome: the coin could land on its edge.
However,
the principle of indifference doesn't say anything about this outcome, as the labels head, tail, and edge are not interchangeable.
One could argue, though, that head and tail remain interchangeable, and therefore Pr(head) and Pr(tail) are equal, and both are equal to 1/2 (1 - Pr(edge)).
Dice
A symmetricSymmetry
Symmetry generally conveys two primary meanings. The first is an imprecise sense of harmonious or aesthetically pleasing proportionality and balance; such that it reflects beauty or perfection...
die
Dice
A die is a small throwable object with multiple resting positions, used for generating random numbers...
has n faces, arbitrarily labeled from 1 to n.
Ordinary cubical dice have n = 6 faces,
although symmetric dice with different numbers of faces can be constructed;
see dice
Dice
A die is a small throwable object with multiple resting positions, used for generating random numbers...
.
We assume that the die must land on one face or another,
and there are no other possible outcomes.
Applying the principle of indifference, we assign each of the possible outcomes a probability of 1/n.
As with coins,
it is assumed that the initial conditions of throwing the dice are not known
with enough precision to predict the outcome according to the laws of mechanics.
Dice are typically thrown so as to bounce on a table or other surface.
This interaction makes prediction of the outcome much more difficult.
Cards
A standard deck contains 52 cards, each given a unique label in an arbitrary fashion, i.e. arbitrarily ordered. We draw a card from the deck; applying the principle of indifference, we assign each of the possible outcomes a probability of 1/52.This example, more than the others, shows the difficulty of actually applying the principle of indifference in real situations. What we really mean by the phrase "arbitrarily ordered" is simply that we don't have any information that would lead us to favor a particular card. In actual practice, this is rarely the case: a new deck of cards is certainly not in arbitrary order, and neither is a deck immediately after a hand of cards. In practice, we therefore shuffle the cards; this does not destroy the information we have, but instead (hopefully) renders our information practically unusable, although it is still usable in principle. In fact, some expert blackjack players can track aces through the deck; for them, the condition for applying the principle of indifference is not satisfied.
Application to continuous variables
Applying the principle of indifference incorrectly can easily lead to nonsensical results, especially in the case of multivariate, continuous variables. A typical case of misuse is the following example.- Suppose there is a cube hidden in a box. A label on the box says the cube has a side length between 3 and 5 cm.
- We don't know the actual side length, but we might assume that all values are equally likely and simply pick the mid-value of 4 cm.
- The information on the label allows us to calculate that the surface area of the cube is between 54 and 150 cm². We don't know the actual surface area, but we might assume that all values are equally likely and simply pick the mid-value of 102 cm².
- The information on the label allows us to calculate that the volume of the cube is between 27 and 125 cm3. We don't know the actual volume, but we might assume that all values are equally likely and simply pick the mid-value of 76 cm3.
- However, we have now reached the impossible conclusion that the cube has a side length of 4 cm, a surface area of 102 cm², and a volume of 76 cm3!
In this example, mutually contradictory estimates of the length, surface area, and volume of the cube arise because we have assumed three mutually contradictory distributions for these parameters: a uniform distribution
Uniform distribution (continuous)
In probability theory and statistics, the continuous uniform distribution or rectangular distribution is a family of probability distributions such that for each member of the family, all intervals of the same length on the distribution's support are equally probable. The support is defined by...
for any one of the variables implies a non-uniform distribution for the other two. (The same paradox arises if we make it discrete: the side is either exactly 3 cm, 4 cm, or 5 cm, mutatis mutandis.) In general, the principle of indifference does not indicate which variable (e.g. in this case, length, surface area, or volume) is to have a uniform epistemic probability distribution.
Another classic example of this kind of misuse is Bertrand's paradox
Bertrand's paradox (probability)
The Bertrand paradox is a problem within the classical interpretation of probability theory. Joseph Bertrand introduced it in his work Calcul des probabilités as an example to show that probabilities may not be well defined if the mechanism or method that produces the random variable is not...
