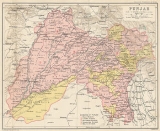
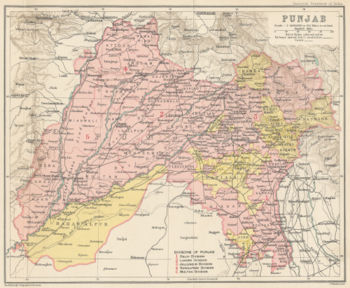
Punjab region
Encyclopedia

Punjabi language
Punjabi is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by inhabitants of the historical Punjab region . For Sikhs, the Punjabi language stands as the official language in which all ceremonies take place. In Pakistan, Punjabi is the most widely spoken language...
: ਪੰਜਾਬ
Gurmukhi script
Gurmukhi is the most common script used for writing the Punjabi language. An abugida derived from the Laṇḍā script and ultimately descended from Brahmi, Gurmukhi was standardized by the second Sikh guru, Guru Angad Dev Ji, in the 16th century. The whole of the Sri Guru Granth Sahib Ji's 1430...
, , ), also spelled Panjab ' onMouseout='HidePop("71044")' href="/topics/Ap_(water)">water
Ap (water)
Ap is the Vedic Sanskrit term for "water", in Classical Sanskrit occurring only in the plural, , whence Hindi . The term is from PIE hxap "water"....
s"), is a geographical region
Region
Region is most commonly found as a term used in terrestrial and astrophysics sciences also an area, notably among the different sub-disciplines of geography, studied by regional geographers. Regions consist of subregions that contain clusters of like areas that are distinctive by their uniformity...
straddling the border between Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
and India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
which includes Punjab province in Pakistan and the states of the Punjab
Punjab (India)
Punjab ) is a state in the northwest of the Republic of India, forming part of the larger Punjab region. The state is bordered by the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh to the east, Haryana to the south and southeast and Rajasthan to the southwest as well as the Pakistani province of Punjab to the...
, Haryana
Haryana
Haryana is a state in India. Historically, it has been a part of the Kuru region in North India. The name Haryana is found mentioned in the 12th century AD by the apabhramsha writer Vibudh Shridhar . It is bordered by Punjab and Himachal Pradesh to the north, and by Rajasthan to the west and south...
, Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh is a state in Northern India. It is spread over , and is bordered by the Indian states of Jammu and Kashmir on the north, Punjab on the west and south-west, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh on the south, Uttarakhand on the south-east and by the Tibet Autonomous Region on the east...
, Chandigarh
Chandigarh
Chandigarh is a union territory of India that serves as the capital of two states, Haryana and Punjab. The name Chandigarh translates as "The Fort of Chandi". The name is from an ancient temple called Chandi Mandir, devoted to the Hindu goddess Chandi, in the city...
and some northern parts of the National Capital Territory of Delhi
Delhi
Delhi , officially National Capital Territory of Delhi , is the largest metropolis by area and the second-largest by population in India, next to Mumbai. It is the eighth largest metropolis in the world by population with 16,753,265 inhabitants in the Territory at the 2011 Census...
in India. The name of the region is Persian
Persian language
Persian is an Iranian language within the Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European languages. It is primarily spoken in Iran, Afghanistan, Tajikistan and countries which historically came under Persian influence...
in origin and signifies "(The Land of) Five Waters" referring to the following rivers: the Jhelum
Jhelum River
Jehlum River or Jhelum River , ) is a river that flows in India and Pakistan. It is the largest and most western of the five rivers of Punjab, and passes through Jhelum District...
, the Chenab, the Ravi
Ravi River
The Ravi is a trans-boundary river flowing through Northwestern India and eastern Pakistan. It is one of the six rivers of the Indus System in Punjab region ....
, the Sutlej
Sutlej
The Sutlej River is the longest of the five rivers that flow through the historic crossroad region of Punjab in northern India and Pakistan. It is located north of the Vindhya Range, south of the Hindu Kush segment of the Himalayas, and east of the Central Sulaiman Range in Pakistan.The Sutlej...
, and the Beas
Beas River
The Beas River is a river in the northern part of India. The river rises in the Himalayas in central Himachal Pradesh, India, and flows for some 470 km to the Sutlej River in the Indian state of Punjab....
. All are tributaries of the Indus River
Indus River
The Indus River is a major river which flows through Pakistan. It also has courses through China and India.Originating in the Tibetan plateau of western China in the vicinity of Lake Mansarovar in Tibet Autonomous Region, the river runs a course through the Ladakh district of Jammu and Kashmir and...
, the Jhelum
Jhelum River
Jehlum River or Jhelum River , ) is a river that flows in India and Pakistan. It is the largest and most western of the five rivers of Punjab, and passes through Jhelum District...
being the largest. Punjab has a long history and rich cultural heritage. The people of the Punjab are called Punjabis
Punjabi people
The Punjabi people , ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ), also Panjabi people, are an Indo-Aryan group from South Asia. They are the second largest of the many ethnic groups in South Asia. They originate in the Punjab region, which has been been the location of some of the oldest civilizations in the world including, the...
and their language is called Punjabi
Punjabi language
Punjabi is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by inhabitants of the historical Punjab region . For Sikhs, the Punjabi language stands as the official language in which all ceremonies take place. In Pakistan, Punjabi is the most widely spoken language...
. The main religion
Religion
Religion is a collection of cultural systems, belief systems, and worldviews that establishes symbols that relate humanity to spirituality and, sometimes, to moral values. Many religions have narratives, symbols, traditions and sacred histories that are intended to give meaning to life or to...
s of the Punjab region are Islam
Islam
Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~...
