
Quality of life (healthcare)
Encyclopedia

Social
The term social refers to a characteristic of living organisms...
, and physical
Physical
Physical may refer to:*Body, the physical structure of an organism**Human body, the physical structure of a human*Physical abuse, abuse involving contact intended to cause feelings of intimidation, injury, or other physical suffering or bodily harm...
aspects of the individual’s life. However, when the phrase is used in reference to medicine
Medicine
Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness....
and healthcare as Health Related Quality of Life, it refers to how the individual’s wellbeing may be impacted over time by a disease
Disease
A disease is an abnormal condition affecting the body of an organism. It is often construed to be a medical condition associated with specific symptoms and signs. It may be caused by external factors, such as infectious disease, or it may be caused by internal dysfunctions, such as autoimmune...
, a disability
Disability
A disability may be physical, cognitive, mental, sensory, emotional, developmental or some combination of these.Many people would rather be referred to as a person with a disability instead of handicapped...
, or a disorder
Disorder
Disorder may refer to :* Chaos, unpredictability and in the metaphysical sense, it is the opposite of law and order* Civil disorder, one or more forms of disturbance caused by a group of people...
.
Ascertaining Health Related Quality of Life
Initial HRQoL measures referred to simple assessments of physical abilities by an external rater (e.g.: patient is able to get up, eat and drink, take care of personal hygiene without any help by others), or even to a single measurement (e.g. the angle to which a limb could be flexed).The current concept of HRQoL acknowledges that subjects put their actual situation in relation to their personal expectation. The latter can vary over time, and react to external influences such as length and severity of illness, family support, etc. As with any situation involving multiple perspectives, patients' and physicians' rating of the same objective situation have been found to differ significantly. Consequently, HRQoL is now usually assessed using patient questionnaires. These are often multidimensional and cover physical
Physical
Physical may refer to:*Body, the physical structure of an organism**Human body, the physical structure of a human*Physical abuse, abuse involving contact intended to cause feelings of intimidation, injury, or other physical suffering or bodily harm...
, social
Social
The term social refers to a characteristic of living organisms...
, emotional, cognitive, work- or role-related, and possibly spiritual
Spirituality
Spirituality can refer to an ultimate or an alleged immaterial reality; an inner path enabling a person to discover the essence of his/her being; or the “deepest values and meanings by which people live.” Spiritual practices, including meditation, prayer and contemplation, are intended to develop...
aspects as well as a wide variety of disease related symptoms, therapy induced side effects, and even the financial impact of medical conditions. Although often used interchangeably with the measurement of health status, both HRQoL and health status measure different concepts.
Similar to other psychometric
Psychometrics
Psychometrics is the field of study concerned with the theory and technique of psychological measurement, which includes the measurement of knowledge, abilities, attitudes, personality traits, and educational measurement...
assessment tools, HRQoL questionnaires should meet certain quality criteria, most importantly with regard to their reliability and validity. As such, hundreds of validated HRQoL questionnaires have been developed to suit the needs of various illnesses. The questionnaires can be generalized into two categories:
- Generic instruments (e.g. SF-36, Short-Form with 36 questions)
- Disease or Disorder specific instruments (e.g. the LC -13 Lung Cancer module from the EORTC Quality of Life questionnaire library, or the Hospital Anxiety and Depression ScaleHospital Anxiety and Depression ScaleHADS is commonly used by doctors to determine the levels of anxiety and depression that a patient is experiencing. It is a 10 point scale such that if a patient scores the lowest possible value of 1 they are considered to possibly need clinical psychiatric treatment...
(HADS) ).
Frequent Statistical Anomalies
It is not considered uncommon for there to be some statistical anomalies during data analysis. Some of the more frequently seen in HRQoL analysis are the ceiling effectCeiling effect
The term ceiling effect has two distinct meanings, referring to the level at which an independent variable no longer has an effect on a dependent variable, or to the level above which variance in an independent variable is no longer measured or estimated...
, the floor effect, and response shift bias.
The ceiling effect refers to how patients who start with a higher quality of life than the average patient do not have much room for improvement when treated. The opposite of this is the floor effect, which refers to patients who have a lower quality of life average have much more room for improvement. Consequentially, if the spectrum of quality of life before treatment is too unbalanced, there is a greater potential for skewing the end results, creating possibility for incorrectly portraying a treatment's effectiveness or lack thereof.
