
Pseudolikelihood
Encyclopedia
In statistical theory
, a pseudolikelihood is an approximation
to the joint probability distribution of a collection of random variable
s. The practical use of this is that it can provide an approximation to the likelihood function
of a set of observed data which may either provide a computationally simpler problem for estimation
, or may provide a way of obtaining explicit estimates of model parameters.
The pseudolikelihood approach was introduced by Julian Besag
in the context of analysing data having spatial dependence
.
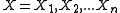 and a set
and a set 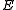 of dependencies between these random variables, where
of dependencies between these random variables, where 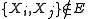 implies
implies 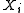 is conditionally independent
is conditionally independent
of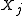 given
given 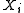 's neighbors, the pseudolikelihood of
's neighbors, the pseudolikelihood of 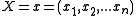 is
is
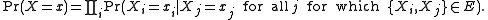
Here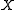 is a vector of variables,
is a vector of variables,  is a vector of values. The expression
is a vector of values. The expression 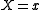 above means that each variable
above means that each variable 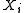 in the vector
in the vector 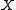 has a corresponding value
has a corresponding value 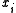 in the vector
in the vector  . The expression
. The expression 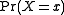 is the probability that the vector of variables
is the probability that the vector of variables 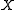 has values equal to the vector
has values equal to the vector  . Because situations can often be described using state variables ranging over a set of possible values, the expression
. Because situations can often be described using state variables ranging over a set of possible values, the expression 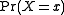 can therefore represent the probability of a certain state among all possible states allowed by the state variables.
can therefore represent the probability of a certain state among all possible states allowed by the state variables.
The Pseudo-log-likelihood is a similar measure derived from the above expression. Thus
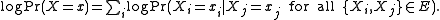
One use of the pseudolikelihood measure is as an approximation for inference about a Markov or Bayesian network
, as the pseudolikelihood of an assignment to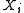 may often be computed more efficiently than the likelihood, particularly when the latter may require marginalization over a large number of variables.
may often be computed more efficiently than the likelihood, particularly when the latter may require marginalization over a large number of variables.
analysis can lead to good estimates, but a straightforward application of the usual likelihood techiques to derive information about estimation uncertainty, or for significance testing
, would in general be incorrect.
Statistical theory
The theory of statistics provides a basis for the whole range of techniques, in both study design and data analysis, that are used within applications of statistics. The theory covers approaches to statistical-decision problems and to statistical inference, and the actions and deductions that...
, a pseudolikelihood is an approximation
Approximation
An approximation is a representation of something that is not exact, but still close enough to be useful. Although approximation is most often applied to numbers, it is also frequently applied to such things as mathematical functions, shapes, and physical laws.Approximations may be used because...
to the joint probability distribution of a collection of random variable
Random variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
s. The practical use of this is that it can provide an approximation to the likelihood function
Likelihood function
In statistics, a likelihood function is a function of the parameters of a statistical model, defined as follows: the likelihood of a set of parameter values given some observed outcomes is equal to the probability of those observed outcomes given those parameter values...
of a set of observed data which may either provide a computationally simpler problem for estimation
Estimation theory
Estimation theory is a branch of statistics and signal processing that deals with estimating the values of parameters based on measured/empirical data that has a random component. The parameters describe an underlying physical setting in such a way that their value affects the distribution of the...
, or may provide a way of obtaining explicit estimates of model parameters.
The pseudolikelihood approach was introduced by Julian Besag
Julian Besag
Julian Ernst Besag FRS was a British statistician known chiefly for his work in spatial statistics , and Bayesian inference .- Biography:Besag was born in Loughborough and was educated at Loughborough Grammar School...
in the context of analysing data having spatial dependence
Spatial dependence
In applications of statistics, spatial dependence is the existence of statistical dependence in a collection of random variables or a collection time series of random variables, each of which is associated with a different geographical location...
.
Definition
Given a set of random variables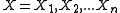 and a set
and a set 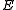 of dependencies between these random variables, where
of dependencies between these random variables, where 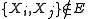 implies
implies 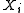 is conditionally independent
is conditionally independentConditional independence
In probability theory, two events R and B are conditionally independent given a third event Y precisely if the occurrence or non-occurrence of R and the occurrence or non-occurrence of B are independent events in their conditional probability distribution given Y...
of
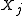 given
given 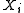 's neighbors, the pseudolikelihood of
's neighbors, the pseudolikelihood of 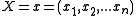 is
is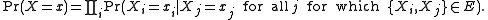
Here
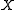 is a vector of variables,
is a vector of variables,  is a vector of values. The expression
is a vector of values. The expression 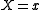 above means that each variable
above means that each variable 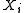 in the vector
in the vector 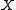 has a corresponding value
has a corresponding value 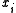 in the vector
in the vector  . The expression
. The expression 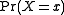 is the probability that the vector of variables
is the probability that the vector of variables 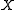 has values equal to the vector
has values equal to the vector  . Because situations can often be described using state variables ranging over a set of possible values, the expression
. Because situations can often be described using state variables ranging over a set of possible values, the expression 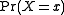 can therefore represent the probability of a certain state among all possible states allowed by the state variables.
can therefore represent the probability of a certain state among all possible states allowed by the state variables.The Pseudo-log-likelihood is a similar measure derived from the above expression. Thus
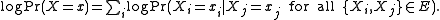
One use of the pseudolikelihood measure is as an approximation for inference about a Markov or Bayesian network
Bayesian network
A Bayesian network, Bayes network, belief network or directed acyclic graphical model is a probabilistic graphical model that represents a set of random variables and their conditional dependencies via a directed acyclic graph . For example, a Bayesian network could represent the probabilistic...
, as the pseudolikelihood of an assignment to
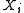 may often be computed more efficiently than the likelihood, particularly when the latter may require marginalization over a large number of variables.
may often be computed more efficiently than the likelihood, particularly when the latter may require marginalization over a large number of variables.Properties
Use of the pseudolikelihood in place of the true likelihood function in a maximum likelihoodMaximum likelihood
In statistics, maximum-likelihood estimation is a method of estimating the parameters of a statistical model. When applied to a data set and given a statistical model, maximum-likelihood estimation provides estimates for the model's parameters....
analysis can lead to good estimates, but a straightforward application of the usual likelihood techiques to derive information about estimation uncertainty, or for significance testing
Statistical significance
In statistics, a result is called statistically significant if it is unlikely to have occurred by chance. The phrase test of significance was coined by Ronald Fisher....
, would in general be incorrect.