, Sikhism
Sikhism
Sikhism is a monotheistic religion founded during the 15th century in the Punjab region, by Guru Nanak Dev and continued to progress with ten successive Sikh Gurus . It is the fifth-largest organized religion in the world and one of the fastest-growing...
and Hinduism
Hinduism
Hinduism is the predominant and indigenous religious tradition of the Indian Subcontinent. Hinduism is known to its followers as , amongst many other expressions...
.
The area now known as the Greater Punjab comprises what were once vast territories of West Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
and northern western India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
. The bigger section of the Punjab at about 60% lies within Islamic Republic of Pakistan and 40% within Republic of India where it has been further divided into three states; Punjab, Haryana and Himachal Pradesh.
The region is populated by Indo-Aryan
Indo-Aryan languages
The Indo-Aryan languages constitutes a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages, itself a branch of the Indo-European language family...
speakers. Of these people there are different religious groups such as Sikhs, Hindus, Muslims, Christians, Jains
Jainism
Jainism is an Indian religion that prescribes a path of non-violence towards all living beings. Its philosophy and practice emphasize the necessity of self-effort to move the soul towards divine consciousness and liberation. Any soul that has conquered its own inner enemies and achieved the state...
and Buddhists. It has also been inhabited by Greeks
Greeks
The Greeks, also known as the Hellenes , are a nation and ethnic group native to Greece, Cyprus and neighboring regions. They also form a significant diaspora, with Greek communities established around the world....
, Persians
Persian people
The Persian people are part of the Iranian peoples who speak the modern Persian language and closely akin Iranian dialects and languages. The origin of the ethnic Iranian/Persian peoples are traced to the Ancient Iranian peoples, who were part of the ancient Indo-Iranians and themselves part of...
, Arabs, Turks
Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are peoples residing in northern, central and western Asia, southern Siberia and northwestern China and parts of eastern Europe. They speak languages belonging to the Turkic language family. They share, to varying degrees, certain cultural traits and historical backgrounds...
, Mughals, Afghans
Demographics of Afghanistan
The population of Afghanistan is around 29,835,392 as of the year 2011, which is unclear if the refugees living outside the country are included or not. The nation is composed of a multi-ethnic and multi-lingual society, reflecting its location astride historic trade and invasion routes between...
, Balochis, and British
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
. In 1947, it was partitioned
Partition of India
The Partition of India was the partition of British India on the basis of religious demographics that led to the creation of the sovereign states of the Dominion of Pakistan and the Union of India on 14 and 15...
between British India's successor states with three out of the five rivers going to Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
and the remaining two rivers were allotted to India.
The Pakistani Punjab
Punjab (Pakistan)
Punjab is the most populous province of Pakistan, with approximately 45% of the country's total population. Forming most of the Punjab region, the province is bordered by Kashmir to the north-east, the Indian states of Punjab and Rajasthan to the east, the Pakistani province of Sindh to the...
now comprises the most densely populated province in Pakistan. In India, the Government further sub-divided Punjab into the modern Indian states of Punjab
Punjab (India)
Punjab ) is a state in the northwest of the Republic of India, forming part of the larger Punjab region. The state is bordered by the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh to the east, Haryana to the south and southeast and Rajasthan to the southwest as well as the Pakistani province of Punjab to the...
, Haryana
Haryana
Haryana is a state in India. Historically, it has been a part of the Kuru region in North India. The name Haryana is found mentioned in the 12th century AD by the apabhramsha writer Vibudh Shridhar . It is bordered by Punjab and Himachal Pradesh to the north, and by Rajasthan to the west and south...
, Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh is a state in Northern India. It is spread over , and is bordered by the Indian states of Jammu and Kashmir on the north, Punjab on the west and south-west, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh on the south, Uttarakhand on the south-east and by the Tibet Autonomous Region on the east...
, Chandigarh
Chandigarh
Chandigarh is a union territory of India that serves as the capital of two states, Haryana and Punjab. The name Chandigarh translates as "The Fort of Chandi". The name is from an ancient temple called Chandi Mandir, devoted to the Hindu goddess Chandi, in the city...
and very little part went to Delhi
Delhi
Delhi , officially National Capital Territory of Delhi , is the largest metropolis by area and the second-largest by population in India, next to Mumbai. It is the eighth largest metropolis in the world by population with 16,753,265 inhabitants in the Territory at the 2011 Census...
which expanded a bit northward post-independence. The Pakistani part of the region West Punjab (which includes the Islamabad Capital Territory
Islamabad Capital Territory
The Islamabad Capital Territory is one of the two federal territories of Pakistan. It includes Islamabad, the capital city of Pakistan, and covers an area of 1,165.5 km² of which 906 km² is Islamabad proper...