. Edwin T. Jaynes introduced the principle of transformation groups
Principle of transformation groups
The principle of transformation groups is a rule for assigning epistemic probabilities in a statistical inference problem. It was first suggested by Edwin T Jaynes and can be seen as a generalisation of the principle of indifference....
, which can yield an epistemic probability distribution for this problem. This generalises the principle of indifference, by saying that one is indifferent between equivalent problems rather than indifference between propositions. This still reduces to the "ordinary" principle of indifference when one considers a "permutation" of the labels as generating equivalent problems (i.e. using the permutation transformation group). To apply this to the above box example, we have three problems, with no reason to think one problem is "our problem" more than any other - we are indifferent between each. If we have no reason to favour one over the other, then our prior probabilities must be related by the rule for changing variables in continuous distributions. Let L be the length, and V be the volume. Then we must have
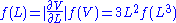
Which has a general solution:
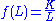 Where K is an arbitrary constant, determined by the range of L, in this case equal to:
Where K is an arbitrary constant, determined by the range of L, in this case equal to: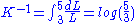
To put this "to the test", we ask for the probability that the length is less than 4. This has probability of:
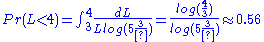 .
.For the volume, this should be equal to the probability that the volume is less than 43 = 64. The pdf of the volume is
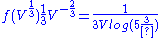 .
.And then probability of volume less than 64 is
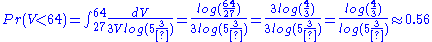 .
.Thus we have achieve invariance with respect to volume and length. You can also show the same invariance with respect to surface area being less than 6(42) = 96. However, note that this probability assignment is not necessarily a "correct" one. For the exact distribution of lengths, volume, or surface area will depend on how the "experiment" is conducted. This probability assignment is very similar to the maximum entropy one, in that the frequency distribution corresponding to the above probability distribution is the most likely to be seen. So, if one was to go to N people individually and simply say "make me a box somewhere between 3 and 5 cm, or a volume between 27 and 125 cm, or a surface area between 54 and 150 cm", then unless there is a systematic influence on how they make the boxes (e.g. they form a group, and choose one particular method of making boxes), about 56% of the boxes will be less than 4 cm - and it will get very close to this amount very quickly. So, for large N, any deviation from this basically indicates the makers of the boxes were "systematic" in how the boxes were made.
The fundamental hypothesis of statistical physics
Statistical physics
Statistical physics is the branch of physics that uses methods of probability theory and statistics, and particularly the mathematical tools for dealing with large populations and approximations, in solving physical problems. It can describe a wide variety of fields with an inherently stochastic...
, that any two microstates of a system with the same total energy are equally probable at equilibrium
Thermodynamic equilibrium
In thermodynamics, a thermodynamic system is said to be in thermodynamic equilibrium when it is in thermal equilibrium, mechanical equilibrium, radiative equilibrium, and chemical equilibrium. The word equilibrium means a state of balance...
, is in a sense an example of the principle of indifference. However, when the microstates are described by continuous variables (such as positions and momenta), an additional physical basis is needed in order to explain under which parameterization the probability density will be uniform. Liouville's theorem
Liouville's theorem (Hamiltonian)
In physics, Liouville's theorem, named after the French mathematician Joseph Liouville, is a key theorem in classical statistical and Hamiltonian mechanics...
justifies the use of canonically conjugate variables, such as positions and their conjugate momenta.
History of the principle of indifference
The original writers on probability, primarily Jacob Bernoulli and Pierre Simon Laplace, considered the principle of indifference to be intuitively obvious and did not even bother to give it a name. Laplace wrote:- The theory of chance consists in reducing all the events of the same kind to a certain number of cases equally possible, that is to say, to such as we may be equally undecided about in regard to their existence, and in determining the number of cases favorable to the event whose probability is sought. The ratio of this number to that of all the cases possible is the measure of this probability, which is thus simply a fraction whose numerator is the number of favorable cases and whose denominator is the number of all the cases possible.
