
Reaction quotient
Encyclopedia
In chemistry
, a reaction quotient: Qr is a function of the activities
or concentration
s of the chemical species involved in a chemical reaction. In the special case that the reaction is at equilibrium
the reaction quotient is equal to the equilibrium constant.
A general chemical reaction in which α moles of a reactant A and β moles of a reactant B react to give σ moles of a product S and τ moles of a product T can be written as
The reaction is written as an equilibrium even though in many cases it may appear to have gone to completion. When a mixture of A and B is made up and the reaction is allowed to occur, the reaction quotient, Qr, is defined as :
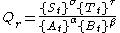
where {Xt} denotes the instantaneous activity
of a species X at time, t.
A compact general definition is (where Пj is the product across all j-indexed variables, and idem for Пi):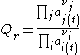
where the numerator is a product of reaction product activities, a j, each raised to the power of a stoichiometric coefficient, ν j, and the denominator is a similar product of reactant activities. All activities refer to a time t.
As the reaction proceeds (assuming that there is no energy barrier to the reaction) with the passage of time the species' activities and hence the reaction quotient change. Eventually the activities become constant and the mixture is then said to be at equilibrium. An equilibrium constant, K, can be expressed symbolically as
though equilibrium will be effectively reached in a finite time in most reactions.
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, a reaction quotient: Qr is a function of the activities
Activity (chemistry)
In chemical thermodynamics, activity is a measure of the “effective concentration” of a species in a mixture, meaning that the species' chemical potential depends on the activity of a real solution in the same way that it would depend on concentration for an ideal solution.By convention, activity...
or concentration
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
s of the chemical species involved in a chemical reaction. In the special case that the reaction is at equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which the concentrations of the reactants and products have not yet changed with time. It occurs only in reversible reactions, and not in irreversible reactions. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same...
the reaction quotient is equal to the equilibrium constant.
A general chemical reaction in which α moles of a reactant A and β moles of a reactant B react to give σ moles of a product S and τ moles of a product T can be written as
- αA + βB σS + τT
The reaction is written as an equilibrium even though in many cases it may appear to have gone to completion. When a mixture of A and B is made up and the reaction is allowed to occur, the reaction quotient, Qr, is defined as :
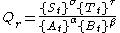
where {Xt} denotes the instantaneous activity
Activity (chemistry)
In chemical thermodynamics, activity is a measure of the “effective concentration” of a species in a mixture, meaning that the species' chemical potential depends on the activity of a real solution in the same way that it would depend on concentration for an ideal solution.By convention, activity...
of a species X at time, t.
A compact general definition is (where Пj is the product across all j-indexed variables, and idem for Пi):
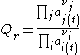
where the numerator is a product of reaction product activities, a j, each raised to the power of a stoichiometric coefficient, ν j, and the denominator is a similar product of reactant activities. All activities refer to a time t.
As the reaction proceeds (assuming that there is no energy barrier to the reaction) with the passage of time the species' activities and hence the reaction quotient change. Eventually the activities become constant and the mixture is then said to be at equilibrium. An equilibrium constant, K, can be expressed symbolically as
- K = Qr (t=∞)
though equilibrium will be effectively reached in a finite time in most reactions.

