
Riefler escapement
Encyclopedia


Escapement
In mechanical watches and clocks, an escapement is a device that transfers energy to the timekeeping element and enables counting the number of oscillations of the timekeeping element...
for precision pendulum clock
Pendulum clock
A pendulum clock is a clock that uses a pendulum, a swinging weight, as its timekeeping element. The advantage of a pendulum for timekeeping is that it is a resonant device; it swings back and forth in a precise time interval dependent on its length, and resists swinging at other rates...
s invented and patented by German instrument maker Sigmund Riefler
Sigmund Riefler
thumb|Sigmund RieflerSigmund Riefler was a German physicist, inventor and precision clockmaker.- Life :...
in 1889. It was used in the astronomical regulator clocks made by his German firm Clemens Riefler from 1890 to 1965, which were perhaps the most accurate all-mechanical pendulum clocks made.
An escapement
Escapement
In mechanical watches and clocks, an escapement is a device that transfers energy to the timekeeping element and enables counting the number of oscillations of the timekeeping element...
is the mechanism in a mechanical clock
Clock
A clock is an instrument used to indicate, keep, and co-ordinate time. The word clock is derived ultimately from the Celtic words clagan and clocca meaning "bell". A silent instrument missing such a mechanism has traditionally been known as a timepiece...
that gives the pendulum
Pendulum
A pendulum is a weight suspended from a pivot so that it can swing freely. When a pendulum is displaced from its resting equilibrium position, it is subject to a restoring force due to gravity that will accelerate it back toward the equilibrium position...
precise impulses to keep it swinging, and allows the gear train
Gear train
A gear train is formed by mounting gears on a frame so that the teeth of the gears engage. Gear teeth are designed to ensure the pitch circles of engaging gears roll on each other without slipping, this provides a smooth transmission of rotation from one gear to the next.The transmission of...
to advance a set amount with each pendulum swing. The Riefler escapement was an improvement of the deadbeat escapement, the standard used in precision clocks. In the deadbeat, the force to keep the pendulum swinging is applied by the teeth of the escape wheel sliding alternately against two angled pallets on arms attached to the pendulum. Therefore, slight variations in the friction
Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and/or material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction:...
of the pallets and in the torque
Torque
Torque, moment or moment of force , is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis, fulcrum, or pivot. Just as a force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist....
from the escape wheel are passed on to the pendulum, disturbing its motion.
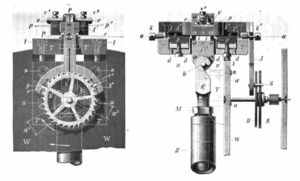
How it works
In the Riefler escapement, the energy required to keep the pendulum swinging is instead supplied by bending the short straight springSpring (device)
A spring is an elastic object used to store mechanical energy. Springs are usually made out of spring steel. Small springs can be wound from pre-hardened stock, while larger ones are made from annealed steel and hardened after fabrication...
strip which suspends the pendulum. The upper end of the suspension spring is not attached to a fixed support as in most clocks, but instead is attached to a heavy metal bearer, which pivots on two aligned knife-edges on its underside which rest on flat agate plates. The bending point of the suspension spring is in alignment with the line of contact of the knife-edges. When the pendulum passes its bottom point, the escape wheel is unlocked and pushes the bearer, and the bearer pivots suddenly on its knife edges by a small angle, flexing the spring. The spring is bent by a small amount in addition to that caused by the swing of the pendulum, and thus provides the impulse for the next swing. So the suspension spring is used for two functions: suspending the pendulum and giving it impulse.
The escapement has better performance than the deadbeat because the force from the pallets, with its variability, is applied not to the pendulum but to the bearer. The escapement has no contact with the pendulum below the suspension spring. The pendulum
Pendulum
A pendulum is a weight suspended from a pivot so that it can swing freely. When a pendulum is displaced from its resting equilibrium position, it is subject to a restoring force due to gravity that will accelerate it back toward the equilibrium position...
is free of disturbance from the escape wheel for most of each swing and the only work it has to do is to unlock the escape wheel once per second. This operation is performed near the ideal place, at the center of each swing.
