
Reaction rate constant
Encyclopedia
In chemical kinetics
a reaction rate constant k or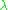 quantifies the speed of a chemical reaction
quantifies the speed of a chemical reaction
.
For a chemical reaction
where substance A and B are reacting to produce C, the reaction rate
has the form:
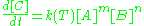
k(T) is the reaction rate constant that depends on temperature.
[C] is the concentration
of substance C in moles
per volume of solution assuming the reaction is taking place throughout the volume of the solution (for a reaction taking place at a boundary it would denote something like moles of C per area).
The exponents m and n are called orders and depend on the reaction mechanism
. They can be determined experimentally.
A single-step reaction can also be written as
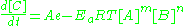
Ea is the activation energy
and R is the Gas constant
. Since at temperature
T the molecules have energies according to a Boltzmann distribution
, one can expect the proportion of collisions with energy greater than Ea to vary with e-Ea/RT. A is the pre-exponential factor
or frequency factor.
The Arrhenius equation
gives the quantitative basis of the relationship between the activation energy
and the reaction rate
at which a reaction proceeds.
:
. First-principle based models should be used for such calculation. It can be done with the help of computer simulation
software.
Chemical kinetics
Chemical kinetics, also known as reaction kinetics, is the study of rates of chemical processes. Chemical kinetics includes investigations of how different experimental conditions can influence the speed of a chemical reaction and yield information about the reaction's mechanism and transition...
a reaction rate constant k or
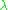 quantifies the speed of a chemical reaction
quantifies the speed of a chemical reactionChemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
.
For a chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
where substance A and B are reacting to produce C, the reaction rate
Reaction rate
The reaction rate or speed of reaction for a reactant or product in a particular reaction is intuitively defined as how fast or slow a reaction takes place...
has the form:
- Reaction: A + B → C
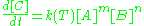
k(T) is the reaction rate constant that depends on temperature.
[C] is the concentration
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
of substance C in moles
Mole (unit)
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
per volume of solution assuming the reaction is taking place throughout the volume of the solution (for a reaction taking place at a boundary it would denote something like moles of C per area).
The exponents m and n are called orders and depend on the reaction mechanism
Reaction mechanism
In chemistry, a reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical change occurs.Although only the net chemical change is directly observable for most chemical reactions, experiments can often be designed that suggest the possible sequence of steps in...
. They can be determined experimentally.
A single-step reaction can also be written as
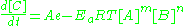
Ea is the activation energy
Activation energy
In chemistry, activation energy is a term introduced in 1889 by the Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius that is defined as the energy that must be overcome in order for a chemical reaction to occur. Activation energy may also be defined as the minimum energy required to start a chemical reaction...
and R is the Gas constant
Gas constant
The gas constant is a physical constant which is featured in many fundamental equations in the physical sciences, such as the ideal gas law and the Nernst equation. It is equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, but expressed in units of energy The gas constant (also known as the molar, universal,...
. Since at temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
T the molecules have energies according to a Boltzmann distribution
Boltzmann distribution
In chemistry, physics, and mathematics, the Boltzmann distribution is a certain distribution function or probability measure for the distribution of the states of a system. It underpins the concept of the canonical ensemble, providing its underlying distribution...
, one can expect the proportion of collisions with energy greater than Ea to vary with e-Ea/RT. A is the pre-exponential factor
Pre-exponential factor
In chemical kinetics, the preexponential factor or A factor is the pre-exponential constant in the Arrhenius equation, an empirical relationship between temperature and rate coefficient...
or frequency factor.
The Arrhenius equation
Arrhenius equation
The Arrhenius equation is a simple, but remarkably accurate, formula for the temperature dependence of the reaction rate constant, and therefore, rate of a chemical reaction. The equation was first proposed by the Dutch chemist J. H. van 't Hoff in 1884; five years later in 1889, the Swedish...
gives the quantitative basis of the relationship between the activation energy
Activation energy
In chemistry, activation energy is a term introduced in 1889 by the Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius that is defined as the energy that must be overcome in order for a chemical reaction to occur. Activation energy may also be defined as the minimum energy required to start a chemical reaction...
and the reaction rate
Reaction rate
The reaction rate or speed of reaction for a reactant or product in a particular reaction is intuitively defined as how fast or slow a reaction takes place...
at which a reaction proceeds.
Units
The units of the rate coefficient depend on the global order of reactionOrder of reaction
In chemical kinetics, the order of reaction with respect to certain reactant, is defined as the power to which its concentration term in the rate equation is raised .For example, given a chemical reaction 2A + B → C with a rate equation...
:
- For order n, the rate coefficient has units of mol1-n·Ln-1·s-1
- For order zero, the rate coefficient has units of mol·L-1·s-1
- For order one, the rate coefficient has units of s-1
- For order two, the rate coefficient has units of L·mol-1·s-1
Plasma and gases
Calculation of rate constants of the processes of generation and relaxation of electronically and vibrationally excited particles are of great importance. It is used for example, in the computer simulation of processes in plasma chemistry or microelectronicsMicroelectronics
Microelectronics is a subfield of electronics. As the name suggests, microelectronics relates to the study and manufacture of very small electronic components. Usually, but not always, this means micrometre-scale or smaller,. These devices are made from semiconductors...
. First-principle based models should be used for such calculation. It can be done with the help of computer simulation
Computer simulation
A computer simulation, a computer model, or a computational model is a computer program, or network of computers, that attempts to simulate an abstract model of a particular system...
software.

