
Reality structure
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, a reality structure on a complex vector space
V is a decomposition of V into two real subspaces, called the real and imaginary parts of V: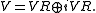
Here VR is a real subspace of V, i.e. a subspace of V considered as a vector space
over the real number
s. If V has complex dimension
n (real dimension 2n), then VR must have real dimension n.
The standard reality structure on the vector space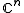 is the decomposition
is the decomposition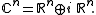
In the presence of a reality structure, every vector in V has a real part and an imaginary part, each of which is a vector in VR: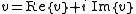
In this case, the complex conjugate
of a vector v is defined as follows: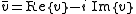
This map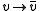 is an antilinear involution, i.e.
is an antilinear involution, i.e.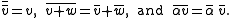
Conversely, given an antilinear involution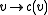 on a complex vector space V, it is possible to define a reality structure on V as follows. Let
on a complex vector space V, it is possible to define a reality structure on V as follows. Let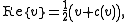
and define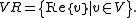
Then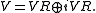
This is actually the decomposition of V as the eigenspaces of the real linear operator c. The eigenvalues of c are +1 and −1, with eigenspaces VR and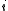 VR, respectively. Typically, the operator c itself, rather than the eigenspace decomposition it entails, is referred to as the reality structure on V.
VR, respectively. Typically, the operator c itself, rather than the eigenspace decomposition it entails, is referred to as the reality structure on V.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, a reality structure on a complex vector space
Complex vector space
A complex vector space is a vector space over the complex numbers. It can also refer to:* a vector space over the real numbers with a linear complex structure...
V is a decomposition of V into two real subspaces, called the real and imaginary parts of V:
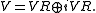
Here VR is a real subspace of V, i.e. a subspace of V considered as a vector space
Vector space
A vector space is a mathematical structure formed by a collection of vectors: objects that may be added together and multiplied by numbers, called scalars in this context. Scalars are often taken to be real numbers, but one may also consider vector spaces with scalar multiplication by complex...
over the real number
Real number
In mathematics, a real number is a value that represents a quantity along a continuum, such as -5 , 4/3 , 8.6 , √2 and π...
s. If V has complex dimension
Complex dimension
In mathematics, complex dimension usually refers to the dimension of a complex manifold M, or complex algebraic variety V. If the complex dimension is d, the real dimension will be 2d...
n (real dimension 2n), then VR must have real dimension n.
The standard reality structure on the vector space
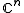 is the decomposition
is the decomposition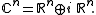
In the presence of a reality structure, every vector in V has a real part and an imaginary part, each of which is a vector in VR:
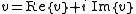
In this case, the complex conjugate
Complex conjugate
In mathematics, complex conjugates are a pair of complex numbers, both having the same real part, but with imaginary parts of equal magnitude and opposite signs...
of a vector v is defined as follows:
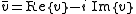
This map
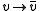 is an antilinear involution, i.e.
is an antilinear involution, i.e.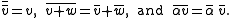
Conversely, given an antilinear involution
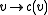 on a complex vector space V, it is possible to define a reality structure on V as follows. Let
on a complex vector space V, it is possible to define a reality structure on V as follows. Let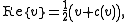
and define
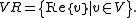
Then
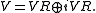
This is actually the decomposition of V as the eigenspaces of the real linear operator c. The eigenvalues of c are +1 and −1, with eigenspaces VR and
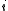 VR, respectively. Typically, the operator c itself, rather than the eigenspace decomposition it entails, is referred to as the reality structure on V.
VR, respectively. Typically, the operator c itself, rather than the eigenspace decomposition it entails, is referred to as the reality structure on V.

