
Public address
Encyclopedia
A public address system (PA system) is an electronic amplification
system with a mixer
, amplifier
and loudspeaker
s, used to reinforce a sound source, e.g., a person giving a speech, a DJ playing prerecorded music, and distributing the sound throughout a venue or building.
Simple PA systems are often used in small venues such as school auditoriums, churches, and small bars. PA systems with a larger number of speakers are widely used in institutional and commercial buildings, to read announcements or declare states of emergency. Intercom
systems, which are often used in schools, also have microphones in each room so that the occupants can reply to the central office.
Sound reinforcement system
s and PA systems may use some similar components, but with differing application. Sound reinforcement systems are for live music or performance, whereas PA systems are for reproduction of speech and recorded music in buildings and institutions. In colloquial British English
, a PA system installed for public address in a building is sometimes referred to as a Tannoy
system after the company of that name now owned by TC Electronic Group
.
 The simplest PA systems consist of a microphone, a modestly powered mixer amplifier and one or more loudspeakers. Simple PA systems of this type, often providing 50 to 200 watts of power, are often used in small venues such as school auditoriums, churches, and small bars. A sound source such as a CD player or radio may be connected to a PA system so that music can be played through the system.
The simplest PA systems consist of a microphone, a modestly powered mixer amplifier and one or more loudspeakers. Simple PA systems of this type, often providing 50 to 200 watts of power, are often used in small venues such as school auditoriums, churches, and small bars. A sound source such as a CD player or radio may be connected to a PA system so that music can be played through the system.
Public address systems typically consist of input sources, preamplifiers and/or signal routers, amplifiers, control and monitoring equipment, and loudspeakers. Input sources refer to the microphones and CD Players that provide a sound input for the system. These input sources are fed into the preamplifiers and signal routers that determine the zones to which the audio signal is fed. The preamplified signals are then passed into the amplifiers. Depending on a country's regulations these amplifiers will amplify the audio signals to 50V, 70V or 100V speaker line level. Control equipment monitors the amplifiers and speaker lines for faults before it reaches the loudspeakers. This control equipment is also used for separating zones in a PA system. The loudspeaker is used to transduce electrical signals into analog sound signals.
Many retailers and offices choose to use the telephone system as the sole access point for the paging system, because the features are integrated. Many schools and other larger institutions are no longer using the large, bulky microphone PA systems and have switched to telephone system paging, as it can be accessed from many different points in the school.
systems that use an Ethernet
or GSM-R
network instead of a centralized amplifier to distribute the audio signal to all paging locations in a building or campus. Network-attached amplifiers and intercom units are used to provide the communication function. At the transmission end, a computer application transmits a digital audio stream via the local area network, using audio from the computer's sound card
inputs or from stored audio recordings. At the receiving end, specialized intercom modules (sometimes known as IP speakers) receive these network transmissions and reproduce the analog audio signal. These are small specialized network appliances addressable by an IP address just like any other computer on the network.
Such systems are inter-connected by the networking infrastructure and thus allow loss less transmission to remote locations across the Internet or a local area or campus network. It is also possible to provide for multiple or relocatable transmission control stations on such a network.
, or GSM-R
, or IP-based networks.
Rail systems typically have an interface with a passenger information system
(PIS) server, at each station linked to train describers which state the location of rolling stock on the network from sensors on trackside signaling equipment. The PIS system invokes a stored message to be played from a local or remote digital voice announcement system, or a series of message fragments to be assembled in the correct order, for example: / the / 13.29 / Virgin_Trains / sleeper_service / from / London_Paddington / to / Penzance / .... / will depart from platform / five / this train is formed of / 12_carriages /. Messages are routed via an IP network and are played on local amplification equipment. Taken together, the PA, routing, DVA, passenger displays and PIS interface are referred to as the customer information system (CIS), a term which itself is often used interchangeably with passenger information system.
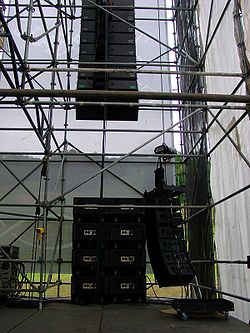 Touring bands will source a large line-array PA system from an audio equipment hire company with reliable service to take from venue to venue along with various other equipment such as lighting and projection. PA hire companies typically will provide "sound solutions" for myriad purposes. Local companies may specialise in small systems tailored to clubs, pubs and small outdoor events whereas larger companies will cater for concert halls.
Touring bands will source a large line-array PA system from an audio equipment hire company with reliable service to take from venue to venue along with various other equipment such as lighting and projection. PA hire companies typically will provide "sound solutions" for myriad purposes. Local companies may specialise in small systems tailored to clubs, pubs and small outdoor events whereas larger companies will cater for concert halls.
At a concert in which live sound reproduction is being used, sound engineers and technicians control the mixing boards for the "main" and "monitor" systems, adjusting the tone, levels, and overall volume of the performance.
