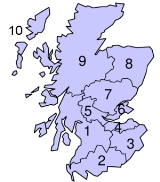
Regions and districts of Scotland
Encyclopedia
The local government areas of Scotland were redefined by the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973
and redefined again by the Local Government etc (Scotland) Act 1994.
The 1973 Act created a system of nine two-tier regions and three islands areas
, and this system completely replaced local government
counties
and burgh
s in 1975. The new regions were generally very different from the counties which had been in use since the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889
. Also, the districts were very different from the subdivisions of counties, also called districts, which had been in use since the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1929
.
published a white paper
titled The Modernization of Local Government in Scotland (Cmnd.2067). This proposed a large decrease in the number of local authorities in the country. There was to be a reduction from thirty-three county councils to between ten and fifteen. At the same time, new "second-tier councils" were proposed, with burghs being merged with the surrounding "landward" rural areas. The minimum population for the areas of these councils was to be 40,000. It was hoped that the reforms could be carried out quickly, with existing authorities agreeing to amalgamation and boundary alterations prior to legislation being passed. The white paper was rejected by the Association of Large Burghs, and by the Scottish Labour Party
. At the 1964 general election
Labour came to power, and the scheme was not pursued. Instead a royal commission
under the chairmanship of Lord Wheatley was appointed in 1966 to enquire into local administration. Wheatley commented that "Our terms of reference are far-reaching: we have a free hand to recommend whatever arrangement of authorities, boundaries and functions seem likely to be right for a long time to come".
The commission's report
was delivered on 25 September 1969, and recommended a two-tier system of 7 regions and 37 districts. The incoming Conservative
government accepted the broad principles of the commission's report in their white paper Reform of Local Government in Scotland (Cmnd. 4583), published in February 1971. The number of regions was increased to 8, and of districts to 49. Also Orkney and Shetland were to become "most-purpose" authorities, separated from the Highland Region. Following consultation, the structure was modified. The Western Isles, which was to have formed four districts of the Highland Region, became an islands area, with the same status as Orkney and Shetland. The number of districts was to remain at 49 in number, but with considerable boundary changes. These were the areas included in the Local Government (Scotland) Bill as introduced to parliament in 1973. Considerable changes were made during the passage of the legislation. Fife
, which was to have been divided between the South-East and East Regions, was to become a region on the same boundaries as the existing county. This increased the number of regions to nine. The number of districts was increased to 53, numerous boundary changes were made and regions and districts renamed.
The first elections to the new district and regional councils were held on 7 May 1974, with the councillors sitting as "shadow authorities" until 16 May 1975 when they came into their powers.
The top tier of local government was the regional council. Services provided at the regional level were those needing greater finance or resources, or best exercised over a wide area. These included police, fire services, consumer protection, education and transport.
Each district had an elected district council. In the case of Aberdeen, Dundee, Edinburgh and Glasgow, the districts had city status
, although this did not confer any additional powers. District councils had responsibility for local services including local planning, housing, libraries and licensing.
now has 32 council areas.
Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973
The Local Government Act 1973 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, that reformed local government in Scotland, on May 16, 1975....
and redefined again by the Local Government etc (Scotland) Act 1994.
The 1973 Act created a system of nine two-tier regions and three islands areas
Islands council areas of Scotland
Between 1975 and 1996 there were three islands council areas of Scotland:* Orkney* Shetland* Western IslesThe islands council areas were the only unitary councils created under the Local Government Act 1973, which came into force in 1975...
, and this system completely replaced local government
Local government of Scotland
Local government in Scotland is organised through 32 unitary authorities designated as Councils which consist of councillors elected every four years by registered voters in each of the council areas....
counties
Counties of Scotland
The counties of Scotland were the principal local government divisions of Scotland until 1975. Scotland's current lieutenancy areas and registration counties are largely based on them. They are often referred to as historic counties....
and burgh
Burgh
A burgh was an autonomous corporate entity in Scotland and Northern England, usually a town. This type of administrative division existed from the 12th century, when King David I created the first royal burghs. Burgh status was broadly analogous to borough status, found in the rest of the United...
s in 1975. The new regions were generally very different from the counties which had been in use since the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889
Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889
The Local Government Act 1889 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which was passed on 26 August 1889. The main effect of the Act was to establish elected county councils in Scotland...
