
Push-pull converter
Encyclopedia
A push–pull converter is a type of DC to DC converter
that uses a transformer
to change the volt
age of a DC power supply. The transformer's ratio is arbitrary but fixed; however, in many circuit implementations the duty cycle
of the switching action can be varied to effect a range of voltage ratios. The primary advantages of push–pull converters are their simplicity and ability to scale up to high power throughput, earning them a place in industrial DC power applications.
The push–pull converter is similar to the flyback converter
and especially the forward converter
.
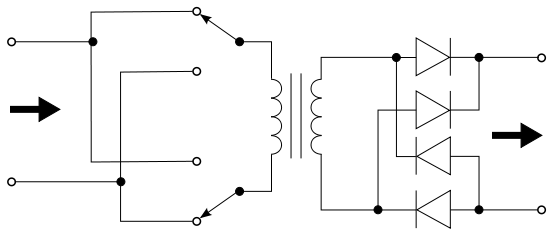
The term push–pull is sometimes used to generally refer to any converter with bidirectional excitation of the transformer. For example, in a full-bridge converter, the switches (connected as an H-bridge
) alternate the voltage across the supply side of the transformer, causing the transformer to function as it would for AC power and produce a voltage on its output side.
However, push–pull more commonly refers to a two-switch topology with a split primary winding.
In any case, the output is then rectified and sent to the load. Capacitor
s are often included at the output to buffer against the inevitable switching noise.
In practice, it is necessary to allow a small interval between powering the transformer one way and powering it the other: the “switches” are usually pairs of transistors (or similar devices), and were the two transistors in the pair to switch simultaneously there would be a risk of shorting out the power supply. Hence, a small wait is needed to avoid this problem. This wait time is called "Dead Time" and is necessary to avoid transistor shoot-through.
A P-type transistor is used to pull up the N-type power transistor gate (common source
) and an N-type transistor is used to pull down the P-type power transistor gate.
Alternatively, all power transistors can be N-type, which offer around three times the gain of their P-type equivalents. In this alternative the N-type transistor used in place of the P-type has to be driven in this way:
The voltage is amplified by one P-type transistor and one N-type transistor in common base
configuration to rail-to-rail amplitude.
Then the power transistor is driven in common drain
configuration to amplify the current.
In high frequency applications both transistors are driven with common source
.
The operation of the circuit means that both transistors are actually pushing, and the pulling is done by a low pass filter (coil
) in general, and by a center tap of the transformer in the converter application. But because the transistors push in an alternating fashion, the device is called a push–pull converter.
If the driver for the transistors is powerful and fast enough, the back EMF has no time to charge the capacity of the windings and of the body-diode of the MOSFET
s to high voltages.
If a microcontroller is used, it can be used to measure the peak voltage and digitally adjust the timing for the transistors, so that the peak only just appears. This is especially useful when the transistors are starting from cold with no peaks, and are in their boot phase.
The cycle starts with no voltage and no current. Then one transistor turns on, a constant voltage is applied to the primary, current increases linearly, and a constant voltage is induced in the secondary. After some time T the transistor is turned off, the parasitic capacities of the transistors and the transformer and the inductance
of the transformer form an LC circuit
which swings to the opposite polarity. Then the other transistor turns on. For the same time T charge flows back into the storage capacitor, then changes the direction automatically, and for another time T the charge flows in the transformer. Then again the first transistor turns on until the current is stopped. Then the cycle is finished, another cycle can start anytime later. The S-shaped current is needed to improve over the simpler converters and deal efficiently with remanence
.
DC to DC converter
A DC-to-DC converter is an electronic circuit which converts a source of direct current from one voltage level to another. It is a class of power converter.- Usage :...
that uses a transformer
Transformer
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors—the transformer's coils. A varying current in the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a varying magnetic field...
to change the volt
Volt
The volt is the SI derived unit for electric potential, electric potential difference, and electromotive force. The volt is named in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta , who invented the voltaic pile, possibly the first chemical battery.- Definition :A single volt is defined as the...
age of a DC power supply. The transformer's ratio is arbitrary but fixed; however, in many circuit implementations the duty cycle
Duty cycle
In engineering, the duty cycle of a machine or system is the time that it spends in an active state as a fraction of the total time under consideration....
of the switching action can be varied to effect a range of voltage ratios. The primary advantages of push–pull converters are their simplicity and ability to scale up to high power throughput, earning them a place in industrial DC power applications.
The push–pull converter is similar to the flyback converter
Flyback converter
The flyback converter is used in both AC/DC and DC/DC conversion with galvanic isolation between the input and any outputs. More precisely, the flyback converter is a buck-boost converter with the inductor split to form a transformer, so that the voltage ratios are multiplied with an additional...
and especially the forward converter
Forward converter
The forward converter is a DC/DC converter that uses transformer windings to buck or boost the voltage and provide galvanic isolation for the load...
.
Circuit operation

The term push–pull is sometimes used to generally refer to any converter with bidirectional excitation of the transformer. For example, in a full-bridge converter, the switches (connected as an H-bridge
H-bridge
An H bridge is an electronic circuit that enables a voltage to be applied across a load in either direction. These circuits are often used in robotics and other applications to allow DC motors to run forwards and backwards...
