
Protostegidae
Encyclopedia
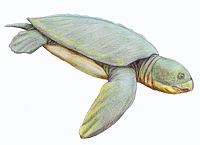
Protostegidae is a family of extinct marine turtles
that lived during the Mesozoic
Era. The family includes some of the largest sea turtles that ever existed. The largest, Archelon
, had a head a meter long. While like most sea turtles, they had flattened bodies and had flippers
for front appendages, protostegids had minimal shells
like leatherback turtles
of modern times.
 As some of the first marine turtles
As some of the first marine turtles
, the protostegids set the general body plan for future species of sea turtles. Protostegids have a generally depressed turtle body plan, complete with four limbs, a short tail and a large head at the end of a relatively short neck. Like other sea turtles, they possess oar-like front appendages specially evolved for swimming in the open ocean. Similar to the closely related and still-extant Dermochelyidae
, protostegids possess extremely reduced carapace
s. Some specimens have skeletal protrusions from their ribs almost wrapping around the turtles' bodies in place of a complete shell. Like modern sea turtles, protostegids had sharp beaks. One of the defining characteristics of the members of the family are their almost-disproportionately large heads. Specifically, some specimens of Archelon
have been found with heads that were a meter long. In addition, the members of the family had somewhat reduced plastrons as well.
studies on the members of the family has provided some insight into the ecological roles of the Protostegidae. Analysis of fossil organs of some protostegids has revealed entire stomachs containing fossilized shellfish
. The turtles themselves are postulated to have been preyed upon by the major predators of the time. Fossil protostegids have been found with tooth impressions from the large lamnid sharks of the time. Two specimens of Protostega gigas have been discovered to have tooth marks from large shark
s. In addition, teeth of the extinct shark Cretoxyrhina mantelli
have been found embedded in at least one Protostega skeleton.
in 1998. The species first appeared during the Early Cretaceous
. As an early sea turtle, Santanachelys had several unspecialized characteristics such as distinguishable digits in its flipper-like arms. Later relatives' flippers were completely fused together for more efficient swimming. As with most large fauna
of the era, the Protostegidae died out during the events of the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction event that led to the extinction of the dinosaur
s. Through phylogenetic analysis, it has been determined that the closest living relatives of this particular family are the leatherback turtles in the family Dermochelyidae
, both of which are monophyletic.
published his classification of the Testudinata within the ninth edition of the Encyclopaedia Britannica. The genus Protostega was placed within the family Sphargidae under the suborder Athecae. A year or so later, the entire suborder was downgraded by Karl Alfred von Zittel
into a family within the Cryptodira
.
In 1994, Hirayama proposed a three-family subdivision of the sea turtle superfamily based on cladistic analysis; Protostegidae was given full, formal family status in the system, containing most of the extinct genera including Archelon
and a previously undescribed protostegid. The unidentified specimen was fully described in 1998, as the species Santanachelys gaffneyi. The genus (Santanachelys
) was appended to the family after the new species was described. This specimen was later to be analyzed to be the family's oldest member.
Sea turtle
Sea turtles are marine reptiles that inhabit all of the world's oceans except the Arctic.-Distribution:...
that lived during the Mesozoic
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic era is an interval of geological time from about 250 million years ago to about 65 million years ago. It is often referred to as the age of reptiles because reptiles, namely dinosaurs, were the dominant terrestrial and marine vertebrates of the time...
Era. The family includes some of the largest sea turtles that ever existed. The largest, Archelon
Archelon
Archelon is a genus of extinct sea turtle, the largest that has ever been documented.-Discovery:...
, had a head a meter long. While like most sea turtles, they had flattened bodies and had flippers
Flipper (anatomy)
A flipper is a typically flat limb evolved for movement through water. Various creatures have evolved flippers, for example penguins , cetaceans A flipper is a typically flat limb evolved for movement through water. Various creatures have evolved flippers, for example penguins (also called...
for front appendages, protostegids had minimal shells
Carapace
A carapace is a dorsal section of the exoskeleton or shell in a number of animal groups, including arthropods such as crustaceans and arachnids, as well as vertebrates such as turtles and tortoises. In turtles and tortoises, the underside is called the plastron.-Crustaceans:In crustaceans, the...
like leatherback turtles
Dermochelyidae
Dermochelyidae is a family of turtles which has eight extinct and one extant genera.-Classification of known genera:*Subfamily Desmatochelyinae** Corochelys ** Desmatochelys *Subfamily Allopleuroninae ** Allopleuron ** Eosphargis...
of modern times.
Anatomy

Sea turtle
Sea turtles are marine reptiles that inhabit all of the world's oceans except the Arctic.-Distribution:...
, the protostegids set the general body plan for future species of sea turtles. Protostegids have a generally depressed turtle body plan, complete with four limbs, a short tail and a large head at the end of a relatively short neck. Like other sea turtles, they possess oar-like front appendages specially evolved for swimming in the open ocean. Similar to the closely related and still-extant Dermochelyidae
Dermochelyidae
Dermochelyidae is a family of turtles which has eight extinct and one extant genera.-Classification of known genera:*Subfamily Desmatochelyinae** Corochelys ** Desmatochelys *Subfamily Allopleuroninae ** Allopleuron ** Eosphargis...
, protostegids possess extremely reduced carapace
Carapace
A carapace is a dorsal section of the exoskeleton or shell in a number of animal groups, including arthropods such as crustaceans and arachnids, as well as vertebrates such as turtles and tortoises. In turtles and tortoises, the underside is called the plastron.-Crustaceans:In crustaceans, the...
s. Some specimens have skeletal protrusions from their ribs almost wrapping around the turtles' bodies in place of a complete shell. Like modern sea turtles, protostegids had sharp beaks. One of the defining characteristics of the members of the family are their almost-disproportionately large heads. Specifically, some specimens of Archelon
Archelon
Archelon is a genus of extinct sea turtle, the largest that has ever been documented.-Discovery:...
have been found with heads that were a meter long. In addition, the members of the family had somewhat reduced plastrons as well.
Trophic ecology
While all members of the family are extinct, palaeoecologicalPaleoecology
Paleoecology uses data from fossils and subfossils to reconstruct the ecosystems of the past. It involves the study of fossil organisms and their associated remains, including their life cycle, living interactions, natural environment, and manner of death and burial to reconstruct the...
studies on the members of the family has provided some insight into the ecological roles of the Protostegidae. Analysis of fossil organs of some protostegids has revealed entire stomachs containing fossilized shellfish
Shellfish
Shellfish is a culinary and fisheries term for exoskeleton-bearing aquatic invertebrates used as food, including various species of molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Although most kinds of shellfish are harvested from saltwater environments, some kinds are found only in freshwater...
. The turtles themselves are postulated to have been preyed upon by the major predators of the time. Fossil protostegids have been found with tooth impressions from the large lamnid sharks of the time. Two specimens of Protostega gigas have been discovered to have tooth marks from large shark
Shark
Sharks are a type of fish with a full cartilaginous skeleton and a highly streamlined body. The earliest known sharks date from more than 420 million years ago....
s. In addition, teeth of the extinct shark Cretoxyrhina mantelli
Cretoxyrhina mantelli
Cretoxyrhina mantelli was a large shark that lived during the Cretaceous period, about 100 to 82 million years ago. It is commonly known as the Ginsu Shark.-Known physiology:-Identification and preserved specimens:...
have been found embedded in at least one Protostega skeleton.
Evolutionary history
The family's oldest member is Santanachelys gaffneyi, known from a specimen excavated from BrazilBrazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
in 1998. The species first appeared during the Early Cretaceous
Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous or the Lower Cretaceous , is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous...
. As an early sea turtle, Santanachelys had several unspecialized characteristics such as distinguishable digits in its flipper-like arms. Later relatives' flippers were completely fused together for more efficient swimming. As with most large fauna
Fauna
Fauna or faunæ is all of the animal life of any particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is flora.Zoologists and paleontologists use fauna to refer to a typical collection of animals found in a specific time or place, e.g. the "Sonoran Desert fauna" or the "Burgess shale fauna"...
of the era, the Protostegidae died out during the events of the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction event that led to the extinction of the dinosaur
Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of animals of the clade and superorder Dinosauria. They were the dominant terrestrial vertebrates for over 160 million years, from the late Triassic period until the end of the Cretaceous , when the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event led to the extinction of...
s. Through phylogenetic analysis, it has been determined that the closest living relatives of this particular family are the leatherback turtles in the family Dermochelyidae
Dermochelyidae
Dermochelyidae is a family of turtles which has eight extinct and one extant genera.-Classification of known genera:*Subfamily Desmatochelyinae** Corochelys ** Desmatochelys *Subfamily Allopleuroninae ** Allopleuron ** Eosphargis...
, both of which are monophyletic.
Taxonomic history
In 1888, the Belgian zoologist George Albert BoulengerGeorge Albert Boulenger
George Albert Boulenger FRS was a Belgian-British zoologist who identified over 2000 new animal species, chiefly fish, reptiles and amphibians.-Life:...
published his classification of the Testudinata within the ninth edition of the Encyclopaedia Britannica. The genus Protostega was placed within the family Sphargidae under the suborder Athecae. A year or so later, the entire suborder was downgraded by Karl Alfred von Zittel
Karl Alfred von Zittel
Karl Alfred Ritter von Zittel was a German palaeontologist.-Biography:He was born at Bahlingen in Baden, and educated at Heidelberg, Paris and Vienna. For a short period he served on the Geological Survey of Austria, and as assistant in the mineralogical museum at Vienna...
into a family within the Cryptodira
Cryptodira
Cryptodira is the taxonomic suborder of Testudines that includes most living tortoises and turtles. Cryptodira differ from Pleurodira in that they lower their necks and pull the heads straight back into the shells; instead of folding their necks sideways along the body under the shells' margins...
.
In 1994, Hirayama proposed a three-family subdivision of the sea turtle superfamily based on cladistic analysis; Protostegidae was given full, formal family status in the system, containing most of the extinct genera including Archelon
Archelon
Archelon is a genus of extinct sea turtle, the largest that has ever been documented.-Discovery:...
and a previously undescribed protostegid. The unidentified specimen was fully described in 1998, as the species Santanachelys gaffneyi. The genus (Santanachelys
Santanachelys
Santanachelys gaffneyi is the earliest known sea turtle. It is the only species in the genus Santanachelys, which itself is a member of the extinct family Protostegidae. The species was first described from a 20-centimeter long fossil specimen unearthed in 1998 in Eastern Brazil...
) was appended to the family after the new species was described. This specimen was later to be analyzed to be the family's oldest member.