. Also, the districts were very different from the subdivisions of counties, also called districts, which had been in use since the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1929
Local Government (Scotland) Act 1929
The Local Government Act 1929 reorganised local government in Scotland from 1930, introducing joint county councils, large and small burghs and district councils...
.
Background
The reorganisation of local government in Scotland was a matter of political debate from the mid 1960s. In June 1963 the Scottish OfficeScottish Office
The Scottish Office was a department of the United Kingdom Government from 1885 until 1999, exercising a wide range of government functions in relation to Scotland under the control of the Secretary of State for Scotland...
published a white paper
White paper
A white paper is an authoritative report or guide that helps solve a problem. White papers are used to educate readers and help people make decisions, and are often requested and used in politics, policy, business, and technical fields. In commercial use, the term has also come to refer to...
titled The Modernization of Local Government in Scotland (Cmnd.2067). This proposed a large decrease in the number of local authorities in the country. There was to be a reduction from thirty-three county councils to between ten and fifteen. At the same time, new "second-tier councils" were proposed, with burghs being merged with the surrounding "landward" rural areas. The minimum population for the areas of these councils was to be 40,000. It was hoped that the reforms could be carried out quickly, with existing authorities agreeing to amalgamation and boundary alterations prior to legislation being passed. The white paper was rejected by the Association of Large Burghs, and by the Scottish Labour Party
Scottish Labour Party
The Scottish Labour Party is the section of the British Labour Party which operates in Scotland....
. At the 1964 general election
United Kingdom general election, 1964
The United Kingdom general election of 1964 was held on 15 October 1964, more than five years after the preceding election, and thirteen years after the Conservative Party had retaken power...
Labour came to power, and the scheme was not pursued. Instead a royal commission
Royal Commission
In Commonwealth realms and other monarchies a Royal Commission is a major ad-hoc formal public inquiry into a defined issue. They have been held in various countries such as the United Kingdom, Australia, Canada, New Zealand, and Saudi Arabia...
under the chairmanship of Lord Wheatley was appointed in 1966 to enquire into local administration. Wheatley commented that "Our terms of reference are far-reaching: we have a free hand to recommend whatever arrangement of authorities, boundaries and functions seem likely to be right for a long time to come".
The commission's report
Wheatley Report
The Wheatley Report is the name generally given to the report published in September 1969 by the Royal Commission on Local Government in Scotland, or Wheatley Commission, under the chairmanship of Lord Wheatley...
was delivered on 25 September 1969, and recommended a two-tier system of 7 regions and 37 districts. The incoming Conservative
Conservative Party (UK)
The Conservative Party, formally the Conservative and Unionist Party, is a centre-right political party in the United Kingdom that adheres to the philosophies of conservatism and British unionism. It is the largest political party in the UK, and is currently the largest single party in the House...
government accepted the broad principles of the commission's report in their white paper Reform of Local Government in Scotland (Cmnd. 4583), published in February 1971. The number of regions was increased to 8, and of districts to 49. Also Orkney and Shetland were to become "most-purpose" authorities, separated from the Highland Region. Following consultation, the structure was modified. The Western Isles, which was to have formed four districts of the Highland Region, became an islands area, with the same status as Orkney and Shetland. The number of districts was to remain at 49 in number, but with considerable boundary changes. These were the areas included in the Local Government (Scotland) Bill as introduced to parliament in 1973. Considerable changes were made during the passage of the legislation. Fife
Fife
Fife is a council area and former county of Scotland. It is situated between the Firth of Tay and the Firth of Forth, with inland boundaries to Perth and Kinross and Clackmannanshire...
