
Decision tree learning
Encyclopedia
Decision tree learning, used in statistics
, data mining
and machine learning
, uses a decision tree
as a predictive model
which maps observations about an item to conclusions about the item's target value. More descriptive names for such tree models are classification trees or regression trees. In these tree structures, leaves represent class labels and branches represent conjunction
s of features that lead to those class labels.
In decision analysis, a decision tree can be used to visually and explicitly represent decisions and decision making
. In data mining
, a decision tree describes data but not decisions; rather the resulting classification tree can be an input for decision making
. This page deals with decision trees in data mining
.
A tree can be "learned" by splitting the source set into subsets based on an attribute value test. This process is repeated on each derived subset in a recursive manner called recursive partitioning
. The recursion
is completed when the subset at a node all has the same value of the target variable, or when splitting no longer adds value to the predictions.
In data mining
, trees can be described also as the combination of mathematical and computational techniques to aid the description, categorisation and generalisation of a given set of data.
Data comes in records of the form:
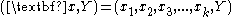
The dependent variable, Y, is the target variable that we are trying to understand, classify or generalise. The vector x is composed of the input variables, x1, x2, x3 etc., that are used for that task.
are of two main types:
The term Classification And Regression Tree (CART) analysis is an umbrella term
used to refer to both of the above procedures, first introduced by Breiman
et al. Trees used for regression and trees used for classification have some similarities - but also some differences, such as the procedure used to determine where to split.
Some techniques use more than one decision tree for their analysis:
There are many specific decision-tree algorithms. Notable ones include:
To compute Gini impurity for a set of items, suppose y takes on values in {1, 2, ..., m}, and let fi = the fraction of items labeled with value i in the set.
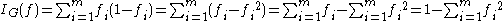
, C4.5
and C5.0 tree generation algorithms. Information gain
is based on the concept of entropy
used in information theory
.
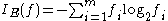
In a decision graph, it is possible to use disjunctions (ORs) to join two more paths together using Minimum Message Length
(MML). Decision graphs have been further extended to allow for previously unstated new attributes to be learnt dynamically and used at different places within the graph. The more general coding scheme results in better predictive accuracy and log-loss probabilistic scoring. In general, decision graphs infer models with fewer leaves than decision trees.
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, data mining
Data mining
Data mining , a relatively young and interdisciplinary field of computer science is the process of discovering new patterns from large data sets involving methods at the intersection of artificial intelligence, machine learning, statistics and database systems...
and machine learning
Machine learning
Machine learning, a branch of artificial intelligence, is a scientific discipline concerned with the design and development of algorithms that allow computers to evolve behaviors based on empirical data, such as from sensor data or databases...
, uses a decision tree
Decision tree
A decision tree is a decision support tool that uses a tree-like graph or model of decisions and their possible consequences, including chance event outcomes, resource costs, and utility. It is one way to display an algorithm. Decision trees are commonly used in operations research, specifically...
as a predictive model
Predictive modelling
Predictive modelling is the process by which a model is created or chosen to try to best predict the probability of an outcome. In many cases the model is chosen on the basis of detection theory to try to guess the probability of an outcome given a set amount of input data, for example given an...
which maps observations about an item to conclusions about the item's target value. More descriptive names for such tree models are classification trees or regression trees. In these tree structures, leaves represent class labels and branches represent conjunction
Conjunction
Conjunction can refer to:* Conjunction , an astronomical phenomenon* Astrological aspect, an aspect in horoscopic astrology* Conjunction , a part of speech** Conjunctive mood , same as subjunctive mood...
s of features that lead to those class labels.
In decision analysis, a decision tree can be used to visually and explicitly represent decisions and decision making
Decision making
Decision making can be regarded as the mental processes resulting in the selection of a course of action among several alternative scenarios. Every decision making process produces a final choice. The output can be an action or an opinion of choice.- Overview :Human performance in decision terms...
. In data mining
Data mining
Data mining , a relatively young and interdisciplinary field of computer science is the process of discovering new patterns from large data sets involving methods at the intersection of artificial intelligence, machine learning, statistics and database systems...
, a decision tree describes data but not decisions; rather the resulting classification tree can be an input for decision making
Decision making
Decision making can be regarded as the mental processes resulting in the selection of a course of action among several alternative scenarios. Every decision making process produces a final choice. The output can be an action or an opinion of choice.- Overview :Human performance in decision terms...
. This page deals with decision trees in data mining
Data mining
Data mining , a relatively young and interdisciplinary field of computer science is the process of discovering new patterns from large data sets involving methods at the intersection of artificial intelligence, machine learning, statistics and database systems...
