
Quadrature booster
Encyclopedia
A phase-shifting transformer, also quadrature booster (quad booster for short), is a specialised form of transformer
used to control the flow of real power on three-phase
electricity transmission
networks.
For an alternating current
transmission line, power flow through the line is proportional to the sine
of the difference in the phase angle
of the voltage between the transmitting end and the receiving end of the line. Where parallel circuits with different capacity exist between two points in a transmission grid (for example, an overhead line and an underground cable), direct manipulation of the phase angle allows control of the division of power flow between the paths, preventing overload. Quadrature boosters thus provide a means of relieving overloads on heavily laden circuits and re-routing power via more favorable paths.
The capital cost of a quadrature booster can be high: as much as four to six million GBP (6-9 million USD) for a unit rated over 2 GVA. However, the utility to transmission system operators in flexibility and speed of operation, and particularly savings in permitting more economical dispatch
of generation, can soon recover the cost of ownership.
 By means of a voltage
By means of a voltage
derived from the supply that is first phase-shifted by 90° (hence is in quadrature), and then re-applied to it, a phase
angle is developed across the quadrature booster. It is this induced phase angle that affects the flow of power through specified circuits
.
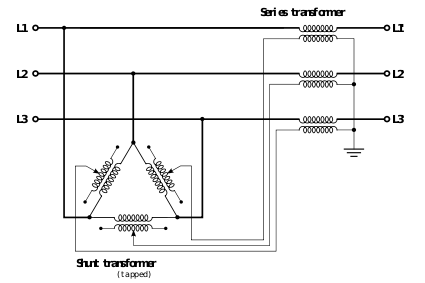
unit and a series
unit. The shunt unit has its winding terminals connected so to shift its output voltage by 90° with respect to the supply. Its output is then applied as input to the series unit, which, because its secondary winding is in series with the main circuit, adds the phase-shifted component. The overall output voltage is hence the vector sum of the supply voltage and the 90° quadrature component.
Tap
connections on the shunt unit allow the magnitude of the quadrature component to be controlled, and thus the magnitude of the phase shift across the quadrature booster. The flow on the circuit containing the quadrature booster may be increased (boost tapping) or reduced (buck tapping). Subject to system conditions, the flow may even be bucked enough to completely reverse from its neutral-tap direction.
below shows the effect of tapping a quadrature booster on a notional 100 MW generator-load system with two parallel transmission line
s, one of which features a quadrature booster (shaded grey) with a tap range of 1 to 19.
In the left-hand image, the quadrature booster is at its center tap position of 10 and has a phase angle of 0°. It thus does not affect the power flow through its circuit and both lines are equally loaded at 50 MW. The right-hand image shows the same network with the quadrature booster tapped down so to buck the power flow. The resulting negative phase angle has transferred 23 MW of loading onto the parallel circuit, while the total load supplied is unchanged at 100 MW. (Note that the values used here are hypothetical; the actual phase angle and transfer in load would depend upon the parameters of the quadrature booster and the transmission lines.)
 The intended effect is opposite: equalizing power on lines where naturally one would be heavily loaded and one would be lightly loaded.
The intended effect is opposite: equalizing power on lines where naturally one would be heavily loaded and one would be lightly loaded.
Transformer
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors—the transformer's coils. A varying current in the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a varying magnetic field...
used to control the flow of real power on three-phase
Three-phase electric power
Three-phase electric power is a common method of alternating-current electric power generation, transmission, and distribution. It is a type of polyphase system and is the most common method used by grids worldwide to transfer power. It is also used to power large motors and other heavy loads...
electricity transmission
Electric power transmission
Electric-power transmission is the bulk transfer of electrical energy, from generating power plants to Electrical substations located near demand centers...
networks.
For an alternating current
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
transmission line, power flow through the line is proportional to the sine
Sine
In mathematics, the sine function is a function of an angle. In a right triangle, sine gives the ratio of the length of the side opposite to an angle to the length of the hypotenuse.Sine is usually listed first amongst the trigonometric functions....
of the difference in the phase angle
Phase angle
In the context of vectors and phasors, the term phase angle refers to the angular component of the polar coordinate representation. The notation A\ang \!\ \theta, for a vector with magnitude A and phase angle θ, is called angle notation.In the context of periodic phenomena, such as a wave,...
of the voltage between the transmitting end and the receiving end of the line. Where parallel circuits with different capacity exist between two points in a transmission grid (for example, an overhead line and an underground cable), direct manipulation of the phase angle allows control of the division of power flow between the paths, preventing overload. Quadrature boosters thus provide a means of relieving overloads on heavily laden circuits and re-routing power via more favorable paths.
The capital cost of a quadrature booster can be high: as much as four to six million GBP (6-9 million USD) for a unit rated over 2 GVA. However, the utility to transmission system operators in flexibility and speed of operation, and particularly savings in permitting more economical dispatch
Economic dispatch
Economic dispatch is the short-term determination of the optimal output of a number of electricity generation facilities, to meet the system load, at the lowest possible cost, while serving power to the public in a robust and reliable manner...
of generation, can soon recover the cost of ownership.
Method of operation

Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
derived from the supply that is first phase-shifted by 90° (hence is in quadrature), and then re-applied to it, a phase
Polyphase system
A polyphase system is a means of distributing alternating current electrical power. Polyphase systems have three or more energized electrical conductors carrying alternating currents with a definite time offset between the voltage waves in each conductor. Polyphase systems are particularly useful...
angle is developed across the quadrature booster. It is this induced phase angle that affects the flow of power through specified circuits
Electrical network
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical elements such as resistors, inductors, capacitors, transmission lines, voltage sources, current sources and switches. An electrical circuit is a special type of network, one that has a closed loop giving a return path for the current...
.
Arrangement
A quadrature booster typically consists of two separate transformers: a shuntSeries and parallel circuits
Components of an electrical circuit or electronic circuit can be connected in many different ways. The two simplest of these are called series and parallel and occur very frequently. Components connected in series are connected along a single path, so the same current flows through all of the...
unit and a series
Series and parallel circuits
Components of an electrical circuit or electronic circuit can be connected in many different ways. The two simplest of these are called series and parallel and occur very frequently. Components connected in series are connected along a single path, so the same current flows through all of the...
unit. The shunt unit has its winding terminals connected so to shift its output voltage by 90° with respect to the supply. Its output is then applied as input to the series unit, which, because its secondary winding is in series with the main circuit, adds the phase-shifted component. The overall output voltage is hence the vector sum of the supply voltage and the 90° quadrature component.
Tap
Tap (transformer)
A transformer tap is a connection point along a transformer winding that allows a certain number of turns to be selected. This means, a transformer with a variable turns ratio is produced, enabling voltage regulation of the output...
connections on the shunt unit allow the magnitude of the quadrature component to be controlled, and thus the magnitude of the phase shift across the quadrature booster. The flow on the circuit containing the quadrature booster may be increased (boost tapping) or reduced (buck tapping). Subject to system conditions, the flow may even be bucked enough to completely reverse from its neutral-tap direction.
Illustration of effect
The one-line diagramOne-line diagram
In power engineering, a one-line diagram or single-line diagram is a simplified notation for representing a three-phase power system. The one-line diagram has its largest application in power flow studies. Electrical elements such as circuit breakers, transformers, capacitors, bus bars, and...
below shows the effect of tapping a quadrature booster on a notional 100 MW generator-load system with two parallel transmission line
Transmission line
In communications and electronic engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable designed to carry alternating current of radio frequency, that is, currents with a frequency high enough that its wave nature must be taken into account...
s, one of which features a quadrature booster (shaded grey) with a tap range of 1 to 19.
In the left-hand image, the quadrature booster is at its center tap position of 10 and has a phase angle of 0°. It thus does not affect the power flow through its circuit and both lines are equally loaded at 50 MW. The right-hand image shows the same network with the quadrature booster tapped down so to buck the power flow. The resulting negative phase angle has transferred 23 MW of loading onto the parallel circuit, while the total load supplied is unchanged at 100 MW. (Note that the values used here are hypothetical; the actual phase angle and transfer in load would depend upon the parameters of the quadrature booster and the transmission lines.)


