
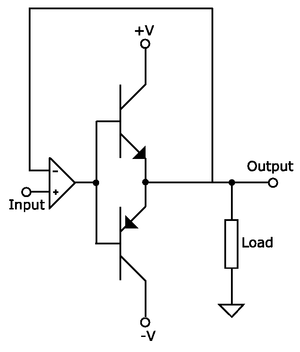
Push-pull output
Encyclopedia
Electronic circuit
An electronic circuit is composed of individual electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes, connected by conductive wires or traces through which electric current can flow...
that can drive either a positive or a negative current into a load. Push–pull outputs are present in TTL
Transistor-transistor logic
Transistor–transistor logic is a class of digital circuits built from bipolar junction transistors and resistors. It is called transistor–transistor logic because both the logic gating function and the amplifying function are performed by transistors .TTL is notable for being a widespread...
and CMOS
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits...
digital logic circuits and in some types of amplifiers
Electronic amplifier
An electronic amplifier is a device for increasing the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude...
, and are usually realized as a complementary pair of transistor
Transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and power. It is composed of a semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current...
s, one dissipating or sinking current from the load to ground or a negative power supply, and the other supplying or sourcing current to the load from a positive power supply.
Vacuum tube
Vacuum tube
In electronics, a vacuum tube, electron tube , or thermionic valve , reduced to simply "tube" or "valve" in everyday parlance, is a device that relies on the flow of electric current through a vacuum...
s (valves) are not available in complementary types (as are pnp/npn transistors), so the tube push–pull amplifier has a pair of identical output tubes or groups of tubes with the control grid
Control grid
The control grid is an electrode used in thermionic valves used to modulate the flow of electrons in the cathode to anode or plate circuit.- Operation :...
s driven in antiphase; these tubes drive current through the two halves of the primary winding of a center-tapped output transformer in such a way that the signal currents add, while the distortion signals due to the non-linear characteristic curves of the tubes subtract. These amplifiers were first designed long before the development of solid-state electronic devices; they are still in use by both audiophile
Audiophile
An audiophile is a person who enjoys listening to recorded music, usually in a home. Some audiophiles are more interested in collecting and listening to music, while others are more interested in collecting and listening to audio components, whose "sound quality" they consider as important as the...
s and musicians who consider them to sound better.
Digital circuits
Totem pole
Totem poles are monumental sculptures carved from large trees, mostly Western Red Cedar, by cultures of the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast of North America...
" outputs.
In simpler digital circuits, especially in CMOS
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits...
, each transistor
Transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and power. It is composed of a semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current...
is switched on only when its complement is switched off.
A disadvantage of simple push–pull outputs is that two or more of them cannot be connected together, because if one tried to pull while another tried to push, the transistors could be damaged. To avoid this restriction, some push–pull outputs have a third state in which both transistors are switched off. In this state, the output is said to be floating (or, to use a proprietary term, tri-stated).
The alternative to a push–pull output is a single switch that connects the load either to ground (called an open collector
Open collector
An open collector is a common type of output found on many integrated circuits . Instead of outputting a signal of a specific voltage or current, the output signal is applied to the base of an internal NPN transistor whose collector is externalized on a pin of the IC. The emitter of the...
or open drain output) or to the power supply (called an open-emitter or open-source output).
Analog circuits
A conventional amplifier stage which is not push–pull is sometimes called single-ended to distinguish it from a push–pull circuit.In analog push–pull power amplifiers the two output devices (transistors, tubes, FETs) or sets of devices operate in antiphase (i.e. 180° apart). The two antiphase outputs are connected to the load in a way that causes the signal outputs to be added, but distortion components due to non-linearity in the output devices to be subtracted from each other; if the non-linearity of both output devices is similar, distortion is much reduced. Symmetrical push–pull circuits must cancel even order harmonics, like f2, f4, f6 and therefore promote odd order harmonics, like (f1), f3, f5 when driven into the nonlinear range.
A push–pull amplifier produces less distortion
Distortion
A distortion is the alteration of the original shape of an object, image, sound, waveform or other form of information or representation. Distortion is usually unwanted, and often many methods are employed to minimize it in practice...
than a single-ended one. This allows a class A or AB push–pull amplifier to have less distortion for the same power as the same devices used in single-ended configuration. Class AB and class B dissipate less power for the same output as class A; distortion can be kept low by negative feedback
Negative feedback
Negative feedback occurs when the output of a system acts to oppose changes to the input of the system, with the result that the changes are attenuated. If the overall feedback of the system is negative, then the system will tend to be stable.- Overview :...
.
Transformer-output transistor power amplifiers
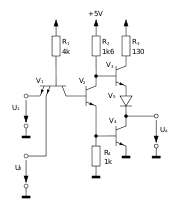
It is now very rare to use output transformers with transistor amplifiers, although such amplifiers offer the best opportunity for matching output devices (with only PNP or only NPN devices required).Totem-pole push-pull output stages
Two matched transistors of the same polarity (or, less often, Vacuum tubes) can be arranged to supply opposite halves of each cycle without the need for an output transformer, although in doing so the driver circuit often is asymmetric and one transistor will be used in a Common-emitter configuration while the other is used as an Emitter follower. This arrangement is less used today than during the 1970s; it can be implemented with few transistors (not so important today) but is relatively difficult to balance and so keep to a low distortion (the highly non-linear TTLTransistor-transistor logic
Transistor–transistor logic is a class of digital circuits built from bipolar junction transistors and resistors. It is called transistor–transistor logic because both the logic gating function and the amplifying function are performed by transistors .TTL is notable for being a widespread...
circuits such as the 7400 use this arrangement).