, which was to have been divided between the South-East and East Regions, was to become a region on the same boundaries as the existing county. This increased the number of regions to nine. The number of districts was increased to 53, numerous boundary changes were made and regions and districts renamed.
The first elections to the new district and regional councils were held on 7 May 1974, with the councillors sitting as "shadow authorities" until 16 May 1975 when they came into their powers.
Regions
Regions had a two-tier system of local government, with each region divided into districts, varying from 3 to 19 in number.The top tier of local government was the regional council. Services provided at the regional level were those needing greater finance or resources, or best exercised over a wide area. These included police, fire services, consumer protection, education and transport.
Each district had an elected district council. In the case of Aberdeen, Dundee, Edinburgh and Glasgow, the districts had city status
City status in the United Kingdom
City status in the United Kingdom is granted by the British monarch to a select group of communities. The holding of city status gives a settlement no special rights other than that of calling itself a "city". Nonetheless, this appellation carries its own prestige and, consequently, competitions...
, although this did not confer any additional powers. District councils had responsibility for local services including local planning, housing, libraries and licensing.
Islands areas
The islands areas were unitary local government areas, exercising the powers of both a regional and district council.Regions and islands areas
Scotland was subdivided into regions and islands areas as follows:
| 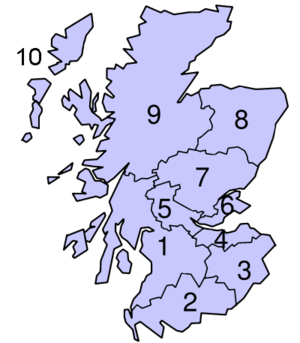 |
Districts
The regions consisted of districts as follows:| Region | Districts | Headquarters | Population estimate 1994 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Borders | Berwickshire | Duns Duns Duns is the county town of the historic county of Berwickshire, within the Scottish Borders.-Early history:Duns law, the original site of the town of Duns, has the remains of an Iron Age hillfort at its summit... |
19,350 |
| Ettrick and Lauderdale | Galashiels Galashiels Galashiels is a burgh in the Scottish Borders, on the Gala Water river. The name is often shortened to "Gala" .Galashiels is a major commercial centre for the Scottish Borders... |
35,000 | |
| Roxburgh | Hawick Hawick Hawick is a town in the Scottish Borders of south east Scotland. It is south-west of Jedburgh and south-southeast of Selkirk. It is one of the farthest towns from the sea in Scotland, in the heart of Teviotdale, and the biggest town in the former county of Roxburghshire. Hawick's architecture is... |
35,350 | |
| Tweeddale | Peebles Peebles Peebles is a burgh in the committee area of Tweeddale, in the Scottish Borders, lying on the River Tweed. According to the 2001 Census, the population was 8,159.-History:... |
15,375 | |
| Central | Clackmannan | Alloa Alloa Alloa is a town and former burgh in Clackmannanshire, set in the Central Lowlands of Scotland. It lies on on the north bank of the Firth of Forth close to the foot of the Ochil Hills, east of Stirling and north of Falkirk.... |
47,643 |
| Falkirk | Falkirk Falkirk Falkirk is a town in the Central Lowlands of Scotland. It lies in the Forth Valley, almost midway between the two most populous cities of Scotland; north-west of Edinburgh and north-east of Glasgow.... |
142,800 | |
| Stirling | Stirling Stirling Stirling is a city and former ancient burgh in Scotland, and is at the heart of the wider Stirling council area. The city is clustered around a large fortress and medieval old-town beside the River Forth... |
81,630 | |
| Dumfries and Galloway | Annandale and Eskdale | Annan Annan, Dumfries and Galloway The royal burgh of Annan is a well-built town, red sandstone being the material mainly used. Each year in July, Annan celebrates the Royal Charter and the boundaries of the Royal Burgh are confirmed when a mounted cavalcade undertakes the Riding of the Marches. Entertainment includes a... |