These earlier writers, Laplace in particular, naively generalized the principle of indifference to the case of continuous parameters, giving the so-called "uniform prior probability distribution", a function which is constant over all real numbers. He used this function to express a complete lack of knowledge as to the value of a parameter.
The principle of insufficient reason was its first name, given to it by later writers, possibly as a play on Leibniz
Gottfried Leibniz
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz was a German philosopher and mathematician. He wrote in different languages, primarily in Latin , French and German ....
's principle of sufficient reason
Principle of sufficient reason
The principle of sufficient reason states that anything that happens does so for a reason: no state of affairs can obtain, and no statement can be true unless there is sufficient reason why it should not be otherwise...
. These later writers (George Boole
George Boole
George Boole was an English mathematician and philosopher.As the inventor of Boolean logic—the basis of modern digital computer logic—Boole is regarded in hindsight as a founder of the field of computer science. Boole said,...
, John Venn
John Venn
Donald A. Venn FRS , was a British logician and philosopher. He is famous for introducing the Venn diagram, which is used in many fields, including set theory, probability, logic, statistics, and computer science....
, and others) objected to the use of the uniform prior for two reasons. The first reason is that the constant function is not normalizable, and thus is not a proper probability distribution. The second reason is its inapplicability to continuous variables, as described above. (However, these paradoxical issues can be resolved. In the first case, a constant, or any more general finite polynomial, is normalizable within any finite range: the range [0,1] is all that matters here. Alternatively, modify the function to be zero outside that range. See uniform distribution
Uniform distribution
-Probability theory:* Discrete uniform distribution* Continuous uniform distribution-Other:* "Uniform distribution modulo 1", see Equidistributed sequence*Uniform distribution , a type of species distribution* Distribution of military uniforms...
. In the second case, there is no ambiguity provided the problem is "well-posed", so that no unwarranted assumptions can be made, or have to be made, thereby fixing the appropriate prior probability density function
Probability density function
In probability theory, a probability density function , or density of a continuous random variable is a function that describes the relative likelihood for this random variable to occur at a given point. The probability for the random variable to fall within a particular region is given by the...
or prior moment generating function (with variables fixed appropriately) to be used for the probability itself. See the Bertrand paradox (probability) for an analogous case.)
The "Principle of insufficient reason" was renamed the "Principle of Indifference" by the economist , who was careful to note that it applies only when there is no knowledge indicating unequal probabilities.
Attempts to put the notion on firmer philosophical
Philosophy
Philosophy is the study of general and fundamental problems, such as those connected with existence, knowledge, values, reason, mind, and language. Philosophy is distinguished from other ways of addressing such problems by its critical, generally systematic approach and its reliance on rational...
ground have generally begun with the concept of equipossibility and progressed from it to equiprobability.
The principle of indifference can be given a deeper logical justification by noting that equivalent states of knowledge should be assigned equivalent epistemic probabilities. This argument was propounded by E.T. Jaynes: it leads to two generalizations, namely the principle of transformation groups
Principle of transformation groups
The principle of transformation groups is a rule for assigning epistemic probabilities in a statistical inference problem. It was first suggested by Edwin T Jaynes and can be seen as a generalisation of the principle of indifference....
as in the Jeffreys prior
Jeffreys prior
In Bayesian probability, the Jeffreys prior, named after Harold Jeffreys, is a non-informative prior distribution on parameter space that is proportional to the square root of the determinant of the Fisher information:...
, and the principle of maximum entropy
Principle of maximum entropy
In Bayesian probability, the principle of maximum entropy is a postulate which states that, subject to known constraints , the probability distribution which best represents the current state of knowledge is the one with largest entropy.Let some testable information about a probability distribution...
.
More generally, one speaks of non-informative priors.

