
Quartering (heraldry)
Encyclopedia
Heraldry
Heraldry is the profession, study, or art of creating, granting, and blazoning arms and ruling on questions of rank or protocol, as exercised by an officer of arms. Heraldry comes from Anglo-Norman herald, from the Germanic compound harja-waldaz, "army commander"...
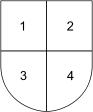
is a method of joining several different coats of arms
Coat of arms
A coat of arms is a unique heraldic design on a shield or escutcheon or on a surcoat or tabard used to cover and protect armour and to identify the wearer. Thus the term is often stated as "coat-armour", because it was anciently displayed on the front of a coat of cloth...
together in one shield by dividing the shield into equal parts and placing different coats of arms in each division.
Typically, a quartering consists of a division into four equal parts, two above and two below (party per cross). An example is the Sovereign Arms of the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, as used outside Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
, which consists of four quarterings, displaying the Arms of England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
, Scotland and Ireland
Ireland
Ireland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
, with the coat for England repeated at the end. (In the royal arms as used in Scotland, the Scottish quartering appears in the first and fourth quarters and the English one second.)
However, in most traditions there is no limit on the number of divisions allowed, and the records of the College of Arms
College of Arms
The College of Arms, or Heralds’ College, is an office regulating heraldry and granting new armorial bearings for England, Wales and Northern Ireland...
include a shield of 323 quarterings for the family of Lloyd of Stockton. These 323 quarterings include numerous repeated attributed arms
Attributed arms
Attributed arms are coats of arms given to legendary figures, or to notable persons from times before the rise of heraldry. Beginning in the 12th century, imaginary arms were assigned to the knights of the Round Table, and soon arms were given to biblical figures, to Roman and Greek heroes, and to...
assigned to Welsh chieftains from the 9th century or earlier.
Another example of a shield of many quarterings is the coat of arms of the Powys-Lybbe family, which contains 64 quarterings. Different rules apply in Scottish heraldry
Scottish heraldry
Heraldry in Scotland, while broadly similar to that practised in England and elsewhere in western Europe, has its own distinctive features. Its heraldic executive is separate from that of the rest of the United Kingdom.-Executive:...
, and may well apply in other jurisdictions like Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
and South Africa
South Africa
The Republic of South Africa is a country in southern Africa. Located at the southern tip of Africa, it is divided into nine provinces, with of coastline on the Atlantic and Indian oceans...
.
The arms of the Queen of the United Kingdom
Monarchy of the United Kingdom
The monarchy of the United Kingdom is the constitutional monarchy of the United Kingdom and its overseas territories. The present monarch, Queen Elizabeth II, has reigned since 6 February 1952. She and her immediate family undertake various official, ceremonial and representational duties...
are arms of dominion, which join together the arms of the ex-kingdoms now part of her kingdom. However, the vast majority of quarterly coats of arms display arms which are claimed by descent: in other words, they join together coats of arms of the ancestors of the bearer of the arms.
Strict rules apply, both as to what arms may be displayed by way of quarterings, and the order in which they may be displayed. Men and women are always entitled to display the arms of their paternal line but are not usually entitled to display by way of quartering the arms of families from whom there is descent only through a female line (for example, the arms of a mother or grandmother or great-grandmother). An exception is made, however, if the female who breaks the male line of descent is a heraldic heiress. A heraldic heiress
Heraldic heiress
In English heraldry an heraldic heiress is a daughter of deceased man who was entitled to a coat of arms and who carries forward the right to those arms for the benefit of her future male descendants...
is a woman who has no brothers, or whose brothers have died without issue. Such a woman is entitled to transmit her father's arms to her own children, who add them as a quartering. If her father was himself entitled to one or more quarterings, these will pass to his daughters' children as quarterings as well. Quarterings are displayed in the order in which they are acquired by a family by marriage, starting with those acquired by the earliest marriage to bring in quarterings. It is permissible to omit quarterings, but if a quartering was brought in by a later quartering, it is essential to show the whole chain of quarterings leading to the quartering displayed, or else to omit the chain altogether.
The larger the number of quarterings, the smaller the space available for each coat of arms, so that most families entitled to many quarterings make a selection of those they ordinarily use. The Duke of Norfolk
Duke of Norfolk
The Duke of Norfolk is the premier duke in the peerage of England, and also, as Earl of Arundel, the premier earl. The Duke of Norfolk is, moreover, the Earl Marshal and hereditary Marshal of England. The seat of the Duke of Norfolk is Arundel Castle in Sussex, although the title refers to the...
, for example, uses only four quarterings, although he is entitled to many more. In Scotland in some cases the plain unquartered coat is the more prized, as entitlement to its use can indicate who is chief of the name and arms and holds the headship of a clan. For example, Flora Fraser, Lady Saltoun of Abernethy
Flora Fraser, 21st Lady Saltoun
Marjorie Flora Fraser, 21st Lady SaltounIt has recently been determined that Margaret Abernethy succeeded her brother, Alexander Abernethy, 9th Lord Saltoun in 1668, but only survived him by about 6 weeks and had not been counted in the title's numbering. This new information has resulted in the...
has arms as chief of Fraser
Frasers of Philorth
The Frasers of Philorth are a Scottish lowland family, originally from the Anjou region of France. Their family seat is in Sauchen, Aberdeenshire, Scotland. Since the time of Alexander Fraser, 11th Lord Saltoun, the heads of the Philorth family are the Lords Saltoun. The current head of the...
— the plain coat of 'azure, three fraises argent' — and a 'private' quartered coat. The Powys-Lybbe family appear, likewise, to usually use only the quarterings of Powys and Lybbe. However these are not true quarterings as the arms were changed in 1907 to be an impartible design of the two arms; the personal arms are precisely this design, with no quarterings despite its appearance. (If this were a quartering the following would apply: when only two different coats of arms are shown, each one is repeated twice in order to fill up the minimum number of four quarterings on such a display.) Prior to the 1907 change, the family did quarter their arms with Lybbe but with the Powys arms in the top left quarter as these were the family arms; the new design has Lybbe in the top left as Lybbe is the last part of the name.