) covers an area of 205344 square kilometres (79,283.8 sq mi), whereas the Indian State of Punjab is 50362 square kilometres (19,444.9 sq mi). Besides the Indian Punjab, the region also includes the Jammu
Jammu
Jammu , also known as Duggar, is one of the three administrative divisions within Jammu and Kashmir, the northernmost state in India.Jammu city is the largest city in Jammu and the winter capital of Jammu and Kashmir...
state of India. The populations of the region are divided as 86,084,000 (2005) in West Punjab (Pakistan) and 24,289,296 (2000) in the present-day State of (East) Punjab (India). Punjabi
Punjabi language
Punjabi is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by inhabitants of the historical Punjab region . For Sikhs, the Punjabi language stands as the official language in which all ceremonies take place. In Pakistan, Punjabi is the most widely spoken language...
is spoken by (approximately) 60% of the entire population in Pakistan mainly in the Punjab province, making it the most spoken language in Pakistan, and 92.2% in Indian Punjab. (3% of overall Indian population). The capital city of undivided Punjab was Lahore
Lahore
Lahore is the capital of the Pakistani province of Punjab and the second largest city in the country. With a rich and fabulous history dating back to over a thousand years ago, Lahore is no doubt Pakistan's cultural capital. One of the most densely populated cities in the world, Lahore remains a...
, which now sits close to the partition line as the capital of West Punjab; while the capital of East Punjab is Chandigarh
Chandigarh
Chandigarh is a union territory of India that serves as the capital of two states, Haryana and Punjab. The name Chandigarh translates as "The Fort of Chandi". The name is from an ancient temple called Chandi Mandir, devoted to the Hindu goddess Chandi, in the city...
, 248 km (154 miles) from Lahore
Lahore
Lahore is the capital of the Pakistani province of Punjab and the second largest city in the country. With a rich and fabulous history dating back to over a thousand years ago, Lahore is no doubt Pakistan's cultural capital. One of the most densely populated cities in the world, Lahore remains a...
. Indian Punjab uses the Gurmukhi script, while Pakistani Punjab uses the Shahmukhi script.
History



Indo-Iranian
Indo-Iranian can refer to:* Indo-Iranian languages* Prehistoric Indo-Iranians * Indo-European languages* Proto-Indo-Iranian religion* Proto-Indo-Iranian language...
(Aryan
Aryan
Aryan is an English language loanword derived from Sanskrit ārya and denoting variously*In scholarly usage:**Indo-Iranian languages *in dated usage:**the Indo-European languages more generally and their speakers...
) heritage identity. As a result of numerous invasions, many ethnic groups and religions make up the cultural heritage of Punjab.
In prehistoric times, one of the earliest known cultures of South Asia
South Asia
South Asia, also known as Southern Asia, is the southern region of the Asian continent, which comprises the sub-Himalayan countries and, for some authorities , also includes the adjoining countries to the west and the east...
, the Harappa
Indus Valley Civilization
The Indus Valley Civilization was a Bronze Age civilization that was located in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, consisting of what is now mainly modern-day Pakistan and northwest India...
civilization, was located in Punjab.
The epic battles described in the Mahabharata
Mahabharata
The Mahabharata is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India and Nepal, the other being the Ramayana. The epic is part of itihasa....
were fought in modern-day Harayana and historic Punjab. The Gandhara
Gandhara
Gandhāra , is the name of an ancient kingdom , located in northern Pakistan and eastern Afghanistan. Gandhara was located mainly in the vale of Peshawar, the Potohar plateau and on the Kabul River...
s, Kambojas
Kambojas
The Kambojas were a kshatriya tribe of Iron Age India, frequently mentioned in Sanskrit and Pali literature.They were an Indo-Iranian tribe situated at the boundary of the Indo-Aryans and the Iranians, and appear to have moved from the Iranian into the Indo-Aryan sphere over time.The Kambojas...
, Trigartas, Andhra, Pauravas, Bahlikas (Bactrian settlers of Punjab), Yaudheyas and others sided with the Kauravas in the great battle fought at Kurukshetra
Kurukshetra
Kurukshetra is a land of historical and religious importance. Historically the land belonged to Punjab now a district in Haryana state of India. It is a holy place and is also known as Dharmakshetra . According to the Puranas, Kurukshetra is named after King Kuru, the ancestor of Kauravas and...
. According to Dr Fauja Singh and Dr L. M. Joshi: "There is no doubt that the Kambojas, Daradas, Kaikayas, Andhra, Pauravas, Yaudheyas, Malavas, Saindhavas and Kurus had jointly contributed to the heroic tradition and composite culture of ancient Punjab".
In 326 BCE, Alexander the Great invaded the Punjab from the north and incorporated it into his empire. His armies entered the region via the Hindu Kush
Hindu Kush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range that stretches between central Afghanistan and northern Pakistan. The highest point in the Hindu Kush is Tirich Mir in the Chitral region of Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan.It is the westernmost extension of the Pamir Mountains, the Karakoram Range, and is a...
in northwest Pakistan and his rule extended up to the city of Sagala
Sagala
Sagala or Sangala, the ancient Greek name for the modern city of Sialkot in present day Pakistan, was a city of located in northern Punjab, Pakistan...
(modern-day Sialkot
Sialkot
Sialkot is a city in Pakistan situated in the north-east of the Punjab province at the foothills of snow-covered peaks of Kashmir near the Chenab river. It is the capital of Sialkot District. The city is about north-west of Lahore and only a few kilometers from Indian-controlled Jammu.The...
) in northeast Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
. In 305 BCE the area was divided between the Maurya Empire
Maurya Empire
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in ancient India, ruled by the Mauryan dynasty from 321 to 185 BC...
and the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom
Greco-Bactrian Kingdom
The Greco-Bactrian Kingdom was the easternmost part of the Hellenistic world, covering Bactria and Sogdiana in Central Asia from 250 to 125 BC...