Response Shift Bias
Response shift bias is an increasing problem within longitudinal studies that rely on patient reported outcomesPatient-reported outcome
A patient-reported outcome or PRO is a questionnaire used in a clinical trial or a clinical setting, where the responses are collected directly from the patient.-Overview:...
. It refers to the potential of a subject’s views, values, or expectations changing over the course of a study, thereby adding an additional factor of change on the end results. Clinicians and healthcare providers must recalibrate surveys over the course of a study to account for Response Shift Bias. The degree of recalibration varies due to factors based on the individual area of investigation and length of study.
Frequently Used HRQoL Measures
Here are some examples of frequently used HRQoL questionnaires:- Healthy Day Measures: A questionnaire with four base questions and ten optional questions used by the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
- Short-Form Health SurveySF-36The Short Form Health Survey is a survey of patient health. The SF-36 is a measure of health status and is commonly used in health economics as a variable in the quality-adjusted life year calculation to determine the cost-effectiveness of a health treatment. The original SF-36 came out from the...
: One example of a widely used questionnaire assessing physical, social, and mental HRQoL, used in clinical trials. Suitable for pharmacoeconomicPharmacoeconomicsPharmacoeconomics refers to the scientific discipline that compares the value of one pharmaceutical drug or drug therapy to another. It is a sub-discipline of health economics. A pharmacoeconomic study evaluates the cost and effects of a pharmaceutical product...
analysis, benefiting healthcare rationing. - Manchester Short Assessment of Quality of Life: 16-item questionnaire for use in psychiatric populations.
- EQ-5DEQ-5DEQ-5D is a standardised measure of health status developed by the EuroQol Group in order to provide a simple, generic measure of health for clinical and economic appraisal...
a simple quality of life questionnaire. - WHO-Quality of life BREF: A general Quality of life survey validated for several countries.
What is the HRQoL used for?
A variety of validated surveys exist for healthcare providers to use for measuring a patient’s Health Related Quality of Life. The results are then used to help determine treatmentTherapy
This is a list of types of therapy .* Adventure therapy* Animal-assisted therapy* Aquatic therapy* Aromatherapy* Art and dementia* Art therapy* Authentic Movement* Behavioral therapy* Bibliotherapy* Buteyko Method* Chemotherapy...
options for the patient based on past results from other patients.
When it is used as a longitudinal study
Longitudinal study
A longitudinal study is a correlational research study that involves repeated observations of the same variables over long periods of time — often many decades. It is a type of observational study. Longitudinal studies are often used in psychology to study developmental trends across the...
device that surveys patients before, during, and after treatment, it can help health care providers determine which treatment plan is the best option, thereby improving healthcare through an evolutionary process.
Why is it important?
There is a growing field of research concerned with developing, evaluating, and applying quality of life measures within health related research (e.g. within randomized controlled studiesRandomized controlled trial
A randomized controlled trial is a type of scientific experiment - a form of clinical trial - most commonly used in testing the safety and efficacy or effectiveness of healthcare services or health technologies A randomized controlled trial (RCT) is a type of scientific experiment - a form of...
, especially in relation to Health Services Research
Health services research
Health services research is a multidisciplinary scientific field that examines how people get access to health care practitioners and health care services, how much care costs, and what happens to patients as a result of this care...
. Well-executed HRQoL research informs those tasked with health rationing or anyone involved in the decision-making process of agencies such as the Food and Drug Administration
Food and Drug Administration
The Food and Drug Administration is an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, one of the United States federal executive departments...
, European Medicines Agency
European Medicines Agency
The European Medicines Agency is a European agency for the evaluation of medicinal products. From 1995 to 2004, the European Medicines Agency was known as European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products.Roughly parallel to the U.S...
or National Institute for Clinical Excellence. Additionally, HRQoL research may be used as the final step in clinical trials of experimental therapies.
The understanding of Quality of Life is recognized as an increasingly important healthcare topic because the relationship between cost and value raises complex problems, often with high emotional attachment because of the potential impact on human life. For instance, healthcare providers must refer to cost-benefit analysis
Cost-benefit analysis
Cost–benefit analysis , sometimes called benefit–cost analysis , is a systematic process for calculating and comparing benefits and costs of a project for two purposes: to determine if it is a sound investment , to see how it compares with alternate projects...
to make economic decisions about access to expensive drugs that may prolong life by short amount of time and/or provide a minimal increase to quality of life. Additionally, these treatment drugs must be weighed against the cost of alternative treatments or preventative medicine. In the case of chronic and/or terminal illness where no effective cure is available, an emphasis is placed on improving HRQoL through interventions such as symptom management, adaptive technology, and palliative care
Palliative care
Palliative care is a specialized area of healthcare that focuses on relieving and preventing the suffering of patients...
