Proembryo
Encyclopedia
Proembryo, or pro-embryo, is a botanical
term that has been used for centuries, to denote the series of cells that are formed after fertilization within the ovule
of a flowering plant, before formation of the embryo
.
More recently, this same term has been given a more extensive meaning, with reference to human egg cells (ova
) that have been fertilized but not yet implanted into a uterus
. This more recent meaning is synonymous with "preembryo" or "pre-embryo," and corresponds to stages with more accepted terms zygote
and blastocyst
.
at least between fertilization and implantation, and is known too as a proembryo. A conceptus between fertilization and implantation is also frequently classified as an embryo.
Even after implantation begins, a preembryo (and proembryo) may exist up until formation of the primitive streak
. Implantation begins at about six days after fertilization, and lasts for about a week, during which time formation of the primitive streak occurs.
Use of the terms preembryo and proembryo, in the context of human development, has drawn criticism from opponents of embryo research, and from scientists who have considered this categorization invalid or unnecessary. One rationale that has been advanced for distinguishing an early fertilized human conceptus from an embryo is that there is a potential for the conceptus to split into identical twins prior to implantation, and so (the argument goes) the conceptus cannot be regarded before implantation as a single human being. However, the conceptus before implantation exhibits self-actuated activity, which has led to the assertion that it is an embryo.
In the United States, a report by the National Institutes of Health
stated that a conceptus could be both a pre-implantation embryo and a pre-embryo at the same time. However, Ann Kiessling
(a leader in stem cell research) has written that those categories are inaccurate.
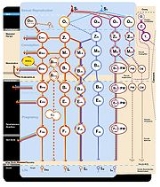
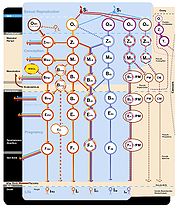 The illustration shows the ontological status of the preembryo, embryo
The illustration shows the ontological status of the preembryo, embryo
, and fetus
:
The colors represent the maternal and paternal genetic contributions.
Botany
Botany, plant science, or plant biology is a branch of biology that involves the scientific study of plant life. Traditionally, botany also included the study of fungi, algae and viruses...
term that has been used for centuries, to denote the series of cells that are formed after fertilization within the ovule
Ovule
Ovule means "small egg". In seed plants, the ovule is the structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells. It consists of three parts: The integument forming its outer layer, the nucellus , and the megaspore-derived female gametophyte in its center...
of a flowering plant, before formation of the embryo
Plant embryogenesis
Plant embryogenesis is the process that produces a plant embryo from a fertilised ovule by asymmetric cell division and the differentiation of undifferentiated cells into tissues and organs. It occurs during seed development, when the single-celled zygote undergoes a programmed pattern of cell...
.
More recently, this same term has been given a more extensive meaning, with reference to human egg cells (ova
Ovum
An ovum is a haploid female reproductive cell or gamete. Both animals and embryophytes have ova. The term ovule is used for the young ovum of an animal, as well as the plant structure that carries the female gametophyte and egg cell and develops into a seed after fertilization...
) that have been fertilized but not yet implanted into a uterus
Uterus
The uterus or womb is a major female hormone-responsive reproductive sex organ of most mammals including humans. One end, the cervix, opens into the vagina, while the other is connected to one or both fallopian tubes, depending on the species...
. This more recent meaning is synonymous with "preembryo" or "pre-embryo," and corresponds to stages with more accepted terms zygote
Zygote
A zygote , or zygocyte, is the initial cell formed when two gamete cells are joined by means of sexual reproduction. In multicellular organisms, it is the earliest developmental stage of the embryo...
and blastocyst
Blastocyst
The blastocyst is a structure formed in the early embryogenesis of mammals, after the formation of the morula. It is a specifically mammalian example of a blastula. It possesses an inner cell mass , or embryoblast, which subsequently forms the embryo, and an outer layer of cells, or trophoblast,...
.
Preembryo in context of human development
A preembryo is a human conceptusConceptus
Conceptus denotes the embryo and its adnexa or associated membranes . The conceptus includes all structures that develop from the zygote, both embryonic and extraembryonic...
at least between fertilization and implantation, and is known too as a proembryo. A conceptus between fertilization and implantation is also frequently classified as an embryo.
Even after implantation begins, a preembryo (and proembryo) may exist up until formation of the primitive streak
Primitive streak
The primitive streak is a structure that forms during the early stages of avian, reptilian and mammalian embryonic development.-Introduction:...
. Implantation begins at about six days after fertilization, and lasts for about a week, during which time formation of the primitive streak occurs.
Use of the terms preembryo and proembryo, in the context of human development, has drawn criticism from opponents of embryo research, and from scientists who have considered this categorization invalid or unnecessary. One rationale that has been advanced for distinguishing an early fertilized human conceptus from an embryo is that there is a potential for the conceptus to split into identical twins prior to implantation, and so (the argument goes) the conceptus cannot be regarded before implantation as a single human being. However, the conceptus before implantation exhibits self-actuated activity, which has led to the assertion that it is an embryo.
In the United States, a report by the National Institutes of Health
National Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health are an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services and are the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and health-related research. Its science and engineering counterpart is the National Science Foundation...
stated that a conceptus could be both a pre-implantation embryo and a pre-embryo at the same time. However, Ann Kiessling
Ann Kiessling
Dr. Ann A. Kiessling is an American reproductive biologist and is currently one of the leaders in human parthenogenic stem cell research at The Bedford Stem Cell Research Foundation. She also has an appointment in the Department of Surgery at Harvard Medical SchoolDr. Kiessling is noted for her...
(a leader in stem cell research) has written that those categories are inaccurate.
Ontological status

Embryo
An embryo is a multicellular diploid eukaryote in its earliest stage of development, from the time of first cell division until birth, hatching, or germination...
, and fetus
Fetus
A fetus is a developing mammal or other viviparous vertebrate after the embryonic stage and before birth.In humans, the fetal stage of prenatal development starts at the beginning of the 11th week in gestational age, which is the 9th week after fertilization.-Etymology and spelling variations:The...
:
The colors represent the maternal and paternal genetic contributions.
See also
- Beginning of pregnancy controversyBeginning of pregnancy controversyControversy over the beginning of pregnancy usually occurs in the context of the abortion debate. Depending on where pregnancy is considered to begin, some methods of birth control or infertility treatment might be considered abortifacient...
- In vitro fertilization
- PregnancyPregnancyPregnancy refers to the fertilization and development of one or more offspring, known as a fetus or embryo, in a woman's uterus. In a pregnancy, there can be multiple gestations, as in the case of twins or triplets...
- Stem cell controversyStem cell controversyThe stem cell controversy is the ethical debate primarily concerning the creation, treatment, and destruction of human embryos incident to research involving embryonic stem cells. Not all stem cell research involves the creation, use, or destruction of human embryos...