. In a long line of succeeding rulers of the area, Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya , was the founder of the Maurya Empire. Chandragupta succeeded in conquering most of the Indian subcontinent. Chandragupta is considered the first unifier of India and its first genuine emperor...
and Ashoka the Great stand out as the most renowned. The Maurya presence in the area was then consolidated in the Indo-Greek Kingdom
Indo-Greek Kingdom
The Indo-Greek Kingdom or Graeco-Indian Kingdom covered various parts of the northwest regions of the Indian subcontinent during the last two centuries BC, and was ruled by more than 30 Hellenistic kings, often in conflict with each other...
in 180 BCE. Menander I
Menander I
Menander I Soter "The Saviour" was one of the rulers of the Indo-Greek Kingdom from either 165 or 155 BC to 130 BC ....
Soter "The Saviour" (known as Milinda in Indian sources) is the most renowned leader of the era. Greek ruling came to an end around 12 BCE, after several invasions by the Yuezhi
Yuezhi
The Yuezhi, or Rouzhi , also known as the Da Yuezhi or Da Rouzhi , were an ancient Central Asian people....
and the Scythian people.
During the establishment and consolidation of Mughal
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire , or Mogul Empire in traditional English usage, was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The Mughal emperors were descendants of the Timurids...
rule, there was conflict, chaos, and political upheaval in the Punjab. However, with the Mughals, prosperity, growth and relative peace were established, particularly under the reign of Jahangir
Jahangir
Jahangir was the ruler of the Mughal Empire from 1605 until his death. The name Jahangir is from Persian جهانگیر,meaning "Conqueror of the World"...
. Muslim empires ruled Punjab for approximately for over 700 years. The period was also notable for the emergence of Guru Nanak (1469–1539). Later mughal emperors conflict with Sikh gurus over power struggle shaped a pathway to division among various religious communities.
Abdali's Indian invasion weakened the Maratha influence, but he could not defeat the Sikhs. At the formation of the Dal Khalsa
Dal Khalsa
Dal Khalsa is a socio-religio-political organization of the Sikh nation, based in the city of Amritsar . The primary aim of Dal Khalsa is to achieve the independence of the Punjabi-speaking Sikh majority region of North West India through peaceful and democratic means in order to establish a...
in 1748 at Amritsar
Amritsar
Amritsar is a city in the northern part of India and is the administrative headquarters of Amritsar district in the state of Punjab, India. The 2001 Indian census reported the population of the city to be over 1,500,000, with that of the entire district numbering 3,695,077...
, the Punjab had been divided into 36 areas and 12 separate Sikh principalities, called misl
Misl
Misl generally refers to the twelve sovereign states in the Sikh Confederacy. The states formed a commonwealth that was described by Antoine Polier as an "aristocratic republic"...
. From this point onward, the beginnings of a Punjabi Sikh Empire emerged. Out of the 36 areas, 22 were united by Maharaja Ranjit Singh
Ranjit Singh
Maharaja Ranjit Singh Ji was the first Maharaja of the Sikh Empire.-Early life:...
. The other 14 accepted British sovereignty
Sovereignty
Sovereignty is the quality of having supreme, independent authority over a geographic area, such as a territory. It can be found in a power to rule and make law that rests on a political fact for which no purely legal explanation can be provided...
. Ten years after Maharaja Ranjit Singh's death, the empire broke up and the British were then able to defeat Punjab with the help of some Hindu Dogra
Dogra
The Dogras are an Indo-Aryan ethnic group in South Asia. Being a diversified group, the Dogras include both Savarnas such as Brahmins, Rajputs and Non-savarnas. The Dogras also incluide merchant castes such as Mahajans...
kings. The Sikh State of Punjab was the only Indian state which was not under European rule at that time.
The British Raj had political, cultural, philosophical and literary consequences in the Punjab, including the establishment of a new system of education. During the independence movement, many Punjabis played a significant role, including Ajit Singh Sandhu
Sardar Ajit Singh
Sardar Ajit Singh Sindhu was an Indian dissident and nationalist during the time of British rule in India. He was an early protester in the Punjab region of India who challenged British rule, and openly criticized the Indian colonial government...
, Bhagat Singh, Udham Singh
Udham Singh
Udham Singh was an Indian independence activist, best known for assassinating Michael O'Dwyer in March 1940 in what has been described as an avenging of the Jallianwalla Bagh Massacre....
, Kartar Singh Sarabha, Bhai Parmanand
Bhai Parmanand
Bhai Parmanand was an Indian nationalist.-Biography:Parmanand was born into a prominent family of the Punjab, descended from the family of the famous Sikh martyr, Bhai Mati Das...
, Muhammad Iqbal
Muhammad Iqbal
Sir Muhammad Iqbal , commonly referred to as Allama Iqbal , was a poet and philosopher born in Sialkot, then in the Punjab Province of British India, now in Pakistan...
, Chaudhary Rehmat Ali, Ilam Din Shaheed and Lajpat Rai.
The Punjabis also played a prominent role in the mutiny of 1857 against the British. Cities like Jhelum and Ludhiana served as centres of rebellion against the British government.
At the time of partition in 1947, the province was split in to East and West Punjab. East Punjab became part of India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, while West Punjab became part of Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
. The Punjab bore the brunt of the civil unrest following the end of the British Raj, with casualties estimated in the millions.
Demographics
Ethnic ancestries of modern Punjabis include Indo-Aryan and some Indo-Scythian and Indo-Parthian settlers of the region, including Indo-Greek. Punjabi people are generally believed to be the descendants of these people . With the advent of IslamIslam
Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~...