, which occurs when sound from the speakers returns to the microphone and is then re-amplified and sent through the speakers again. Sound engineers take several steps to maximize gain before feedback
, including ensuring that directional microphones are not pointed towards speakers, keeping the onstage volume levels down, and lowering gain levels at frequencies where the feedback is occurring, using a graphic equalizer, a parametric equalizer, or a notch filter.
Electronic amplifier
An electronic amplifier is a device for increasing the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude...
system with a mixer
Mixing console
In professional audio, a mixing console, or audio mixer, also called a sound board, mixing desk, or mixer is an electronic device for combining , routing, and changing the level, timbre and/or dynamics of audio signals. A mixer can mix analog or digital signals, depending on the type of mixer...
, amplifier
Amplifier
Generally, an amplifier or simply amp, is a device for increasing the power of a signal.In popular use, the term usually describes an electronic amplifier, in which the input "signal" is usually a voltage or a current. In audio applications, amplifiers drive the loudspeakers used in PA systems to...
and loudspeaker
Loudspeaker
A loudspeaker is an electroacoustic transducer that produces sound in response to an electrical audio signal input. Non-electrical loudspeakers were developed as accessories to telephone systems, but electronic amplification by vacuum tube made loudspeakers more generally useful...
s, used to reinforce a sound source, e.g., a person giving a speech, a DJ playing prerecorded music, and distributing the sound throughout a venue or building.
Simple PA systems are often used in small venues such as school auditoriums, churches, and small bars. PA systems with a larger number of speakers are widely used in institutional and commercial buildings, to read announcements or declare states of emergency. Intercom
Intercom
An intercom , talkback or doorphone is a stand-alone voice communications system for use within a building or small collection of buildings, functioning independently of the public telephone network. Intercoms are generally mounted permanently in buildings and vehicles...
systems, which are often used in schools, also have microphones in each room so that the occupants can reply to the central office.
Sound reinforcement system
Sound reinforcement system
A sound reinforcement system is the combination of microphones, signal processors, amplifiers, and loudspeakers that makes live or pre-recorded sounds louder and may also distribute those sounds to a larger or more distant audience...
s and PA systems may use some similar components, but with differing application. Sound reinforcement systems are for live music or performance, whereas PA systems are for reproduction of speech and recorded music in buildings and institutions. In colloquial British English
British English
British English, or English , is the broad term used to distinguish the forms of the English language used in the United Kingdom from forms used elsewhere...
, a PA system installed for public address in a building is sometimes referred to as a Tannoy
Tannoy
Tannoy Ltd is a Scottish-based manufacturer of loudspeakers and public-address systems. The company was founded in London, England as Tulsemere Manufacturing Company in 1926, but has been based in Coatbridge, Scotland, since the 1970s...
system after the company of that name now owned by TC Electronic Group
TC Electronic
TC Electronic is a Danish audio equipment manufacturer.Its current product ranges include guitar effects, bass amplification, computer audio interfaces, audio plug-in software, live sound equalisers, studio and post production equipment, studio effect processors and broadcast loudness processors...
.
Small systems

Public address systems typically consist of input sources, preamplifiers and/or signal routers, amplifiers, control and monitoring equipment, and loudspeakers. Input sources refer to the microphones and CD Players that provide a sound input for the system. These input sources are fed into the preamplifiers and signal routers that determine the zones to which the audio signal is fed. The preamplified signals are then passed into the amplifiers. Depending on a country's regulations these amplifiers will amplify the audio signals to 50V, 70V or 100V speaker line level. Control equipment monitors the amplifiers and speaker lines for faults before it reaches the loudspeakers. This control equipment is also used for separating zones in a PA system. The loudspeaker is used to transduce electrical signals into analog sound signals.
Large systems
Some PA systems have speakers that cover an entire campus of a college or industrial site, or an entire outdoor complex (e.g., an athletic stadium). More than often this PA system will be used as voice alarm system that make announcement during emergency to evacuate the occupants in a building.Telephone paging systems
Some analog or IP private branch exchange (PBX) telephone systems use a paging facility that acts as a liaison between the telephone and a PA amplifier. In other systems, paging equipment is not built into the telephone system. Instead the system includes a separate paging controller connected to a trunk port of the telephone system. The paging controller is accessed as either a designated directory number or central office line. In many modern systems, the paging function is integrated into the telephone system, and allows announcements to be played over the phone speakers.Many retailers and offices choose to use the telephone system as the sole access point for the paging system, because the features are integrated. Many schools and other larger institutions are no longer using the large, bulky microphone PA systems and have switched to telephone system paging, as it can be accessed from many different points in the school.