.
General
Decision tree learning is a method commonly used in data mining. The goal is to create a model that predicts the value of a target variable based on several input variables. An example is shown on the right. Each interior node corresponds to one of the input variables; there are edges to children for each of the possible values of that input variable. Each leaf represents a value of the target variable given the values of the input variables represented by the path from the root to the leaf.A tree can be "learned" by splitting the source set into subsets based on an attribute value test. This process is repeated on each derived subset in a recursive manner called recursive partitioning
Recursive partitioning
Recursive partitioning is a statistical method for multivariable analysis. Recursive partitioning creates a decision tree that strives to correctly classify members of the population based on several dichotomous dependent variables....
. The recursion
Recursion
Recursion is the process of repeating items in a self-similar way. For instance, when the surfaces of two mirrors are exactly parallel with each other the nested images that occur are a form of infinite recursion. The term has a variety of meanings specific to a variety of disciplines ranging from...
is completed when the subset at a node all has the same value of the target variable, or when splitting no longer adds value to the predictions.
In data mining
Data mining
Data mining , a relatively young and interdisciplinary field of computer science is the process of discovering new patterns from large data sets involving methods at the intersection of artificial intelligence, machine learning, statistics and database systems...
, trees can be described also as the combination of mathematical and computational techniques to aid the description, categorisation and generalisation of a given set of data.
Data comes in records of the form:
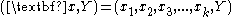
The dependent variable, Y, is the target variable that we are trying to understand, classify or generalise. The vector x is composed of the input variables, x1, x2, x3 etc., that are used for that task.
Types
Decision trees used in data miningData mining
Data mining , a relatively young and interdisciplinary field of computer science is the process of discovering new patterns from large data sets involving methods at the intersection of artificial intelligence, machine learning, statistics and database systems...
are of two main types:
- Classification tree analysis is when the predicted outcome is the class to which the data belongs.
- Regression tree analysis is when the predicted outcome can be considered a real number (e.g. the price of a house, or a patient’s length of stay in a hospital).
The term Classification And Regression Tree (CART) analysis is an umbrella term
Umbrella term
An umbrella term is a word that provides a superset or grouping of concepts that all fall under a single common category. Umbrella term is also called a hypernym. For example, cryptology is an umbrella term that encompasses cryptography and cryptanalysis, among other fields...
used to refer to both of the above procedures, first introduced by Breiman
Leo Breiman
Leo Breiman was a distinguished statistician at the University of California, Berkeley. He was the recipient of numerous honors and awards, and was a member of the United States National Academy of Science....
et al. Trees used for regression and trees used for classification have some similarities - but also some differences, such as the procedure used to determine where to split.
Some techniques use more than one decision tree for their analysis:
- A Random ForestRandom forestRandom forest is an ensemble classifier that consists of many decision trees and outputs the class that is the mode of the class's output by individual trees. The algorithm for inducing a random forest was developed by Leo Breiman and Adele Cutler, and "Random Forests" is their trademark...
classifier uses a number of decision trees, in order to improve the classification rate. - Boosted Trees can be used for regression-type and classification-type problems.
There are many specific decision-tree algorithms. Notable ones include:
- ID3 algorithmID3 algorithmIn decision tree learning, ID3 is an algorithm used to generate a decision tree invented by Ross Quinlan. ID3 is the precursor to the C4.5 algorithm.-Algorithm:The ID3 algorithm can be summarized as follows:...
- C4.5 algorithmC4.5 algorithmC4.5 is an algorithm used to generate a decision tree developed by Ross Quinlan. C4.5 is an extension of Quinlan's earlier ID3 algorithm. The decision trees generated by C4.5 can be used for classification, and for this reason, C4.5 is often referred to as a statistical classifier.-Algorithm:C4.5...
- CHi-squared Automatic Interaction Detector (CHAIDCHAIDCHAID is a type of decision tree technique, based upon adjusted significance testing . The technique was developed in South Africa and was published in 1980 by Gordon V. Kass, who had completed a PhD thesis on this topic...
). Performs multi-level splits when computing classification trees. - MARSMultivariate adaptive regression splinesMultivariate adaptive regression splines is a form of regression analysis introduced by Jerome Friedman in 1991. It is a non-parametric regression techniqueand can be seen as an extension of linear models that...