, settlers from Persia, Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
, Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
and Central Asia
Central Asia
Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north...
have also integrated into Punjabi society, from whom many Pakistani Punjabis claim descent. However the majority of Punjab is still made up of the native Arains, Jatts, Chamars, Scheduled Castes, Rajputs, Maliks, Khatris, Aheer
Aheer
Aheer is a Jat tribe found mainly in the western districts of Punjab and Sindh in Pakistan. -History and origin:The tribe is also known as Heer or Purewal depending on the dialect of the speaker. Those that tend to speak dialects of Lahanda, such as Seraiki or Pothari tend to refer to themselves...
s and Gujjars. The vast majority of Pakistani Punjabis inhabiting the fertile regions of four out of the five major rivers are Muslim
Muslim
A Muslim, also spelled Moslem, is an adherent of Islam, a monotheistic, Abrahamic religion based on the Quran, which Muslims consider the verbatim word of God as revealed to prophet Muhammad. "Muslim" is the Arabic term for "submitter" .Muslims believe that God is one and incomparable...
s by faith, but also include numerous minority faiths such as Ahmadi Muslims, Sikhs, Hindu
Hindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
s, Christians and Parsi
Parsi
Parsi or Parsee refers to a member of the larger of the two Zoroastrian communities in South Asia, the other being the Irani community....
s. Sikhism
Sikhism
Sikhism is a monotheistic religion founded during the 15th century in the Punjab region, by Guru Nanak Dev and continued to progress with ten successive Sikh Gurus . It is the fifth-largest organized religion in the world and one of the fastest-growing...
, a reformist religion of the late 15th century, is the main religion practiced in Indian Punjab – it arose in the Punjab itself. About 60% of the population of Indian Punjab is Sikh, 37% is Hindu
Hindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
, and the rest are Muslims, Christians, and Jains
Jainism
Jainism is an Indian religion that prescribes a path of non-violence towards all living beings. Its philosophy and practice emphasize the necessity of self-effort to move the soul towards divine consciousness and liberation. Any soul that has conquered its own inner enemies and achieved the state...
. However, due to large scale migration from Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh abbreviation U.P. , is a state located in the northern part of India. With a population of over 200 million people, it is India's most populous state, as well as the world's most populous sub-national entity...
, Rajasthan
Rajasthan
Rājasthān the land of Rajasthanis, , is the largest state of the Republic of India by area. It is located in the northwest of India. It encompasses most of the area of the large, inhospitable Great Indian Desert , which has an edge paralleling the Sutlej-Indus river valley along its border with...
, Bihar
Bihar
Bihar is a state in eastern India. It is the 12th largest state in terms of geographical size at and 3rd largest by population. Almost 58% of Biharis are below the age of 25, which is the highest proportion in India....
, Bengal
Bengal
Bengal is a historical and geographical region in the northeast region of the Indian Subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. Today, it is mainly divided between the sovereign land of People's Republic of Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal, although some regions of the previous...
and Orissa
Orissa
Orissa , officially Odisha since Nov 2011, is a state of India, located on the east coast of India, by the Bay of Bengal. It is the modern name of the ancient nation of Kalinga, which was invaded by the Maurya Emperor Ashoka in 261 BC. The modern state of Orissa was established on 1 April...
demographics of Punjab have become more skewed than reported earlier. Indian Punjab contains the holy Sikh
Sikh
A Sikh is a follower of Sikhism. It primarily originated in the 15th century in the Punjab region of South Asia. The term "Sikh" has its origin in Sanskrit term शिष्य , meaning "disciple, student" or शिक्ष , meaning "instruction"...
city of Amritsar
Amritsar
Amritsar is a city in the northern part of India and is the administrative headquarters of Amritsar district in the state of Punjab, India. The 2001 Indian census reported the population of the city to be over 1,500,000, with that of the entire district numbering 3,695,077...
. The states of Haryana
Haryana
Haryana is a state in India. Historically, it has been a part of the Kuru region in North India. The name Haryana is found mentioned in the 12th century AD by the apabhramsha writer Vibudh Shridhar . It is bordered by Punjab and Himachal Pradesh to the north, and by Rajasthan to the west and south...
and Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh is a state in Northern India. It is spread over , and is bordered by the Indian states of Jammu and Kashmir on the north, Punjab on the west and south-west, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh on the south, Uttarakhand on the south-east and by the Tibet Autonomous Region on the east...
, formerly constituents of the British province of Punjab, are mostly Hindu-majority. Indian Punjabis speak Punjabi language
Punjabi language
Punjabi is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by inhabitants of the historical Punjab region . For Sikhs, the Punjabi language stands as the official language in which all ceremonies take place. In Pakistan, Punjabi is the most widely spoken language...
written in Gurmukhi script. Islam
Islam
Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~...
is the religion of more than 90% of the population of the Punjab in Pakistan, followed by a small Christian minority of about 3–5%. There is also a small number of Sikh, Zorastrian and Hindu minorities among others. Pakistan uses the Shahmukhi script, that is closer to Persian
Persian language
Persian is an Iranian language within the Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European languages. It is primarily spoken in Iran, Afghanistan, Tajikistan and countries which historically came under Persian influence...
script and has considerable Persian loan words. In total, Pakistan has 88 million Punjabi's, and India has 55 million Punjabi's. In greater Punjab there are 143 million Punjabi's.