The Riefler escape wheel and pallets are of a special design. There are actually two escape wheels mounted on the same shaft and two surfaces on each of the two pallet pins. The front locking wheel has forward pointing teeth rather like a dead-beat escapement, and catches on the flat surface of the pallet to lock the wheel. The rear impulse wheel has teeth with a sloping surface facing the direction of rotation
Rotation
A rotation is a circular movement of an object around a center of rotation. A three-dimensional object rotates always around an imaginary line called a rotation axis. If the axis is within the body, and passes through its center of mass the body is said to rotate upon itself, or spin. A rotation...
. The round part of each pallet is acted upon by this surface to give the impulse.
Riefler clocks

Second
The second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock....
s per day. and were guaranteed to be within 30 milliseconds. With over 600 made, they were one of the most widely used astronomical regulators, and became the highest standard for timekeeping in the early 20th century. They were used worldwide in astronomical observatories, naval observatories, and as primary standards for electrical time dissemination services, which delivered time signal
Time signal
A time signal is a visible, audible, mechanical, or electronic signal used as a reference to determine the time of day.-Audible and visible time signals:...
s by telegraph wire. Riefler clocks had internal switch
Switch
In electronics, a switch is an electrical component that can break an electrical circuit, interrupting the current or diverting it from one conductor to another....
contacts for this purpose, which delivered a 1 Hz
Hertz
The hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
time signal to external equipment. The first time standard for the United States, provided by the Bureau of Standards (now NIST), was from 1904 to 1929 generated by Riefler clocks.
In addition to the Riefler escapement, Riefler clocks' mechanism had several other innovations which were responsible for their accuracy. They were one of the first clocks to use a pendulum rod made of the low thermal expansion
Thermal expansion
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change in volume in response to a change in temperature.When a substance is heated, its particles begin moving more and thus usually maintain a greater average separation. Materials which contract with increasing temperature are rare; this effect is...
alloy invar
Invar
Invar, also known generically as FeNi36 , is a nickel steel alloy notable for its uniquely low coefficient of thermal expansion . The name, Invar, comes from the word invariable, referring to its lack of expansion or contraction with temperature changes.It was invented in 1896 by Swiss scientist...
, to prevent the pendulum from changing length with temperature changes, causing error. The most accurate models were mounted in a low pressure tank to eliminate the effect of changes in atmospheric pressure on the pendulum. They were powered by a gravity remontoire
Remontoire
In mechanical horology, a remontoire, is a small secondary source of power, a weight or spring, which runs the timekeeping mechanism and is itself periodically rewound by the timepiece's main power source, such as a mainspring...
, a small weight which was wound up by an electric motor
Electric motor
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
every 30 seconds, to eliminate the effect of changes in drive force on the mechanism.
Working Riefler precision pendulum clocks on display to the public are located at the Deutsches Museum
Deutsches Museum
The Deutsches Museum in Munich, Germany, is the world's largest museum of technology and science, with approximately 1.5 million visitors per year and about 28,000 exhibited objects from 50 fields of science and technology. The museum was founded on June 28, 1903, at a meeting of the Association...
in Munich
Munich
Munich The city's motto is "" . Before 2006, it was "Weltstadt mit Herz" . Its native name, , is derived from the Old High German Munichen, meaning "by the monks' place". The city's name derives from the monks of the Benedictine order who founded the city; hence the monk depicted on the city's coat...
, the National Watch and Clock Museum
National Watch and Clock Museum
The National Watch and Clock Museum , located in Columbia, Pennsylvania, is one of a very few museums in the United States dedicated solely to horology, which is the history, science and art of timekeeping and timekeepers....
in Columbia PA, the Musée international d'horlogerie in La Chaux-de-Fonds
La Chaux-de-Fonds
La Chaux-de-Fonds is a Swiss city of the district of La Chaux-de-Fonds in the canton of Neuchâtel. It is located in the Jura mountains at an altitude of 1000 m, a few kilometres from the French border. After Geneva and Lausanne, it is the third largest city of Romandie, the French-speaking part of...
, the Musée d'horlogerie in Le Locle
Le Locle
Le Locle is a municipality in the district of Le Locle in the canton of Neuchâtel in Switzerland.It is situated in the Jura mountains, a few kilometers from the city of La Chaux-de-Fonds....
, the Deutsches Uhrenmuseum
Deutsches Uhrenmuseum
The German Clock Museum is situated near the centre of the Black Forest town of Furtwangen im Schwarzwald, a historic centre of clockmaking. It features permanent and temporary exhibits on the history of timekeeping...
in Furtwangen, and at the US Naval Observatory (by appointment only) in Washington DC.