.
Future Implications of HRQoL
The Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is using their HRQoL survey, Healthy Day Measures, as part of research to identify health disparities, track population trends, and build broad coalitions around a measure of population health. This information can then be used by multiple levels of government or other officials to "increase quality and years of life" and to "eliminate health disparaties" for equal opportunity.Research Pertaining to HRQoL
Research revolving around Health Related Quality of Life is extremely important because of the implications that it can have on current and future treatments and health protocols. Thereby, validated HRQoL questionnaires can become an integral part of clinical trials in determining the trial drugs' value in a cost-benefit analysis.The Remarkable .5 of Standard Deviation
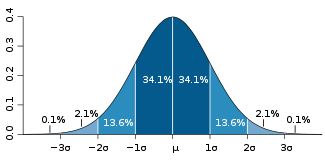
Standard deviation
Standard deviation is a widely used measure of variability or diversity used in statistics and probability theory. It shows how much variation or "dispersion" there is from the average...
. Norman et al. theorized that this is due to the limited human discrimination ability as identified by George A. Miller
George A. Miller
George Armitage Miller is the author of one of the most highly cited papers in psychology, "The Magical Number Seven, Plus or Minus Two" published in 1956 in Psychological Review...
in 1956. Utilizing the Magic Number of 7 ± 2
The Magical Number Seven, Plus or Minus Two
"The Magical Number Seven, Plus or Minus Two: Some Limits on Our Capacity for Processing Information" is one of the most highly cited papers in psychology. It was published in 1956 by the cognitive psychologist George A. Miller of Princeton University's Department of Psychology in Psychological...
, Miller theorized that when the scale on a survey extends beyond 7 ± 2, humans fail to be consistent and lose ability to differentiate individual steps on the scale because of channel capacity
Channel capacity
In electrical engineering, computer science and information theory, channel capacity is the tightest upper bound on the amount of information that can be reliably transmitted over a communications channel...
.
Norman et al. proposed HRQoL surveys use a half standard deviation as the statistically significant benefit of a treatment instead of calculating survey-specific “minimally important differences", which are the supposed real-life improvements reported by the subjects. In other words, Norman et al. proposed all HRQoL survey scales be set to a half standard deviation instead of calculating a scale for each survey validation study where the steps are referred to as "minimally important differences".
Ethics for HRQoL
The quality of life ethic refers to an ethical principle that uses assessments of the quality of life that a person could potentially experience as a foundation for making decisions about the continuation or termination of life. It is often used in contrast to or in opposition to the sanctity of life ethicInviolability
In religion and ethics, inviolability or sanctity of life is a principle of implied protection regarding aspects of sentient life which are said to be holy, sacred, or otherwise of such value that they are not to be violated...
.
See also
- Health services researchHealth services researchHealth services research is a multidisciplinary scientific field that examines how people get access to health care practitioners and health care services, how much care costs, and what happens to patients as a result of this care...
- Medical lawMedical lawMedical law is the branch of law which concerns the prerogatives and responsibilities of medical professionals and the rights of the patient. It should not be confused with medical jurisprudence, which is a branch of medicine, rather than a branch of law....
- Patient-reported outcomePatient-reported outcomeA patient-reported outcome or PRO is a questionnaire used in a clinical trial or a clinical setting, where the responses are collected directly from the patient.-Overview:...
- PharmacoeconomicsPharmacoeconomicsPharmacoeconomics refers to the scientific discipline that compares the value of one pharmaceutical drug or drug therapy to another. It is a sub-discipline of health economics. A pharmacoeconomic study evaluates the cost and effects of a pharmaceutical product...
- medical ethicsMedical ethicsMedical ethics is a system of moral principles that apply values and judgments to the practice of medicine. As a scholarly discipline, medical ethics encompasses its practical application in clinical settings as well as work on its history, philosophy, theology, and sociology.-History:Historically,...
External links
- ProQolid (Patient-Reported Outcome & Quality of Life Instruments Database)
- Mapi Research Trust ("Non-profit organization advancing the art & the use of scientific approaches to Patient-Reported Outcome (PRO) measures")
- Quality-of-Life-Recorder (Project to bring QoL measurement to routine practice. Platform & library of electronic questionnaires, Shareware/Freeware)
- The International Society for Quality of Life
- Health and Quality of Life Outcomes
- http://www.healthmeasurement.org/