: extends decision trees to better handle numerical data
Formulae
The algorithms that are used for constructing decision trees usually work top-down by choosing a variable at each step that is the next best variable to use in splitting the set of items. "Best" is defined by how well the variable splits the set into homogeneous subsets that have the same value of the target variable. Different algorithms use different formulae for measuring "best". This section presents a few of the most common formulae. These formulae are applied to each candidate subset, and the resulting values are combined (e.g., averaged) to provide a measure of the quality of the split.Gini impurity
Used by the CART algorithm, Gini impurity is a measure of how often a randomly chosen element from the set would be incorrectly labeled if it were randomly labeled according to the distribution of labels in the subset. Gini impurity can be computed by summing the probability of each item being chosen times the probability of a mistake in categorizing that item. It reaches its minimum (zero) when all cases in the node fall into a single target category.To compute Gini impurity for a set of items, suppose y takes on values in {1, 2, ..., m}, and let fi = the fraction of items labeled with value i in the set.
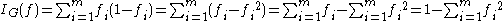
Information gain
Used by the ID3ID3 algorithm
In decision tree learning, ID3 is an algorithm used to generate a decision tree invented by Ross Quinlan. ID3 is the precursor to the C4.5 algorithm.-Algorithm:The ID3 algorithm can be summarized as follows:...
, C4.5
C4.5 algorithm
C4.5 is an algorithm used to generate a decision tree developed by Ross Quinlan. C4.5 is an extension of Quinlan's earlier ID3 algorithm. The decision trees generated by C4.5 can be used for classification, and for this reason, C4.5 is often referred to as a statistical classifier.-Algorithm:C4.5...
and C5.0 tree generation algorithms. Information gain
Information gain in decision trees
In information theory and machine learning, information gain is an alternative synonym for Kullback–Leibler divergence.In particular, the information gain about a random variable X obtained from an observation that a random variable A takes the value A=a is the Kullback-Leibler divergence DKL of...
is based on the concept of entropy
Information entropy
In information theory, entropy is a measure of the uncertainty associated with a random variable. In this context, the term usually refers to the Shannon entropy, which quantifies the expected value of the information contained in a message, usually in units such as bits...
used in information theory
Information theory
Information theory is a branch of applied mathematics and electrical engineering involving the quantification of information. Information theory was developed by Claude E. Shannon to find fundamental limits on signal processing operations such as compressing data and on reliably storing and...
.
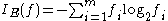
Decision tree advantages
Amongst other data mining methods, decision trees have various advantages:- Simple to understand and interpret. People are able to understand decision tree models after a brief explanation.
- Requires little data preparation. Other techniques often require data normalisation, dummy variables need to be created and blank values to be removed.
- Able to handle both numerical and categorical data. Other techniques are usually specialised in analysing datasets that have only one type of variable. Ex: relation rules can be used only with nominal variables while neural networks can be used only with numerical variables.
- Uses a white boxWhite box (software engineering)In software engineering white box, in contrast to a black box, is a subsystem whose internals can be viewed, but usually cannot be altered. This is useful during white box testing, where a system is examined to make sure that it fulfills its requirements....
model. If a given situation is observable in a model the explanation for the condition is easily explained by boolean logic. An example of a black box model is an artificial neural networkArtificial neural networkAn artificial neural network , usually called neural network , is a mathematical model or computational model that is inspired by the structure and/or functional aspects of biological neural networks. A neural network consists of an interconnected group of artificial neurons, and it processes...
since the explanation for the results is difficult to understand. - Possible to validate a model using statistical tests. That makes it possible to account for the reliability of the model.
- RobustRobust statisticsRobust statistics provides an alternative approach to classical statistical methods. The motivation is to produce estimators that are not unduly affected by small departures from model assumptions.- Introduction :...
. Performs well even if its assumptions are somewhat violated by the true model from which the data were generated. - Performs well with large data in a short time. Large amounts of data can be analysed using standard computing resources.
Limitations
- The problem of learning an optimal decision tree is known to be NP-completeNP-completeIn computational complexity theory, the complexity class NP-complete is a class of decision problems. A decision problem L is NP-complete if it is in the set of NP problems so that any given solution to the decision problem can be verified in polynomial time, and also in the set of NP-hard...
under several aspects of optimality and even for simple concepts. Consequently, practical decision-tree learning algorithms are based on heuristic algorithms such as the greedy algorithmGreedy algorithmA greedy algorithm is any algorithm that follows the problem solving heuristic of making the locally optimal choice at each stagewith the hope of finding the global optimum....
where locally optimal decisions are made at each node. Such algorithms cannot guarantee to return the globally optimal decision tree. - Decision-tree learners can create over-complex trees that do not generalise the data well. This is called overfittingOverfittingIn statistics, overfitting occurs when a statistical model describes random error or noise instead of the underlying relationship. Overfitting generally occurs when a model is excessively complex, such as having too many parameters relative to the number of observations...
