
Pruning (decision trees)
Encyclopedia
Pruning is a technique in machine learning
that reduces the size of decision tree
s by removing sections of the tree that provide little power to classify instances. The dual goal of pruning is reduced complexity of the final classifier as well as better predictive accuracy by the reduction of overfitting
and removal of sections of a classifier that may be based on noisy or erroneous
data.
the training data and poorly generalizing to new samples. A small tree might not capture important structural information about the sample space. However, it is hard to tell when a tree algorithm should stop because it is impossible to tell if the addition of a single extra node will dramatically decrease error. This problem is known as the horizon effect
. A common strategy is to grow the tree until each node contains a small number of instances then use pruning to remove nodes that do not provide additional information.
Pruning should reduce the size of a learning tree without reducing predictive accuracy as measured by a test set or using cross-validation. There are many techniques for tree pruning that differ in the measurement that is used to optimize performance.
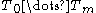 where
where 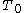 is the initial tree and
is the initial tree and 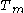 is the root alone. At step
is the root alone. At step 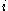 the tree is created by removing a subtree from tree
the tree is created by removing a subtree from tree  and replacing it with a leaf node with value chosen as in the tree building algorithm. The subtree that is removed is chosen as follows. Define the error rate of tree
and replacing it with a leaf node with value chosen as in the tree building algorithm. The subtree that is removed is chosen as follows. Define the error rate of tree 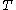 over data set
over data set 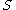 as
as 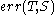 . The subtree that minimizes
. The subtree that minimizes
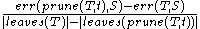
is chosen for removal. The function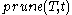 defines the tree gotten by pruning the subtrees
defines the tree gotten by pruning the subtrees  from the tree
from the tree 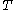 . Once the series of trees has been created, the best tree is chosen by generalized accuracy as measured by a training set or cross-validation.
. Once the series of trees has been created, the best tree is chosen by generalized accuracy as measured by a training set or cross-validation.
Machine learning
Machine learning, a branch of artificial intelligence, is a scientific discipline concerned with the design and development of algorithms that allow computers to evolve behaviors based on empirical data, such as from sensor data or databases...
that reduces the size of decision tree
Decision tree learning
Decision tree learning, used in statistics, data mining and machine learning, uses a decision tree as a predictive model which maps observations about an item to conclusions about the item's target value. More descriptive names for such tree models are classification trees or regression trees...
s by removing sections of the tree that provide little power to classify instances. The dual goal of pruning is reduced complexity of the final classifier as well as better predictive accuracy by the reduction of overfitting
Overfitting
In statistics, overfitting occurs when a statistical model describes random error or noise instead of the underlying relationship. Overfitting generally occurs when a model is excessively complex, such as having too many parameters relative to the number of observations...
and removal of sections of a classifier that may be based on noisy or erroneous
Errors and residuals in statistics
In statistics and optimization, statistical errors and residuals are two closely related and easily confused measures of the deviation of a sample from its "theoretical value"...
data.
Introduction
One of the questions that arises in a decision tree algorithm is the optimal size of the final tree. A tree that is too large risks overfittingOverfitting
In statistics, overfitting occurs when a statistical model describes random error or noise instead of the underlying relationship. Overfitting generally occurs when a model is excessively complex, such as having too many parameters relative to the number of observations...
the training data and poorly generalizing to new samples. A small tree might not capture important structural information about the sample space. However, it is hard to tell when a tree algorithm should stop because it is impossible to tell if the addition of a single extra node will dramatically decrease error. This problem is known as the horizon effect
Horizon effect
The horizon effect is a problem in artificial intelligence where, in many games, the number of possible states or positions is immense and computers can only feasibly search a small portion of it, typically a few ply down the game tree...
. A common strategy is to grow the tree until each node contains a small number of instances then use pruning to remove nodes that do not provide additional information.
Pruning should reduce the size of a learning tree without reducing predictive accuracy as measured by a test set or using cross-validation. There are many techniques for tree pruning that differ in the measurement that is used to optimize performance.
Techniques
Pruning can occur in a top down or bottom up fashion. A top down pruning will traverse nodes and trim subtrees starting at the root, while a bottom up pruning will start at the leaf nodes. Below are several popular pruning algorithms.Reduced error pruning
One of the simplest forms of pruning is reduced error pruning. Starting at the leaves, each node is replaced with its most popular class. If the prediction accuracy is not affected then the change is kept. While somewhat naive, reduced error pruning has the advantage of simplicity and speed.Cost complexity pruning
Cost complexity pruning generates a series of trees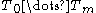 where
where 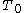 is the initial tree and
is the initial tree and 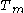 is the root alone. At step
is the root alone. At step 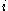 the tree is created by removing a subtree from tree
the tree is created by removing a subtree from tree  and replacing it with a leaf node with value chosen as in the tree building algorithm. The subtree that is removed is chosen as follows. Define the error rate of tree
and replacing it with a leaf node with value chosen as in the tree building algorithm. The subtree that is removed is chosen as follows. Define the error rate of tree 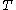 over data set
over data set 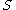 as
as 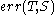 . The subtree that minimizes
. The subtree that minimizes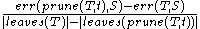
is chosen for removal. The function
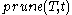 defines the tree gotten by pruning the subtrees
defines the tree gotten by pruning the subtrees  from the tree
from the tree 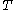 . Once the series of trees has been created, the best tree is chosen by generalized accuracy as measured by a training set or cross-validation.
. Once the series of trees has been created, the best tree is chosen by generalized accuracy as measured by a training set or cross-validation.See also
- Alpha-beta pruningAlpha-beta pruningAlpha-beta pruning is a search algorithm which seeks to decrease the number of nodes that are evaluated by the minimax algorithm in its search tree. It is an adversarial search algorithm used commonly for machine playing of two-player games...
- Decision treeDecision tree learningDecision tree learning, used in statistics, data mining and machine learning, uses a decision tree as a predictive model which maps observations about an item to conclusions about the item's target value. More descriptive names for such tree models are classification trees or regression trees...
- Artificial neural networkArtificial neural networkAn artificial neural network , usually called neural network , is a mathematical model or computational model that is inspired by the structure and/or functional aspects of biological neural networks. A neural network consists of an interconnected group of artificial neurons, and it processes...
- Null-move heuristicNull-move heuristicIn computer chess programs, the null-move heuristic is a heuristic technique used to enhance the speed of the alpha-beta pruning algorithm.- Rationale :...
Further reading
- MDL based decision tree pruning
- Decision tree pruning using backpropagation
- Neural networks