PA over IP
PA over IP refers to PA paging and intercomIntercom
An intercom , talkback or doorphone is a stand-alone voice communications system for use within a building or small collection of buildings, functioning independently of the public telephone network. Intercoms are generally mounted permanently in buildings and vehicles...
systems that use an Ethernet
Ethernet
Ethernet is a family of computer networking technologies for local area networks commercially introduced in 1980. Standardized in IEEE 802.3, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies....
or GSM-R
GSM-R
GSM-R, Global System for Mobile Communications - Railway or GSM-Railway is an international wireless communications standard for railway communication and applications. A sub-system of European Rail Traffic Management System , it is used for communication between train and railway regulation...
network instead of a centralized amplifier to distribute the audio signal to all paging locations in a building or campus. Network-attached amplifiers and intercom units are used to provide the communication function. At the transmission end, a computer application transmits a digital audio stream via the local area network, using audio from the computer's sound card
Sound card
A sound card is an internal computer expansion card that facilitates the input and output of audio signals to and from a computer under control of computer programs. The term sound card is also applied to external audio interfaces that use software to generate sound, as opposed to using hardware...
inputs or from stored audio recordings. At the receiving end, specialized intercom modules (sometimes known as IP speakers) receive these network transmissions and reproduce the analog audio signal. These are small specialized network appliances addressable by an IP address just like any other computer on the network.
Such systems are inter-connected by the networking infrastructure and thus allow loss less transmission to remote locations across the Internet or a local area or campus network. It is also possible to provide for multiple or relocatable transmission control stations on such a network.
Long line PA
A Long-line public address (LLPA) system is any public address system with a distributed architecture, normally across a wide geographic area. Systems of this type are commonly found in the rail, light rail and metro industries and allow announcements to be triggered from one or several locations to the rest of the network over low bandwidth legacy copper, normally PSTN lines using DSL modems, or media such as optical fiberOptical fiber
An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of a pure glass not much wider than a human hair. It functions as a waveguide, or "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of...
, or GSM-R
GSM-R
GSM-R, Global System for Mobile Communications - Railway or GSM-Railway is an international wireless communications standard for railway communication and applications. A sub-system of European Rail Traffic Management System , it is used for communication between train and railway regulation...
, or IP-based networks.
Rail systems typically have an interface with a passenger information system
Passenger information system
A passenger information [display] system is an electronic information system which provides real-time passenger information. It may include both predictions about arrival and departure times, as well as information about the nature and causes of disruptions...
(PIS) server, at each station linked to train describers which state the location of rolling stock on the network from sensors on trackside signaling equipment. The PIS system invokes a stored message to be played from a local or remote digital voice announcement system, or a series of message fragments to be assembled in the correct order, for example: / the / 13.29 / Virgin_Trains / sleeper_service / from / London_Paddington / to / Penzance / .... / will depart from platform / five / this train is formed of / 12_carriages /. Messages are routed via an IP network and are played on local amplification equipment. Taken together, the PA, routing, DVA, passenger displays and PIS interface are referred to as the customer information system (CIS), a term which itself is often used interchangeably with passenger information system.
PA on Tour

Large venue systems
For popular music concerts, a more powerful and more complicated PA System is used to provide live sound reproduction. In a concert setting, there are typically two complete PA systems: the "main" system and the "monitor" system. Each system consists of microphones, a mixing board, sound processing equipment, amplifiers, and speakers.- The "main" system (also known as "Front of HouseFront of HouseFront of house is primarily a theatrical term, referring to the portion of the building that is open to the public. In theatre and live music venues, it typically refers to the auditorium and foyer, as opposed to the stage and backstage areas...
", commonly abbreviated FOH), which provides the amplified sound for the audience, will typically use a number of powerful amplifiers driving a range of large, heavy-duty loudspeakers including low-frequency speaker cabinets called subwoofers, full-range speaker cabinets, and high-range horns. A large club may use amplifiers to provide 3000 to 5000 watts of power to the "main" speakers; an outdoor concert may use 10,000 or more watts. - The "monitorFoldback (sound engineering)Foldback is the use of rear-facing heavy-duty loudspeakers known as monitor speaker cabinets on stage during live music performances. The sound is amplified with power amplifiers or a public address system and the speakers are aimed at the on-stage performers rather than the audience...
" system reproduces the sounds of the performance and directs them towards the onstage performers (typically using wedge-shaped monitor speaker cabinets), to help them to hear the instruments and vocals. In British English, the monitor system is referred to as the "foldback". The monitor system in a large club may provide 500 to 1000 watts of power to several foldback speakers; at an outdoor concert, there may be several thousand watts of power going to the monitor system.
At a concert in which live sound reproduction is being used, sound engineers and technicians control the mixing boards for the "main" and "monitor" systems, adjusting the tone, levels, and overall volume of the performance.
Acoustic feedback
All PA systems have a potential for audio feedbackAudio feedback
Audio feedback is a special kind of positive feedback which occurs when a sound loop exists between an audio input and an audio output...
, which occurs when sound from the speakers returns to the microphone and is then re-amplified and sent through the speakers again. Sound engineers take several steps to maximize gain before feedback
Gain before feedback
In live sound mixing, gain before feedback is a practical measure of how much a microphone can be amplified in a sound reinforcement system before causing audio feedback. In audiology, GBF is a measure of hearing aid performance...
, including ensuring that directional microphones are not pointed towards speakers, keeping the onstage volume levels down, and lowering gain levels at frequencies where the feedback is occurring, using a graphic equalizer, a parametric equalizer, or a notch filter.

