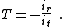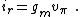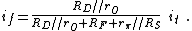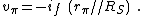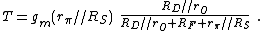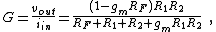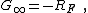Return ratio
Encyclopedia
The return ratio of a dependent source in a linear electrical circuit is the negative of the ratio of the current (voltage) returned to the site of the dependent source to the current (voltage) of a replacement independent source. The terms loop gain and return ratio are often used interchangeably; however, they are necessarily equivalent only in the case of a single feedback loop system with unilateral blocks.
 The steps for calculating the return ratio of a source are as follows:
The steps for calculating the return ratio of a source are as follows:
" SPICE
models or when measuring the return ratio experimentally.
For SPICE
simulations, one potential workaround is to manually replace non-linear devices by their small-signal equivalent model, with exposed dependent sources. However this will have to be redone if the bias point changes.
A result by Rosenstark shows that return ratio can be calculated by breaking the loop at any unilateral point in the circuit. The problem is now finding how to break the loop without affecting the bias point and altering the results. Middlebrookand Rosenstark have proposed several methods for experimental evaluation of return ratio (loosely referred to by these authors as simply loop gain), and similar methods have been adapted for use in SPICE
by Hurst. See Spectrum user note or Roberts, or Sedra, and especially Tuinenga.
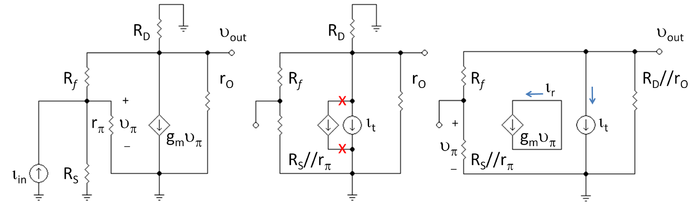 Figure 1 (top right) shows a bipolar amplifier with feedback bias resistor Rf driven by a Norton signal source
Figure 1 (top right) shows a bipolar amplifier with feedback bias resistor Rf driven by a Norton signal source
. Figure 2 (left panel) shows the corresponding small-signal circuit obtained by replacing the transistor with its hybrid-pi model
. The objective is to find the return ratio of the dependent current source in this amplifier. To reach the objective, the steps outlined above are followed. Figure 2 (center panel) shows the application of these steps up to Step 4, with the dependent source moved to the left of the inserted source of value it, and the leads targeted for cutting marked with an x. Figure 2 (right panel) shows the circuit set up for calculation of the return ratio T, which is
The return current is
The feedback current in Rf is found by current division to be:
The base-emitter voltage vπ is then, from Ohm's law
:
Consequently,
with R1 = RS || rπ and R2 = RD || rO.
This expression can be rewritten in the form used by the asymptotic gain model, which expresses the overall gain of a feedback amplifier in terms of several independent factors that are often more easily derived separately than the overall gain itself, and that often provide insight into the circuit. This form is:
where the so-called asymptotic gain G∞ is the gain at infinite gm, namely:
and the so-called feed forward or direct feedthrough G0 is the gain for zero gm, namely:
For additional applications of this method, see asymptotic gain model.
Calculating the return ratio

- Set all independent sources to zero.
- Select the dependent source for which the return ratio is sought.
- Place an independent source of the same type (voltage or current) and polarity in parallel with the selected dependent source.
- Move the dependent source to the side of the inserted source and cut the two leads joining the dependent source to the independent source.
- For a voltage source the return ratio is minus the ratio of the voltage across the dependent source divided by the voltage of the independent replacement source.
- For a current source, short-circuit the broken leads of the dependent source. The return ratio is minus the ratio of the resulting short-circuit current to the current of the independent replacement source.
Other Methods
These steps may not be feasible when the dependent sources inside the devices are not directly accessible, for example when using built-in "black boxBlack box
A black box is a device, object, or system whose inner workings are unknown; only the input, transfer, and output are known characteristics.The term black box can also refer to:-In science and technology:*Black box theory, a philosophical theory...
" SPICE
SPICE
SPICE is a general-purpose, open source analog electronic circuit simulator.It is a powerful program that is used in integrated circuit and board-level design to check the integrity of circuit designs and to predict circuit behavior.- Introduction :Unlike board-level designs composed of discrete...
models or when measuring the return ratio experimentally.
For SPICE
SPICE
SPICE is a general-purpose, open source analog electronic circuit simulator.It is a powerful program that is used in integrated circuit and board-level design to check the integrity of circuit designs and to predict circuit behavior.- Introduction :Unlike board-level designs composed of discrete...
simulations, one potential workaround is to manually replace non-linear devices by their small-signal equivalent model, with exposed dependent sources. However this will have to be redone if the bias point changes.
A result by Rosenstark shows that return ratio can be calculated by breaking the loop at any unilateral point in the circuit. The problem is now finding how to break the loop without affecting the bias point and altering the results. Middlebrookand Rosenstark have proposed several methods for experimental evaluation of return ratio (loosely referred to by these authors as simply loop gain), and similar methods have been adapted for use in SPICE
SPICE
SPICE is a general-purpose, open source analog electronic circuit simulator.It is a powerful program that is used in integrated circuit and board-level design to check the integrity of circuit designs and to predict circuit behavior.- Introduction :Unlike board-level designs composed of discrete...
by Hurst. See Spectrum user note or Roberts, or Sedra, and especially Tuinenga.
Example: Collector-to-base biased bipolar amplifier

Norton's theorem
Norton's theorem for linear electrical networks, known in Europe as the Mayer–Norton theorem, states that any collection of voltage sources, current sources, and resistors with two terminals is electrically equivalent to an ideal current source, I, in parallel with a single resistor, R...
. Figure 2 (left panel) shows the corresponding small-signal circuit obtained by replacing the transistor with its hybrid-pi model
Hybrid-pi model
The hybrid-pi model is a popular circuit model used for analyzing the small signal behavior of bipolar junction and field effect transistors. The model can be quite accurate for low-frequency circuits and can easily be adapted for higher frequency circuits with the addition of appropriate...
. The objective is to find the return ratio of the dependent current source in this amplifier. To reach the objective, the steps outlined above are followed. Figure 2 (center panel) shows the application of these steps up to Step 4, with the dependent source moved to the left of the inserted source of value it, and the leads targeted for cutting marked with an x. Figure 2 (right panel) shows the circuit set up for calculation of the return ratio T, which is
The return current is
The feedback current in Rf is found by current division to be:
The base-emitter voltage vπ is then, from Ohm's law
Ohm's law
Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference across the two points...
:
Consequently,
Application in asymptotic gain model
The overall transresistance gain of this amplifier can be shown to be:with R1 = RS || rπ and R2 = RD || rO.
This expression can be rewritten in the form used by the asymptotic gain model, which expresses the overall gain of a feedback amplifier in terms of several independent factors that are often more easily derived separately than the overall gain itself, and that often provide insight into the circuit. This form is:
where the so-called asymptotic gain G∞ is the gain at infinite gm, namely:
and the so-called feed forward or direct feedthrough G0 is the gain for zero gm, namely:
For additional applications of this method, see asymptotic gain model.