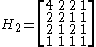Pseudo-Hadamard transform
Encyclopedia
The pseudo-Hadamard transform is a reversible transformation of a bit string that provides cryptographic diffusion. See Hadamard transform
.
The bit string must be of even length, so it can be split into two bit strings a and b of equal lengths, each of n bits. To compute the transform, a' and b' , from these we use the equations:
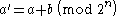
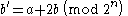
To reverse this, clearly:
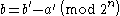
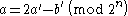
, by considering a and b as two elements of a vector, and the transform itself as multiplication by a matrix of the form:
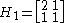
The inverse can then be derived by inverting the matrix.
However, the matrix can be generalised to higher dimensions, allowing vectors of any power-of-two size to be transformed, using the following recursive rule:
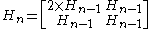
For example:
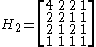
Hadamard transform
The Hadamard transform is an example of a generalized class of Fourier transforms...
.
The bit string must be of even length, so it can be split into two bit strings a and b of equal lengths, each of n bits. To compute the transform, a
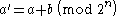
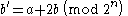
To reverse this, clearly:
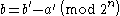
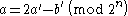
Generalisation
The above equations can be expressed in matrix algebraMatrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix is a rectangular array of numbers, symbols, or expressions. The individual items in a matrix are called its elements or entries. An example of a matrix with six elements isMatrices of the same size can be added or subtracted element by element...
, by considering a and b as two elements of a vector, and the transform itself as multiplication by a matrix of the form:
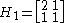
The inverse can then be derived by inverting the matrix.
However, the matrix can be generalised to higher dimensions, allowing vectors of any power-of-two size to be transformed, using the following recursive rule:
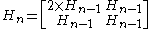
For example: