
Quadrature modulation
Encyclopedia
Quadrature modulation is the general technique of modulating two carriers.
Examples include Quadrature amplitude modulation
, Phase-shift keying
, and Minimum-shift keying
.
Constellation diagram
s are used to examine the modulation in the 2-D signal space.
consists of sending the function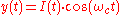
where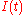 is the signal to encode and
is the signal to encode and 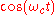 is the carrier wave,
is the carrier wave, 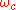 is the carrier frequency – one is changing the amplitude of a carrier wave to encode the signal, hence amplitude modulation.
is the carrier frequency – one is changing the amplitude of a carrier wave to encode the signal, hence amplitude modulation.
In general one could also change the phase of the carrier wave, as in phase modulation
– there is a dimension of phase that is not being used. In fact, one can encode another signal that is 90° out of phase by using a sine wave, as in: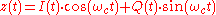
this 90° (the angle of a rectangle, or a 1/4 turn) is why it is called "quadrature" modulation, and the symbols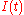 and
and 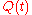 indicate the "in-phase" signal and "quadrature" signal.
indicate the "in-phase" signal and "quadrature" signal.
In terms of Euler's formula
, amplitude modulation encodes a 1-dimensional real signal, while quadrature modulation encodes a 2-dimensional complex signal. This viewpoint, that a wave of a given frequency can encode 2 dimensions of data, is elaborated in Fourier analysis, and is the principle that quadrature modulation exploits.
amplitude modulation encodes a 1-dimensional real signal, while quadrature modulation encodes a 2-dimensional complex signal. This viewpoint, that a wave of a given frequency can encode 2 dimensions of data, is elaborated in Fourier analysis, and is the principle that quadrature modulation exploits.
An amplitude-modulated signal is self-clocking
– it has zero-crossings at a regular frequency as a clock pulse. A quadrature-modulated signal, by contrast, has no such pulse, and thus sender and receiver must share a clock or otherwise send a clock signal – if the clocks drift by phase φ, which corresponds to rotation by φ in the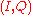 plane, then the I and Q signal bleed into each other, yielding crosstalk.
plane, then the I and Q signal bleed into each other, yielding crosstalk.
In this context, the clock signal is called a "phase reference" – in NTSC
, which uses quadrature amplitude modulation
, this is conveyed by the color burst, a synchronization signal.
By contrast, in polar modulation, clock drift simply degrades the phase-modulated signal.
, and was developed earlier, in the 1874 quadruplex telegraph
by Thomas Edison
.
Examples include Quadrature amplitude modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation is both an analog and a digital modulation scheme. It conveys two analog message signals, or two digital bit streams, by changing the amplitudes of two carrier waves, using the amplitude-shift keying digital modulation scheme or amplitude modulation analog...
, Phase-shift keying
Phase-shift keying
Phase-shift keying is a digital modulation scheme that conveys data by changing, or modulating, the phase of a reference signal ....
, and Minimum-shift keying
Minimum-shift keying
In digital modulation, minimum-shift keying is a type of continuous-phase frequency-shift keying that was developed in the late 1950s and 1960s. Similar to OQPSK, MSK is encoded with bits alternating between quadrature components, with the Q component delayed by half the symbol period. However,...
.
Constellation diagram
Constellation diagram
A constellation diagram is a representation of a signal modulated by a digital modulation scheme such as quadrature amplitude modulation or phase-shift keying. It displays the signal as a two-dimensional scatter diagram in the complex plane at symbol sampling instants...
s are used to examine the modulation in the 2-D signal space.
Explanation
Sending a signal by amplitude modulationAmplitude modulation
Amplitude modulation is a technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting information via a radio carrier wave. AM works by varying the strength of the transmitted signal in relation to the information being sent...
consists of sending the function
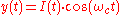
where
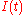 is the signal to encode and
is the signal to encode and 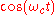 is the carrier wave,
is the carrier wave, 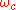 is the carrier frequency – one is changing the amplitude of a carrier wave to encode the signal, hence amplitude modulation.
is the carrier frequency – one is changing the amplitude of a carrier wave to encode the signal, hence amplitude modulation.In general one could also change the phase of the carrier wave, as in phase modulation
Phase modulation
Phase modulation is a form of modulation that represents information as variations in the instantaneous phase of a carrier wave.Unlike its more popular counterpart, frequency modulation , PM is not very widely used for radio transmissions...