37,130 |
| Nithsdale | Dumfries Dumfries Dumfries is a market town and former royal burgh within the Dumfries and Galloway council area of Scotland. It is near the mouth of the River Nith into the Solway Firth. Dumfries was the county town of the former county of Dumfriesshire. Dumfries is nicknamed Queen of the South... |
57,220 | |
| Stewartry | Kirkcudbright Kirkcudbright Kirkcudbright, is a town in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland.The town lies south of Castle Douglas and Dalbeattie, in the part of Dumfries and Galloway known as the Stewartry, at the mouth of the River Dee, some six miles from the sea... |
23,690 | |
| Wigtown (originally named Merrick) | Stranraer Stranraer Stranraer is a town in the southwest of Scotland. It lies in the west of Dumfries and Galloway and in the county of Wigtownshire.Stranraer lies on the shores of Loch Ryan on the northern side of the isthmus joining the Rhins of Galloway to the mainland... |
30,077 | |
| Fife | Dunfermline | Dunfermline Dunfermline Dunfermline is a town and former Royal Burgh in Fife, Scotland, on high ground from the northern shore of the Firth of Forth. According to a 2008 estimate, Dunfermline has a population of 46,430, making it the second-biggest settlement in Fife. Part of the town's name comes from the Gaelic word... |
129,830 |
| Kirkcaldy | Kirkcaldy Kirkcaldy Kirkcaldy is a town and former royal burgh in Fife, on the east coast of Scotland. The town lies on a shallow bay on the northern shore of the Firth of Forth; SSE of Glenrothes, ENE of Dunfermline, WSW of Dundee and NNE of Edinburgh... |
148,450 | |
| North East Fife | Cupar Cupar Cupar is a town and former royal burgh in Fife, Scotland. The town is situated between Dundee and the New Town of Glenrothes.According to a recent population estimate , Cupar had a population around 8,980 making the town the ninth largest settlement in Fife.-History:The town is believed to have... |
69,930 | |
| Grampian | Aberdeen, City of | Aberdeen Aberdeen Aberdeen is Scotland's third most populous city, one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas and the United Kingdom's 25th most populous city, with an official population estimate of .... |
213,000 |
| Banff and Buchan | Banff Banff, Aberdeenshire Banff is a town in the Banff and Buchan area of Aberdeenshire, Scotland. Banff is situated on Banff Bay and faces the town of Macduff across the estuary of the River Deveron... |
88,020 | |
| Gordon | Inverurie Inverurie Inverurie is a Royal Burgh and town in Aberdeenshire, Scotland, approximately north west of Aberdeen on the A96 road and is served by Inverurie railway station on the Aberdeen to Inverness Line... |
77,080 | |
| Kincardine and Deeside | Stonehaven Stonehaven Stonehaven is a town in Aberdeenshire, Scotland. It lies on Scotland's northeast coast and had a population of 9,577 in 2001 census.Stonehaven, county town of Kincardineshire, grew around an Iron Age fishing village, now the "Auld Toon" , and expanded inland from the seaside... |
54,990 | |
| Moray | Elgin Elgin, Moray Elgin is a former cathedral city and Royal Burgh in Moray, Scotland. It is the administrative and commercial centre for Moray. The town originated to the south of the River Lossie on the higher ground above the flood plain. Elgin is first documented in the Cartulary of Moray in 1190... |
83,616 | |
| Highland | Badenoch and Strathspey | Kingussie Kingussie Kingussie is a small town in the Highland region of Scotland. It is one settlement in the Highland Council ward of Badenoch and Strathspey, and is the capital of the district of Badenoch. It lies beside the A9 road, although the old route of the A9 serves as the town's main street... |
10,399 |
| Caithness | Wick | 26,710 | |
| Inverness | Inverness Inverness Inverness is a city in the Scottish Highlands. It is the administrative centre for the Highland council area, and is regarded as the capital of the Highlands of Scotland... |
