
Quinhydrone electrode
Encyclopedia
The quinhydrone electrode is a type of redox
electrode
which can be used to measure the hydrogen ion concentration (pH
) of a solution in a chemical experiment. It provides an alternative to the commonly used glass electrode
in a pH meter
.
The electrode consists of an inert metal electrode (usually a platinum
wire) in contact with quinhydrone crystals and a water-based solution. Quinhydrone is slightly soluble in water, dissolving to form a mixture of two substances, quinone and hydroquinone, with the two substances present at equal concentration. Each one of the two substances can easily be oxidised or reduced to the other.
The potential at the inert electrode depends on the ratio of the activity
of two substances (quinone
-hydroquinone
), and also the hydrogen ion concentration. The electrode half-reaction is:
Hydroquinone ↔ Quinone + 2H+ +2e-
Because the electrode half-reaction
involves hydrogen ions, the electrode potential
depends on the activity of hydrogen ions. From the Nernst equation
: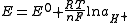
For practical pH measurement, a second pH independent reference electrode (such as a silver chloride electrode
) is also used. This reference electrode does not respond to the pH. The difference between the potential of the two electrodes depends (primarily) on the activity of H+ in the solution. It is this potential difference which is measured and converted to a pH
value.
The quinhydrone electrode is not reliable above pH 8. It is also unreliable in the presence of strong oxidising or reducing agents, which would disturb the equilibrium between hydroquinone and quinone. It is also subject to errors in solutions containing proteins or high concentrations of salts.
Other electrodes commonly used for measuring pH are the glass electrode
, the hydrogen electrode, the antimony – antimony oxide electrode, and the ion-sensitive field effect transistor ISFET
electrode.
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
electrode
Electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit...
which can be used to measure the hydrogen ion concentration (pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
) of a solution in a chemical experiment. It provides an alternative to the commonly used glass electrode
Glass electrode
A glass electrode is a type of ion-selective electrode made of a doped glass membrane that is sensitive to a specific ion. It is an important part of the instrumentation for chemical analysis and physico-chemical studies. In modern practice, widely used membranous ion-selective electrodes are part...
in a pH meter
PH meter
A pH meter is an electronic instrument used for measuring the pH of a liquid...
.
The electrode consists of an inert metal electrode (usually a platinum
Platinum
Platinum is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Pt and an atomic number of 78. Its name is derived from the Spanish term platina del Pinto, which is literally translated into "little silver of the Pinto River." It is a dense, malleable, ductile, precious, gray-white transition metal...
wire) in contact with quinhydrone crystals and a water-based solution. Quinhydrone is slightly soluble in water, dissolving to form a mixture of two substances, quinone and hydroquinone, with the two substances present at equal concentration. Each one of the two substances can easily be oxidised or reduced to the other.
The potential at the inert electrode depends on the ratio of the activity
Activity (chemistry)
In chemical thermodynamics, activity is a measure of the “effective concentration” of a species in a mixture, meaning that the species' chemical potential depends on the activity of a real solution in the same way that it would depend on concentration for an ideal solution.By convention, activity...
of two substances (quinone
Quinone
A quinone is a class of organic compounds that are formally "derived from aromatic compounds [such as benzene or naphthalene] by conversion of an even number of –CH= groups into –C– groups with any necessary rearrangement of double bonds," resulting in "a fully conjugated cyclic dione structure."...
-hydroquinone
Hydroquinone
Hydroquinone, also benzene-1,4-diol or quinol, is an aromatic organic compound that is a type of phenol, having the chemical formula C6H42. Its chemical structure, shown in the table at right, has two hydroxyl groups bonded to a benzene ring in a para position. It is a white granular solid...
), and also the hydrogen ion concentration. The electrode half-reaction is:
Hydroquinone ↔ Quinone + 2H+ +2e-
Because the electrode half-reaction
Half-reaction
A half reaction is either the oxidation or reduction reaction component of a redox reaction. A half reaction is obtained by considering the change in oxidation states of individual substances involved in the redox reaction.-Example:...
involves hydrogen ions, the electrode potential
Electrode potential
Electrode potential, E, in electrochemistry, according to an IUPAC definition, is the electromotive force of a cell built of two electrodes:* on the left-hand side is the standard hydrogen electrode, and...
depends on the activity of hydrogen ions. From the Nernst equation
Nernst equation
In electrochemistry, the Nernst equation is an equation that can be used to determine the equilibrium reduction potential of a half-cell in an electrochemical cell. It can also be used to determine the total voltage for a full electrochemical cell...
:
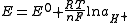
For practical pH measurement, a second pH independent reference electrode (such as a silver chloride electrode
Silver chloride electrode
A silver chloride electrode is a type of reference electrode, commonly used in electrochemical measurements. For example, it is usually the internal reference electrode in pH meters...
) is also used. This reference electrode does not respond to the pH. The difference between the potential of the two electrodes depends (primarily) on the activity of H+ in the solution. It is this potential difference which is measured and converted to a pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
value.
The quinhydrone electrode is not reliable above pH 8. It is also unreliable in the presence of strong oxidising or reducing agents, which would disturb the equilibrium between hydroquinone and quinone. It is also subject to errors in solutions containing proteins or high concentrations of salts.
Other electrodes commonly used for measuring pH are the glass electrode
Glass electrode
A glass electrode is a type of ion-selective electrode made of a doped glass membrane that is sensitive to a specific ion. It is an important part of the instrumentation for chemical analysis and physico-chemical studies. In modern practice, widely used membranous ion-selective electrodes are part...
, the hydrogen electrode, the antimony – antimony oxide electrode, and the ion-sensitive field effect transistor ISFET
ISFET
ISFET pH electrode also redirects here.An ISFET is an ion-sensitive field-effect transistor used for measuring ion concentrations in solution; when the ion concentration changes, the current through the transistor will change accordingly. Here, the solution is used as the gate electrode...
electrode.