Economy

India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
and Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
's food output, respectively. The agricultural output of the Punjab region in Pakistan contributes significantly to Pakistan's GDP. The region is important for wheat
Wheat
Wheat is a cereal grain, originally from the Levant region of the Near East, but now cultivated worldwide. In 2007 world production of wheat was 607 million tons, making it the third most-produced cereal after maize and rice...
growing. In addition, rice
Rice
Rice is the seed of the monocot plants Oryza sativa or Oryza glaberrima . As a cereal grain, it is the most important staple food for a large part of the world's human population, especially in East Asia, Southeast Asia, South Asia, the Middle East, and the West Indies...
, cotton
Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective capsule, around the seeds of cotton plants of the genus Gossypium. The fiber is almost pure cellulose. The botanical purpose of cotton fiber is to aid in seed dispersal....
, sugarcane
Sugarcane
Sugarcane refers to any of six to 37 species of tall perennial grasses of the genus Saccharum . Native to the warm temperate to tropical regions of South Asia, they have stout, jointed, fibrous stalks that are rich in sugar, and measure two to six metres tall...
, fruit
Fruit
In broad terms, a fruit is a structure of a plant that contains its seeds.The term has different meanings dependent on context. In non-technical usage, such as food preparation, fruit normally means the fleshy seed-associated structures of certain plants that are sweet and edible in the raw state,...
and vegetables are also major crops. Both Indian and Pakistani Punjab are considered to have the best infrastructure of their respective countries. The Indian Punjab has been estimated to be the richest state in India. The Pakistani Punjab produces 68% of Pakistan's food grain production. Its share of Pakistan's GDP has historically ranged from 51.8% to 54.7%.
Called "The Granary of India" or "The Bread Basket of India", Indian Punjab produces 1% of the world's rice, 2% of its wheat, and 2% of its cotton. In 2001, it was recorded that farmers made up 39% of Indian Punjab's workforce.
Timeline
- 3300 - 1500 BCE: Harappan civilizationIndus Valley CivilizationThe Indus Valley Civilization was a Bronze Age civilization that was located in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, consisting of what is now mainly modern-day Pakistan and northwest India...
(located in modern-day Pakistan) - 1500 - 1000 BCE: (RigvedicRigvedaThe Rigveda is an ancient Indian sacred collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns...
) Vedic civilization - 1000 - 500 BCE: Middle and late Vedic Period
- 599 BCE: Birth of MahaviraMahaviraMahāvīra is the name most commonly used to refer to the Indian sage Vardhamāna who established what are today considered to be the central tenets of Jainism. According to Jain tradition, he was the 24th and the last Tirthankara. In Tamil, he is referred to as Arukaṉ or Arukadevan...
- 567 - 487 BCE: Time of Gautama BuddhaGautama BuddhaSiddhārtha Gautama was a spiritual teacher from the Indian subcontinent, on whose teachings Buddhism was founded. In most Buddhist traditions, he is regarded as the Supreme Buddha Siddhārtha Gautama (Sanskrit: सिद्धार्थ गौतम; Pali: Siddhattha Gotama) was a spiritual teacher from the Indian...
- 550 BCE - 600 CE: BuddhismBuddhismBuddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
remained prevalent - 550 - 515 BCE: Achaemenid Invasion to west of Indus RiverIndus RiverThe Indus River is a major river which flows through Pakistan. It also has courses through China and India.Originating in the Tibetan plateau of western China in the vicinity of Lake Mansarovar in Tibet Autonomous Region, the river runs a course through the Ladakh district of Jammu and Kashmir and...
- 326 BCE: Alexander's Invasion of Punjab (part which is now in Pakistan)
- 322 - 298 BCE: Chandragupta IChandragupta IThe Gupta dynasty first seems to be in eminence with the accession of Chandra Gupta I, son of Ghatotkacha to the throne of the ancestral Gupta kingdom. While his two ancestors were given the title of Maharaja , Chandra Gupta I is described in his inscriptions as Maharajadhiraj signifying a rise in...
, Maurya period - 273 - 232 BCE: Reign of AshokaAshokaAshok Maurya or Ashoka , popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was an Indian emperor of the Maurya Dynasty who ruled almost all of the Indian subcontinent from ca. 269 BC to 232 BC. One of India's greatest emperors, Ashoka reigned over most of present-day India after a number of military conquests...
- 125 - 160 BCE: Rise of the SakaSakaThe Saka were a Scythian tribe or group of tribes....
s - 2 BCE: Beginning of Rule of the Sakas.
- 45 - 180 : Rule of the Kushanas
- 320 - 550 : Gupta EmpireGupta EmpireThe Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed approximately from 320 to 550 CE and covered much of the Indian Subcontinent. Founded by Maharaja Sri-Gupta, the dynasty was the model of a classical civilization. The peace and prosperity created under leadership of Guptas enabled the...
- 500 : HunnicHunsThe Huns were a group of nomadic people who, appearing from east of the Volga River, migrated into Europe c. AD 370 and established the vast Hunnic Empire there. Since de Guignes linked them with the Xiongnu, who had been northern neighbours of China 300 years prior to the emergence of the Huns,...
Invasion - 510 - 650 : VardhanaHarshaHarsha or Harsha Vardhana or Harshvardhan was an Indian emperor who ruled northern India from 606 to 647 AD. He was the son of Prabhakara Vardhana and younger brother of Rajya Vardhana, a king of Thanesar, Haryana...
's Era - 1003 - c. 1320: Lohara dynastyLohara dynastyThe Lohara dynasty were Hindu rulers of Kashmir between 1003 and approximately 1320. The weak rule, internecine fighting and corruption endemic during this period, with only brief years of respite, gave rise to the growth of Islamic supremacy in the region...