62,245 | |
| Lochaber | Fort William Fort William, Scotland Fort William is the second largest settlement in the highlands of Scotland and the largest town: only the city of Inverness is larger.Fort William is a major tourist centre with Glen Coe just to the south, Aonach Mòr to the north and Glenfinnan to the west, on the Road to the Isles... |
19,195 | |
| Nairn | Nairn Nairn Nairn is a town and former burgh in the Highland council area of Scotland. It is an ancient fishing port and market town around east of Inverness... |
10,600 | |
| Ross and Cromarty | Dingwall Dingwall Dingwall is a town and former royal burgh in the Highland council area of Scotland. It has a population of 5,026. It was formerly an east-coast harbor but now lies inland. Dingwall Castle was once the biggest castle north of Stirling. On the town's present-day outskirts lies Tulloch Castle, parts... |
49,184 | |
| Skye and Lochalsh | Portree Portree Portree is the largest town on Skye in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. It is the location for the only secondary school on the Island, Portree High school. Public transport services are limited to buses.... |
11,870 | |
| Sutherland | Golspie Golspie Golspie is a coastal village in Sutherland, Highland, Scotland. It has a population of around 1,650 people. It is located picturesquely on the shores of the North Sea in the shadow of Ben Bhraggie .... |
13,190 | |
| Lothian | East Lothian | Haddington Haddington, East Lothian The Royal Burgh of Haddington is a town in East Lothian, Scotland. It is the main administrative, cultural and geographical centre for East Lothian, which was known officially as Haddingtonshire before 1921. It lies about east of Edinburgh. The name Haddington is Anglo-Saxon, dating from the 6th... |
85,140 |
| Edinburgh, City of | Edinburgh Edinburgh Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland, the second largest city in Scotland, and the eighth most populous in the United Kingdom. The City of Edinburgh Council governs one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas. The council area includes urban Edinburgh and a rural area... |
418,914 | |
| Midlothian | Dalkeith Dalkeith Dalkeith is a town in Midlothian, Scotland, lying on the River North Esk. It was granted a burgh of barony in 1401 and a burgh of regality in 1540... |
79,910 | |
| West Lothian | Bathgate Bathgate Bathgate is a town in West Lothian, Scotland, on the M8 motorway west of Livingston. Nearby towns are Blackburn, Armadale, Whitburn, Livingston, and Linlithgow. Edinburgh Airport is away... |
146,430 | |
| Strathclyde | Argyll and Bute (originally Argyll) | Lochgilphead Lochgilphead Lochgilphead is a town and former burgh in Scotland, with a population of around 3,000 people. It is the administrative centre of Argyll and Bute. The town lies at the end of Loch Gilp and lies on the banks of the Crinan Canal.... |
63,350 |
| Bearsden and Milngavie | Bearsden Bearsden Bearsden ) is a town in East Dunbartonshire, Scotland. It lies on the northwestern fringe of Greater Glasgow, approximately from the City Centre, and is effectively a suburb, with housing development coinciding with the introduction of a railway line in 1863, and from where the town gets its name... |
41,000 | |
| Clydebank | Clydebank Clydebank Clydebank is a town in West Dunbartonshire, in the Central Lowlands of Scotland. Situated on the north bank of the River Clyde, Clydebank borders Dumbarton, the town with which it was combined to form West Dunbartonshire, as well as the town of Milngavie in East Dunbartonshire, and the Yoker and... |
47,500 | |
| Clydesdale (originally named Lanark: renamed 1980) | Lanark Lanark Lanark is a small town in the central belt of Scotland. Its population of 8,253 makes it the 100th largest settlement in Scotland. The name is believed to come from the Cumbric Lanerc meaning "clear space, glade".... |
58,290 | |
