Prurigo nodularis
Encyclopedia
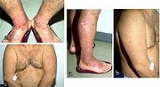
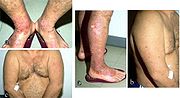
Prurigo nodularis is a skin disease characterised by pruritic (itch
y) nodules which usually appear on the arms or legs. Patients often present with multiple excoriated lesions caused by scratching. PN is also known as Hyde prurigo nodularis, Picker nodules, lichen simplex chronicus, atypical nodular form of neurodermatitis circumscripta, lichen corneus obtusus.
Lichen simplex chronicus
is actually a distinct clinical entity.
, linear IgA disease, an autoimmune condition, liver disease and T cells. Systemic pruritus has been linked to cholestasis, thyroid disease, polycythaemia rubra vera, uraemia, Hodgkins disease, HIV
and other immunodeficiency diseases. Internal malignancies, liver failure, renal failure, and psychiatric illnesses may induce PN, although more recent research has refuted a psychiatric cause for PN. Patients report an ongoing battle to distinguish themselves from those with psychiatric disorders such as delusions of parasitosis and other psychiatric conditions.
and repetitive scratching, picking, or rubbing of the nodules may result in permanent changes to the skin, including nodular lichenification, hyperkeratosis, hyperpigmentation, and skin thickening. Unhealed, excoriated lesions are often scaly, crusted or scabbed. Many patients report a lack of wound healing even when medications relieve the itching and subsequent scratching.
Patients often:
in PN. A culture of at least one lesion will rule out staphylococcus infection, which has been significantly linked to atopic dermatitis.
, thalidomide
and UVB light
. In the event that staphylococcus or other infection is present, antibiotics have proven effective. In at least one case, the root cause of PN was MRSA which was treated with intravenous vancomycin, affecting a complete cure(paper in progress; treat as anecdotal).
A physician may administer a strong dose of prednisone
, which will almost immediately stop the itch/scratch cycle. However, cessation of steroids allows relapse to occur, usually within a few weeks. Horiuchi et al. recently reported significant improvement in PN with antibiotic therapy.
Itch
Itch is a sensation that causes the desire or reflex to scratch. Itch has resisted many attempts to classify it as any one type of sensory experience. Modern science has shown that itch has many similarities to pain, and while both are unpleasant sensory experiences, their behavioral response...
y) nodules which usually appear on the arms or legs. Patients often present with multiple excoriated lesions caused by scratching. PN is also known as Hyde prurigo nodularis, Picker nodules, lichen simplex chronicus, atypical nodular form of neurodermatitis circumscripta, lichen corneus obtusus.
Lichen simplex chronicus
Lichen simplex chronicus
Lichen simplex chronicus is a skin disorder characterized by chronic itching and scratching. The constant scratching causes thick, leathery, brownish skin.- Causes :...
is actually a distinct clinical entity.
Signs and symptoms

- Nodules are discrete, generally symmetric, hyperpigmented or purpuric, and firm. They are greater than 0.5 cm in both width and depth (as opposed to papules which are less than 0.5 cm). They can appear on any part of the body, but generally begin on the arms and legs.
- Excoriated lesions are often flat, umbilicated, or have a crusted top.
- Nodules may appear to begin in the hair follicles.
- Nodule pattern may be follicular.
- In true prurigo nodularis, a nodule forms before any itching begins. Typically, these nodules are extremely pruritic and are alleviated only by steroids.
Causes
The cause of prurigo nodularis is unknown, although other conditions may induce PN. PN has been linked to Becker's nevusBecker's nevus
Becker's nevus is a skin disorder predominantly affecting males...
, linear IgA disease, an autoimmune condition, liver disease and T cells. Systemic pruritus has been linked to cholestasis, thyroid disease, polycythaemia rubra vera, uraemia, Hodgkins disease, HIV
HIV
Human immunodeficiency virus is a lentivirus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome , a condition in humans in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive...
and other immunodeficiency diseases. Internal malignancies, liver failure, renal failure, and psychiatric illnesses may induce PN, although more recent research has refuted a psychiatric cause for PN. Patients report an ongoing battle to distinguish themselves from those with psychiatric disorders such as delusions of parasitosis and other psychiatric conditions.
Pathophysiology
ChronicHabit (psychology)
Habits are routines of behavior that are repeated regularly and tend to occur subconsciously. Habitual behavior often goes unnoticed in persons exhibiting it, because a person does not need to engage in self-analysis when undertaking routine tasks...
and repetitive scratching, picking, or rubbing of the nodules may result in permanent changes to the skin, including nodular lichenification, hyperkeratosis, hyperpigmentation, and skin thickening. Unhealed, excoriated lesions are often scaly, crusted or scabbed. Many patients report a lack of wound healing even when medications relieve the itching and subsequent scratching.
Patients often:
- seek treatment during middle-age, although PN can occur at any age.
- have a history of chronic severe pruritus.
- have a significant medical history for unrelated conditions.
- suffer from liver or kidney dysfunctions.
- suffer secondary skin infections.
- have a personal or family history of atopic dermatitisAtopic dermatitisAtopic dermatitis is an inflammatory, chronically relapsing, non-contagious and pruritic skin disorder...
. - have other autoimmune disorders.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is based on visual examination and the presence of itching. A skin biopsy is often performed to exclude other diseases. Lesion biopsies will typically show a high level of eosinophilsEosinophil granulocyte
Eosinophil granulocytes, usually called eosinophils or eosinophiles , are white blood cells that are one of the immune system components responsible for combating multicellular parasites and certain infections in vertebrates. Along with mast cells, they also control mechanisms associated with...
in PN. A culture of at least one lesion will rule out staphylococcus infection, which has been significantly linked to atopic dermatitis.
Treatment
Prurigo nodularis is very hard to treat, but current therapies include steroids, vitamins, cryosurgeryCryosurgery
Cryosurgery is the application of extreme cold to destroy abnormal or diseased tissue. The term comes from the Greek words cryo and surgery meaning "hand work" or "handiwork"....
, thalidomide
Thalidomide
Thalidomide was introduced as a sedative drug in the late 1950s that was typically used to cure morning sickness. In 1961, it was withdrawn due to teratogenicity and neuropathy. There is now a growing clinical interest in thalidomide, and it is introduced as an immunomodulatory agent used...
and UVB light
Light therapy
Light therapy or phototherapy consists of exposure to daylight or to specific wavelengths of light using lasers, light-emitting diodes, fluorescent lamps, dichroic lamps or very bright, full-spectrum light, usually controlled with various devices...
. In the event that staphylococcus or other infection is present, antibiotics have proven effective. In at least one case, the root cause of PN was MRSA which was treated with intravenous vancomycin, affecting a complete cure(paper in progress; treat as anecdotal).
A physician may administer a strong dose of prednisone
Prednisone
Prednisone is a synthetic corticosteroid drug that is particularly effective as an immunosuppressant drug. It is used to treat certain inflammatory diseases and some types of cancer, but has significant adverse effects...
, which will almost immediately stop the itch/scratch cycle. However, cessation of steroids allows relapse to occur, usually within a few weeks. Horiuchi et al. recently reported significant improvement in PN with antibiotic therapy.