) alternate the voltage across the supply side of the transformer, causing the transformer to function as it would for AC power and produce a voltage on its output side.
However, push–pull more commonly refers to a two-switch topology with a split primary winding.
In any case, the output is then rectified and sent to the load. Capacitor
Capacitor
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
s are often included at the output to buffer against the inevitable switching noise.
In practice, it is necessary to allow a small interval between powering the transformer one way and powering it the other: the “switches” are usually pairs of transistors (or similar devices), and were the two transistors in the pair to switch simultaneously there would be a risk of shorting out the power supply. Hence, a small wait is needed to avoid this problem. This wait time is called "Dead Time" and is necessary to avoid transistor shoot-through.
Transistors
N-type and P-type power transistors can be used. Power MOSFETs are often chosen for this role due to their high current switching capability and their inherently low ON resistance. The gates (base) of the power transistors are tied via a resistor to one of the supply voltages.A P-type transistor is used to pull up the N-type power transistor gate (common source
Common source
In electronics, a common-source amplifier is one of three basic single-stage field-effect transistor amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage or transconductance amplifier. The easiest way to tell if a FET is common source, common drain, or common gate is to examine where the signal...
) and an N-type transistor is used to pull down the P-type power transistor gate.
Alternatively, all power transistors can be N-type, which offer around three times the gain of their P-type equivalents. In this alternative the N-type transistor used in place of the P-type has to be driven in this way:
The voltage is amplified by one P-type transistor and one N-type transistor in common base
Common base
In electronics, a common-base amplifier is one of three basic single-stage bipolar junction transistor amplifier topologies, typically used as a current buffer or voltage amplifier...
configuration to rail-to-rail amplitude.
Then the power transistor is driven in common drain
Common drain
In electronics, a common-drain amplifier, also known as a source follower, is one of three basic single-stage field effect transistor amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage buffer. In this circuit the gate terminal of the transistor serves as the input, the source is the output, and the...
configuration to amplify the current.
In high frequency applications both transistors are driven with common source
Common source
In electronics, a common-source amplifier is one of three basic single-stage field-effect transistor amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage or transconductance amplifier. The easiest way to tell if a FET is common source, common drain, or common gate is to examine where the signal...
.
The operation of the circuit means that both transistors are actually pushing, and the pulling is done by a low pass filter (coil
Coil
A coil is a series of loops. A coiled coil is a structure in which the coil itself is in turn also looping.-Electromagnetic coils:An electromagnetic coil is formed when a conductor is wound around a core or form to create an inductor or electromagnet...
) in general, and by a center tap of the transformer in the converter application. But because the transistors push in an alternating fashion, the device is called a push–pull converter.
Timing
If both transistors are in their on state, a short circuit results. On the other hand if both transistors are in their off state, high voltage peaks appear due to back EMF.If the driver for the transistors is powerful and fast enough, the back EMF has no time to charge the capacity of the windings and of the body-diode of the MOSFET
MOSFET
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor is a transistor used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. The basic principle of this kind of transistor was first patented by Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925...
s to high voltages.
If a microcontroller is used, it can be used to measure the peak voltage and digitally adjust the timing for the transistors, so that the peak only just appears. This is especially useful when the transistors are starting from cold with no peaks, and are in their boot phase.
The cycle starts with no voltage and no current. Then one transistor turns on, a constant voltage is applied to the primary, current increases linearly, and a constant voltage is induced in the secondary. After some time T the transistor is turned off, the parasitic capacities of the transistors and the transformer and the inductance
Inductance
In electromagnetism and electronics, inductance is the ability of an inductor to store energy in a magnetic field. Inductors generate an opposing voltage proportional to the rate of change in current in a circuit...
of the transformer form an LC circuit
LC circuit
An LC circuit, also called a resonant circuit or tuned circuit, consists of an inductor, represented by the letter L, and a capacitor, represented by the letter C...
which swings to the opposite polarity. Then the other transistor turns on. For the same time T charge flows back into the storage capacitor, then changes the direction automatically, and for another time T the charge flows in the transformer. Then again the first transistor turns on until the current is stopped. Then the cycle is finished, another cycle can start anytime later. The S-shaped current is needed to improve over the simpler converters and deal efficiently with remanence
Remanence
Remanence or remanent magnetization is the magnetization left behind in a ferromagnetic material after an external magnetic field is removed. It is also the measure of that magnetization. Colloquially, when a magnet is "magnetized" it has remanence...
.
See also
- Inverter (electrical)Inverter (electrical)An inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current to alternating current ; the converted AC can be at any required voltage and frequency with the use of appropriate transformers, switching, and control circuits....
- Push–pull output
- Class B or AB push–pull
- RectifierRectifierA rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current , which periodically reverses direction, to direct current , which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification...
External links
- Switchmode PSU for car audio 12V to symmetric output push–pull converter used for powering car audio amplifiers. This is a true push–pull topology with two switches and a center-tapped transformer.
- Push-Pull converter basics An article covering the basic operating principles of the push-pull converter.