| Cumbernauld and Kilsyth (originally named Cumbernauld) | Cumbernauld Cumbernauld Cumbernauld is a Scottish new town in North Lanarkshire. It was created in 1956 as a population overspill for Glasgow City. It is the eighth most populous settlement in Scotland and the largest in North Lanarkshire... |
63,930 | |
| Cumnock and Doon Valley | Cumnock Cumnock Cumnock is a town in East Ayrshire, Scotland. The town sits at the confluence of the Glaisnock Water and the Lugar Water... |
42,954 | |
| Cunninghame | Irvine Irvine, North Ayrshire Irvine is a new town on the coast of the Firth of Clyde in North Ayrshire, Scotland. According to 2007 population estimates, the town is home to 39,527 inhabitants, making it the biggest settlement in North Ayrshire.... |
139,020 | |
| Dumbarton | Dumbarton | 77,222 | |
| East Kilbride | East Kilbride East Kilbride East Kilbride is a large suburban town in the South Lanarkshire council area, in the West Central Lowlands of Scotland. Designated as Scotland's first new town in 1947, it forms part of the Greater Glasgow conurbation... |
82,777 | |
| Eastwood | Giffnock Giffnock Giffnock is a wealthy, dormitory suburb of Glasgow in the East Renfrewshire Council area, within the historic county of Renfrewshire in the west central Lowlands of Scotland... |
60,600 | |
| Glasgow, City of | Glasgow Glasgow Glasgow is the largest city in Scotland and third most populous in the United Kingdom. The city is situated on the River Clyde in the country's west central lowlands... |
681,470 | |
| Hamilton | Hamilton Hamilton, South Lanarkshire Hamilton is a town in South Lanarkshire, in the west-central Lowlands of Scotland. It serves as the main administrative centre of the South Lanarkshire council area. It is the fifth-biggest town in Scotland after Paisley, East Kilbride, Livingston and Cumbernauld... |
105,202 | |
| Inverclyde | Greenock Greenock Greenock is a town and administrative centre in the Inverclyde council area in United Kingdom, and a former burgh within the historic county of Renfrewshire, located in the west central Lowlands of Scotland... |
90,103 | |
| Kilmarnock and Loudoun Kilmarnock and Loudoun (district) Kilmarnock and Loudoun was one of nineteen local government districts in the Strathclyde region of Scotland from 1975 to 1996.... |
Kilmarnock Kilmarnock Kilmarnock is a large burgh in East Ayrshire, Scotland, with a population of 44,734. It is the second largest town in Ayrshire. The River Irvine runs through its eastern section, and the Kilmarnock Water passes through it, giving rise to the name 'Bank Street'... |
79,861 | |
| Kyle and Carrick | Ayr Ayr Ayr is a town and port situated on the Firth of Clyde in south-west Scotland. With a population of around 46,000, Ayr is the largest settlement in Ayrshire, of which it is the county town, and has held royal burgh status since 1205... |
112,658 | |
| Monklands | Coatbridge Coatbridge Coatbridge is a town in North Lanarkshire, Scotland, about east of Glasgow city centre, set in the central Lowlands. The town, with neighbouring Airdrie, is part of the Greater Glasgow urban area. The first settlement of the area stretches back to the Stone Age era... |
102,379 | |
| Motherwell | Motherwell Motherwell Motherwell is a town and former burgh in North Lanarkshire, Scotland, south east of Glasgow. The name "Moderwelt" appears on a map of Lanarkshire made by Timothy Pont some time between 1583 and 1611 and printed in the Netherlands in around 1652, although the settlement was probably little more... |
143,730 | |
| Renfrew | Paisley Paisley Paisley is the largest town in the historic county of Renfrewshire in the west central Lowlands of Scotland and serves as the administrative centre for the Renfrewshire council area... |
201,000 | |
| Strathkelvin (originally named Bishopbriggs and Kirkintilloch) | Kirkintilloch Kirkintilloch Kirkintilloch is a town and former burgh in East Dunbartonshire, Scotland. It lies on the Forth and Clyde Canal, about eight miles northeast of central Glasgow... |
85,191 | |