, Kashmir - 647 - 1192 : RajputRajputA Rajput is a member of one of the patrilineal clans of western, central, northern India and in some parts of Pakistan. Rajputs are descendants of one of the major ruling warrior classes in the Indian subcontinent, particularly North India...
period - 711 - 713 century : Muhammad bin QasimMuhammad bin QasimMuhammad bin Qasim Al-Thaqafi was a Umayyad general who, at the age of 17, began the conquest of the Sindh and Punjab regions along the Indus River for the Umayyad Caliphate. He was born in the city of Taif...
conquer Sindh and Punjab regions along the Indus River (modern day Pakistan) for the Umayyad Caliphate. - 713 - 1300 : Muslim empires (Turks and Afghans) invade. Islam is being accepted, and a Hindu majority lives along side the muslims.
- 1206 - 1290 : Mamluk dynasty establishes by Mohammad Ghori
- 1290 - 1320 : Khilji dynastyKhilji dynastyThe Khilji Sultanate was a dynasty of Turko-Afghan Khalaj origin who ruled large parts of South Asia from 1290 - 1320. They were the second dynasty to rule the Delhi Sultanate of India...
establishes by Jalal ud din Firuz KhiljiJalal ud din Firuz KhiljiJalaluddin Firuz Khilji was the first sultan of the Khilji dynasty, who reigned from 1290 to 1296. He built his capital at Kilughari, a few miles from the city of Delhi and completed the unfinished palace and gardens of Sultan Qaiqabad.) He ruled from there for six years.-Early life and... - 1320 - 1413 : Tughlaq dynastyTughlaq dynastyThe Tughlaq dynasty of north India started in 1321 in Delhi when Ghazi Malik assumed the throne under the title of Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq. The Tughluqs were a Muslim family of Turkic origin...
established by Ghiyasuddin Tughlaq - 1414 - 1451 : Sayyid dynastySayyid dynastyThe Sayyid dynasty ruled Delhi sultanate in India from 1414 to 1451. They succeeded the Tughlaq dynasty and ruled that sultanate until they were displaced by the Lodi dynasty.This family claimed to be Sayyids, or descendants of Prophet Muhammad...
established by Khizr Khan - 1451 - 1526 : Lodhi dynastyLodhi dynastyLodi Dynasty was a Pashtun dynasty that was the last dynasty to rule the Delhi Sultanate. The dynasty founded by Bahlul Lodi ruled from 1451 to 1526...
establishes by Bahlul Khan LodhiBahlul Khan LodhiBahlul Khan Lodi was the founder of the Afghan Lodi Dynasty of the Delhi Sultanate in India upon the abdication of the last claimant from the previous Sayyid rule. He was born into an Pashtun family of traders, and became a renowned warrior and governor of Sirhind . He became the first sultan of... - 1526 - 1707 : MughalMughal EmpireThe Mughal Empire , or Mogul Empire in traditional English usage, was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The Mughal emperors were descendants of the Timurids...
rule - 1526 – 1530: Zaheeruddin Muhammad Babur
- 1530 – 1540: Nasiruddin Muhammad Humayun
- 1540 – 1545: Sher Shah SuriSher Shah SuriSher Shah Suri , birth name Farid Khan, also known as Sher Khan , was the founder of the short-lived Sur Empire in northern India, with its capital at Delhi, before its demise in the hands of the resurgent Mughal Empire...
- 1545 – 1554: Islam Shah SuriIslam Shah SuriIslam Shah Suri was the second ruler of the Sur dynasty which ruled part of India in the mid-16th century. His original name was Jalal Khan and he was the second son of Sher Shah Suri. On his father's death, an emergency meeting of nobles chose him to be successor instead of his elder brother Adil...
- 1555 – 1556: Nasiruddin Muhammad Humayun
- 1556 – 1605: Jalaluddin Muhammad Akbar
- 1605 – 1627: Nooruddin Muhammad Jahangir
- 1627 – 1658: Shahaabuddin Muhammad Shah JahanShah JahanShah Jahan Shah Jahan (also spelled Shah Jehan, Shahjehan, , Persian: شاه جهان) (January 5, 1592 – January 22, 1666) Shah Jahan (also spelled Shah Jehan, Shahjehan, , Persian: شاه جهان) (January 5, 1592 – January 22, 1666) (Full title: His Imperial Majesty Al-Sultan al-'Azam wal Khaqan...
- 1658 – 1707: Mohiuddin Muhammad Aurangzeb Alamgir
- 1469 - 1539 : Guru Nanak Dev Ji (1st Sikh Guru)
- 1518 - 1565 : Mir Chakar Khan RindMir Chakar Khan RindMir Chakar Khan Rind or Meer Chaakar Khan Rind or Chakar-i-Azam was a Baloch chieftain in the 15th century...
- 1539 - 1675 : Period of 8 Sikh Gurus from Guru Angad DevGuru Angad DevGuru Angad Dev Ji was the second of the ten Sikh Gurus. He was born in the village of Sarae Naga in Muktsar district in Punjab, on 31 March 1504 and given the name Lehna shortly after his birth as was the custom of his Hindu parents. He was the son of a small successful trader named Pheru Mal...
Ji to Guru Tegh Bahadur Ji - 1675 - 1708 : Guru Gobind SinghGuru Gobind SinghGuru Gobind Singh is the tenth and last Sikh guru in a sacred lineage of ten Sikh gurus. Born in Patna, Bihar in India, he was also a warrior, poet and philosopher. He succeeded his father Guru Tegh Bahadur as the leader of Sikhs at a young age of nine...