. Mechanisms such as pruningPruning (decision trees)Pruning is a technique in machine learning that reduces the size of decision trees by removing sections of the tree that provide little power to classify instances...
are necessary to avoid this problem. - There are concepts that are hard to learn because decision trees do not express them easily, such as XOR, parity or multiplexerMultiplexerIn electronics, a multiplexer is a device that selects one of several analog or digital input signals and forwards the selected input into a single line. A multiplexer of 2n inputs has n select lines, which are used to select which input line to send to the output...
problems. In such cases, the decision tree becomes prohibitively large. Approaches to solve the problem involve either changing the representation of the problem domain (known as propositionalisation) or using learning algorithms based on more expressive representations (such as statistical relational learningStatistical relational learningStatistical relational learning is a subdiscipline of artificial intelligence and machine learning that is concerned with models of domains that exhibit both uncertainty and complex, relational structure...
or inductive logic programmingInductive logic programmingInductive logic programming is a subfield of machine learning which uses logic programming as a uniform representation for examples, background knowledge and hypotheses...
).
- For data including categorical variables with different number of levels, information gain in decision treesInformation gain in decision treesIn information theory and machine learning, information gain is an alternative synonym for Kullback–Leibler divergence.In particular, the information gain about a random variable X obtained from an observation that a random variable A takes the value A=a is the Kullback-Leibler divergence DKL of...
are biased in favor of those attributes with more levels.
Decision graphs
In a decision tree, all paths from the root node to the leaf node proceed by way of conjunction, or AND.In a decision graph, it is possible to use disjunctions (ORs) to join two more paths together using Minimum Message Length
Minimum message length
Minimum message length is a formal information theory restatement of Occam's Razor: even when models are not equal in goodness of fit accuracy to the observed data, the one generating the shortest overall message is more likely to be correct...
(MML). Decision graphs have been further extended to allow for previously unstated new attributes to be learnt dynamically and used at different places within the graph. The more general coding scheme results in better predictive accuracy and log-loss probabilistic scoring. In general, decision graphs infer models with fewer leaves than decision trees.
Search through Evolutionary Algorithms
Evolutionary algorithms have been used to avoid local optimal decisions and search the decision tree space with little a priori bias.See also
- Decision tree pruning
- Binary decision diagramBinary decision diagramIn the field of computer science, a binary decision diagram or branching program, like a negation normal form or a propositional directed acyclic graph , is a data structure that is used to represent a Boolean function. On a more abstract level, BDDs can be considered as a compressed...
- CART
- Decision stumpDecision stumpA decision stump is a machine learning model consisting of a one-level decision tree. That is, it is a decision tree with one internal node which is immediately connected to the terminal nodes. A decision stump makes a prediction based on the value of just a single input feature...
- Incremental decision treeIncremental decision treeMost decision tree methods take a complete data set and build a tree using that data. This tree cannot be changed if new data is acquired later.Incremental decision trees are built using methods that allow an existing tree to be updated or revised using new, individual data instances...
- Alternating decision treeAlternating decision treeAn alternating decision tree is a machine learning method for classification. It generalizes decision trees and has connections to boosting.-History:...
- Structured data analysis (statistics)Structured data analysis (statistics)Structured data analysis is the statistical data analysis of structured data. This can arise either in the form of an a priori structure such as multiple-choice questionnaires or in situations with the need to search for structure that fits the given data, either exactly or approximately...
Implementations
- WekaWeka (machine learning)Weka is a popular suite of machine learning software written in Java, developed at the University of Waikato, New Zealand...
, a free and open-source data mining suite, contains many decision tree algorithms - OrangeOrange (software)Orange is a component-based data mining and machine learning software suite, featuring friendly yet powerful and flexible visual programming front-end for explorative data analysis and visualization, and Python bindings and libraries for scripting...
, a free data mining software suite, module orngTree - KNIMEKNIMEKNIME, the Konstanz Information Miner, is a user friendly, coherent open source data analytics, reporting and integration platform. KNIME integrates various components for machine learning and data mining through its modular data pipelining concept...
External links
- Building Decision Trees in Python From O'Reilly.
- An Addendum to "Building Decision Trees in Python" From O'Reilly.
- Decision Trees page at aaai.org, a page with commented links.
- Decision tree implementation in Ruby (AI4R)