Symmetrical Push-pull
Each half of the output pair "mirror" the other, in that an NPN (or N-Channel FETFet
Fet is a municipality in Akershus county, Norway. It is part of the Romerike traditional region. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Fetsund.Fet was established as a municipality on 1 January 1838...
) device in one half will be matched by a PNP (or P-Channel FET
Fet
Fet is a municipality in Akershus county, Norway. It is part of the Romerike traditional region. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Fetsund.Fet was established as a municipality on 1 January 1838...
) in the other. This type of arrangement tends to give lower distortion than quasi-symmetric stages because even harmonics are cancelled more effectively with greater symmetry.
Quasi-symmetrical push-pull
In the past when good quality PNP complements for high power NPN silicon transistors were limited, a workaround was to use identical NPN output devices, but fed from complementary PNP and NPN driver circuits in such a way that the combination was close to being symmetrical (but never as good as having symmetry throughout), and so distortion due to mismatched gain on each half of the cycle could be a significant problem.Super-symmetric output stages
Employing some duplication in the whole driver circuit, to allow symmetrical drive circuits can improve matching further, although driver asymmetry is a small fraction of the distortion generating process. Using a Bridge-tied loadBridge-tied load
A bridge-tied load , also known as bridged transformerless and bridged mono, is an output configuration for audio amplifiers, a form of impedance bridging used mainly in professional audio applications. The two channels of a stereo amplifier are fed the same monaural audio signal, with one...
arrangement allows a much greater degree of matching between positive and negative halves, compensating for the inevitable small differences between NPN and PNP devices.
Square-law push-pull
The output devices, usually MOSFETMOSFET
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor is a transistor used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. The basic principle of this kind of transistor was first patented by Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925...
s, are configured so that their square-law transfer characteristics (that generate second harmonic Distortion
Distortion
A distortion is the alteration of the original shape of an object, image, sound, waveform or other form of information or representation. Distortion is usually unwanted, and often many methods are employed to minimize it in practice...
is used in a single-ended circuit) cancel distortion to a large extent. That is, as the voltage across one transistor's gate-source voltage increases the remaining bias voltage to the complementary device is reduced by that amount and the drain current change in the second device approximately corrects for the non-linearity in the increase of the first.
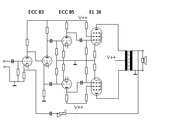
Push-pull tube (valve) output stages
See article: Valve audio amplifier – technical#The push-pull power amplifier.These usually involve an output transformer to drop the output impedance to levels suitable for loudspeakers, although Output-transformerless (OTL)
Output TransformerLess
Output transformerless is a term which describes a subset of vacuum tube audio power amplifier topologies, all of which omit an output transformer for the purpose of greater linearity and fidelity. Conventional vacuum tube amplifier designs rely upon an output transformer to couple the amplifier's...
tube stages exist (such as for headphones, for 100 Volt line Public address
Public address
A public address system is an electronic amplification system with a mixer, amplifier and loudspeakers, used to reinforce a sound source, e.g., a person giving a speech, a DJ playing prerecorded music, and distributing the sound throughout a venue or building.Simple PA systems are often used in...
sound systems, or for rare high-impedance loudspeakers).
Ultra-linear push-pull
PentodePentode
A pentode is an electronic device having five active electrodes. The term most commonly applies to a three-grid vacuum tube , which was invented by the Dutchman Bernhard D.H. Tellegen in 1926...
s and Tetrode
Tetrode
A tetrode is an electronic device having four active electrodes. The term most commonly applies to a two-grid vacuum tube. It has the three electrodes of a triode and an additional screen grid which significantly changes its behaviour.-Control grid:...
s can have their screen grid fed from a percentage of the primary voltage on the output transformer, giving efficiency and distortion that is a good compromise between triode (or Triode-strapped) power amplifiers circuits and conventional pentode or tetrode output circuits where the screen is fed from a relatively constant voltage source. See article: Ultra-Linear
Ultra-Linear
Ultra-linear is a term used to describe a type of electronic circuit that is used to couple a tetrode or pentode vacuum-tube to a load ....
.
See also
- Single-ended triodeSingle-ended triodeA single-ended triode vacuum tube electronic amplifier uses a single triode to produce an output, in contrast to a push-pull amplifier which uses a pair of devices with antiphase inputs to generate an output with the wanted signals added and the distortion components subtracted...
- Push–pull converter for more details on implementation
- Open collectorOpen collectorAn open collector is a common type of output found on many integrated circuits . Instead of outputting a signal of a specific voltage or current, the output signal is applied to the base of an internal NPN transistor whose collector is externalized on a pin of the IC. The emitter of the...
External links
- Push–pull vs. single-ended output in analogue tube amplifiers