Ji (10th Sikh Guru) - 1699 : Birth of the KhalsaKhalsa+YouWebImagesVideosMapsNewsMailMoreTranslateFrom: ArabicTo: EnglishEnglishHindiEnglishAllow phonetic typingHindiEnglishArabicAssumptionGoogle Translate for Business:Translator ToolkitWebsite TranslatorGlobal Market Finder...
- 1708 - 1713 : Conquests of Banda BahadurBanda BahadurBanda Singh Bahadur was a Sikh warrior and martyr. He became part of struggle against the Mughal Empire in the early 18th century, after meeting Guru Gobind Singh. Guru Gobind Singh gave him the new name of Banda Singh Bahadur...
- 1714 - 1759 : Sikh warriors (SardarSardarSardar is a title of Indo-Aryan origin that was originally used to denote feudal princes, noblemen, and other aristocrats. It was later applied to indicate a Head of State, a Commander-in-chief, and an Army military rank...
s) perform warfare against Afghans & Mughal Governors - 1739 : Invasion of Nadir Shah and warfare with Sikh Armies
- 1739- Durrani EmpireDurrani EmpireThe Durrani Empire was a Pashtun dynasty centered in Afghanistan and included northeastern Iran, the Kashmir region, the modern state of Pakistan, and northwestern India. It was established at Kandahar in 1747 by Ahmad Shah Durrani, an Afghan military commander under Nader Shah of Persia and chief...
- 1760s- Durrani (Afghan empire)
- 1756 - 1759 : Sikh and Maratha EmpireMaratha EmpireThe Maratha Empire or the Maratha Confederacy was an Indian imperial power that existed from 1674 to 1818. At its peak, the empire covered much of South Asia, encompassing a territory of over 2.8 million km²....
cooperation in the Punjab - 1761 : The Third Battle of Panipat, between the Durrani Empire against the Maratha Empire
- 1762 : 2nd massacre (Ghalughara) from Ahmed Shah's 2nd invasion
- 1761 - 1801 : Rule of the Sikh MislMislMisl generally refers to the twelve sovereign states in the Sikh Confederacy. The states formed a commonwealth that was described by Antoine Polier as an "aristocratic republic"...
s (Confederacy) - 1801 - 1839 : Rule by Maharaja Ranjit SinghRanjit SinghMaharaja Ranjit Singh Ji was the first Maharaja of the Sikh Empire.-Early life:...
- 1845 - 1846 : First Anglo-Sikh WarFirst Anglo-Sikh WarThe First Anglo-Sikh War was fought between the Sikh Empire and the British East India Company between 1845 and 1846. It resulted in partial subjugation of the Sikh kingdom.-Background and causes of the war:...
- 1848 - 1849 : Second Anglo-Sikh WarSecond Anglo-Sikh WarThe Second Anglo-Sikh War took place in 1848 and 1849, between the Sikh Empire and the British East India Company. It resulted in the subjugation of the Sikh Empire, and the annexation of the Punjab and what subsequently became the North-West Frontier Province by the East India Company.-Background...
- 1849 : Complete annexation of Punjab into British India
- 1849 - 1947: British rule
- 1947 : Partition of British India thus Punjab into 2 parts the Eastern part (or two rivers) became the Indian Punjab and the Western majority part (3 rivers) the Pakistan Punjab
See also
- Punjabi culturePunjabi CulturePunjabi Culture is the culture of the Punjab region. It is one of the oldest in world history, dating from ancient antiquity to the modern era. The Punjabi culture is the culture of the Punjabi people who are now distributed throughout the world. The scope, history, sophistication and complexity of...
- Punjabi languagePunjabi languagePunjabi is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by inhabitants of the historical Punjab region . For Sikhs, the Punjabi language stands as the official language in which all ceremonies take place. In Pakistan, Punjabi is the most widely spoken language...
- Punjabi cuisinePunjabi cuisinePunjabi cuisine is food from the Punjab region of northwestern India and eastern Pakistan. It can be non-vegetarian or completely vegetarian. One of the main features of Punjabi cuisine is its diverse range of dishes...
- Punjabi dance
- Music of PunjabMusic of PunjabPunjab is a region in the South Asia, divided into two parts Western Punjab and Eastern Punjab . Punjabi music has a diverse style of music, ranging from Folk and Sufi to Classical, notably the Patiala gharana-Sufi Music :...
- SikhismSikhismSikhism is a monotheistic religion founded during the 15th century in the Punjab region, by Guru Nanak Dev and continued to progress with ten successive Sikh Gurus . It is the fifth-largest organized religion in the world and one of the fastest-growing...
Further reading
- [Quraishee 73] Punjabi Adab De Kahani, Abdul Hafeez Quaraihee, Azeez Book Depot, Lahore, 1973.
- [Chopra 77] The Punjab as a sovereign state, Gulshan Lal Chopra, Al-Biruni , Lahore, 1977.
- Patwant Singh. 1999. The Sikhs. New York: Doubleday. ISBN 0-385-50206-0.
- The evolution of Heroic Tradition in Ancient Panjab, 1971, Buddha Parkash.
- Social and Political Movements in ancient Panjab, Delhi, 1962, Buddha Parkash.
- History of Porus, Patiala, Buddha Parkash.
- History of the Panjab, Patiala, 1976, Fauja Singh, L. M. Joshi (Ed).
- The Legacy of The Punjab, 1997, R M Chopra.