| Tayside | Angus | Forfar Forfar Forfar is a parish, town and former royal burgh of approximately 13,500 people in Angus, located in the East Central Lowlands of Scotland. Forfar is the county town of Angus, which was officially known as Forfarshire from the 18th century until 1929, when the ancient name was reinstated, and... |
96,500 |
| Dundee, City of | Dundee Dundee Dundee is the fourth-largest city in Scotland and the 39th most populous settlement in the United Kingdom. It lies within the eastern central Lowlands on the north bank of the Firth of Tay, which feeds into the North Sea... |
171,520 | |
| Perth and Kinross | Perth Perth, Scotland Perth is a town and former city and royal burgh in central Scotland. Located on the banks of the River Tay, it is the administrative centre of Perth and Kinross council area and the historic county town of Perthshire... |
129,070 |
Alphabetical list of districts
| District | Region |
|---|---|
| Aberdeen | Grampian |
| Angus | Tayside |
| Annandale and Eskdale | Dumfries and Galloway |
| Argyll or Argyll and Bute | Strathclyde |
| Badenoch and Strathspey | Highland |
| Banff and Buchan | Grampian |
| Bearsden and Milngavie | Strathclyde |
| Berwickshire | Borders |
| Caithness | Highland |
| Clackmannan | Central |
| Clydebank | Strathclyde |
| Clydesdale | Strathclyde |
| Cumbernauld and Kilsyth | Strathclyde |
| Cumnock and Doon Valley | Strathclyde |
| Cunninghame | Strathclyde |
| Dumbarton | Strathclyde |
| Dundee | Tayside |
| Dunfermline | Fife |
| East Kilbride | Strathclyde |
| East Lothian | Lothian |
| Eastwood | Strathclyde |
| Edinburgh | Lothian |
| Ettrick and Lauderdale | Borders |
| Falkirk | Central |
| Glasgow | Strathclyde |
| Gordon | Grampian |
| Hamilton | Strathclyde |
| Inverclyde | Strathclyde |
| Inverness | Highland |
| Kilmarnock and Loudoun | Strathclyde |
| Kincardine and Deeside | Grampian |
| Kirkcaldy | Fife |
| Kyle and Carrick | Strathclyde |
| Lochaber | Highland |
| Midlothian | Lothian |
| Monklands | Strathclyde |
| Moray | Grampian |
| Motherwell | Strathclyde |
| Nairn | Highland |
| Nithsdale | Dumfries and Galloway |
| North-East Fife | Fife |
| Perth and Kinross | Tayside |
| Renfrew | Strathclyde |
| Ross and Cromarty | Highland |
| Roxburgh | Borders |
| Skye and Lochalsh | Highland |
| Stewartry | Dumfries and Galloway |
| Stirling | Central |
| Strathkelvin | Strathclyde |
| Sutherland | Highland |
| Tweeddale | Borders |
| West Lothian | Lothian |
| Wigtown | Dumfries and Galloway |
Abolition
The 1994 Act created 29 new unitary local government areas, which completely replaced the regions and districts on 1 April 1996. The islands council areas continued in use and, therefore, ScotlandScotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
now has 32 council areas.
See also
- List of burghs in Scotland
- Counties of ScotlandCounties of ScotlandThe counties of Scotland were the principal local government divisions of Scotland until 1975. Scotland's current lieutenancy areas and registration counties are largely based on them. They are often referred to as historic counties....
- Lieutenancy areas of ScotlandLieutenancy areas of ScotlandThe lieutenancy areas of Scotland are the areas used for the ceremonial lord-lieutenants, the monarch's representatives, in Scotland. They are different from the local government council areas, the committee areas, the sheriffdoms, the registration counties, the former regions and districts, the...
- Subdivisions of ScotlandSubdivisions of ScotlandFor local government purposes, Scotland is divided into 32 areas designated as "council areas" which are all governed by unitary authorities designated as "councils"...
- List of places in Scotland
- Local government in the United KingdomLocal government in the United KingdomThe pattern of local government in England is complex, with the distribution of functions varying according to the local arrangements. Legislation concerning local government in England is decided by the Parliament and Government of the United Kingdom, because England does not have a devolved...