– there is a dimension of phase that is not being used. In fact, one can encode another signal that is 90° out of phase by using a sine wave, as in:
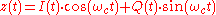
this 90° (the angle of a rectangle, or a 1/4 turn) is why it is called "quadrature" modulation, and the symbols
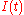 and
and 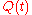 indicate the "in-phase" signal and "quadrature" signal.
indicate the "in-phase" signal and "quadrature" signal.In terms of Euler's formula
Euler's formula
Euler's formula, named after Leonhard Euler, is a mathematical formula in complex analysis that establishes the deep relationship between the trigonometric functions and the complex exponential function...
,
 amplitude modulation encodes a 1-dimensional real signal, while quadrature modulation encodes a 2-dimensional complex signal. This viewpoint, that a wave of a given frequency can encode 2 dimensions of data, is elaborated in Fourier analysis, and is the principle that quadrature modulation exploits.
amplitude modulation encodes a 1-dimensional real signal, while quadrature modulation encodes a 2-dimensional complex signal. This viewpoint, that a wave of a given frequency can encode 2 dimensions of data, is elaborated in Fourier analysis, and is the principle that quadrature modulation exploits.Clocking
The added channel capacity is not costless, however.An amplitude-modulated signal is self-clocking
Self-clocking signal
In telecommunications and electronics, a self-clocking signal is one that can be decoded without the need for a separate clock signal or other source of synchronization...
– it has zero-crossings at a regular frequency as a clock pulse. A quadrature-modulated signal, by contrast, has no such pulse, and thus sender and receiver must share a clock or otherwise send a clock signal – if the clocks drift by phase φ, which corresponds to rotation by φ in the
 plane, then the I and Q signal bleed into each other, yielding crosstalk.
plane, then the I and Q signal bleed into each other, yielding crosstalk.In this context, the clock signal is called a "phase reference" – in NTSC
NTSC
NTSC, named for the National Television System Committee, is the analog television system that is used in most of North America, most of South America , Burma, South Korea, Taiwan, Japan, the Philippines, and some Pacific island nations and territories .Most countries using the NTSC standard, as...
, which uses quadrature amplitude modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation is both an analog and a digital modulation scheme. It conveys two analog message signals, or two digital bit streams, by changing the amplitudes of two carrier waves, using the amplitude-shift keying digital modulation scheme or amplitude modulation analog...
, this is conveyed by the color burst, a synchronization signal.
By contrast, in polar modulation, clock drift simply degrades the phase-modulated signal.
Polar modulation
Quadrature modulates two signals by changing the in-phase and quadrature phase components, corresponding to Cartesian coordinates. By contrast, one can instead consider this to be changing the amplitude and phase of a wave, which corresponds to polar coordinates. The corresponding modulation is called polar modulationPolar modulation
Polar modulation is analogous to quadrature modulation in the same way that polar coordinates are analogous to Cartesian coordinates. Quadrature modulation makes use of Cartesian coordinates, x and y. When considering quadrature modulation, the x axis is called the I axis, and the y axis is...
, and was developed earlier, in the 1874 quadruplex telegraph
Quadruplex telegraph
The Quadruplex telegraph is a type of electrical telegraph which allows a total of four separate signals to be transmitted and received on a single wire at the same time Quadruplex telegraphy thus implements a form of multiplexing.The technology was invented by American inventor Thomas Edison, who...
by Thomas Edison
Thomas Edison
Thomas Alva Edison was an American inventor and businessman. He developed many devices that greatly influenced life around the world, including the phonograph, the motion picture camera, and a long-lasting, practical electric light bulb. In addition, he created the world’s first industrial...
.

