
Ring oscillator
Encyclopedia

Logic gate
A logic gate is an idealized or physical device implementing a Boolean function, that is, it performs a logical operation on one or more logic inputs and produces a single logic output. Depending on the context, the term may refer to an ideal logic gate, one that has for instance zero rise time and...
whose output oscillates
Oscillation
Oscillation is the repetitive variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value or between two or more different states. Familiar examples include a swinging pendulum and AC power. The term vibration is sometimes used more narrowly to mean a mechanical oscillation but sometimes...
between two voltage levels, representing true and false. The NOT gates, or inverters, are attached in a chain; the output of the last inverter is fed back into the first.
Details
Because a single inverter computes the logical NOT of its input, it can be shown that the last output of a chain of an odd number of inverters is the logical NOT of the first input. This final output is asserted a finite amount of time after the first input is asserted; the feedback of this last output to the input causes oscillation.A circular chain composed of an even number of inverters cannot be used as a ring oscillator; the last output in this case is the same as the input. However, this configuration of inverter feedback can be used as a storage element; it is the basic building block of static random access memory
Static random access memory
Static random-access memory is a type of semiconductor memory where the word static indicates that, unlike dynamic RAM , it does not need to be periodically refreshed, as SRAM uses bistable latching circuitry to store each bit...
, or SRAM.
A real ring oscillator only requires power to operate; above a certain threshold voltage
Threshold voltage
The threshold voltage of a MOSFET is usually defined as the gate voltage where an inversion layer forms at the interface between the insulating layer and the substrate of the transistor. The purpose of the inversion layer's forming is to allow the flow of electrons through the gate-source junction...
, oscillations begin spontaneously. To increase the frequency of oscillation, two methods may be used. Firstly, the applied voltage may be increased; this increases both the frequency of the oscillation and the power consumed, which is dissipated as heat. The heat dissipated limits the speed of a given oscillator. Secondly, a smaller ring oscillator may be fabricated; this results in a higher frequency of oscillation given a certain power consumption.
Operation
To understand the operation of a ring oscillator, one must first understand gate delay. In a physical device, no gate can switch instantaneously; in a device fabricated with MOSFETMOSFET
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor is a transistor used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. The basic principle of this kind of transistor was first patented by Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925...
s, for example, the gate capacitance
Capacitance
In electromagnetism and electronics, capacitance is the ability of a capacitor to store energy in an electric field. Capacitance is also a measure of the amount of electric potential energy stored for a given electric potential. A common form of energy storage device is a parallel-plate capacitor...
must be charged before current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
can flow between the source and the drain. Thus, the output of every inverter of a ring oscillator changes a finite amount of time after the input has changed. From here, it can be easily seen that adding more inverters to the chain increases the total gate delay, reducing the frequency of oscillation.
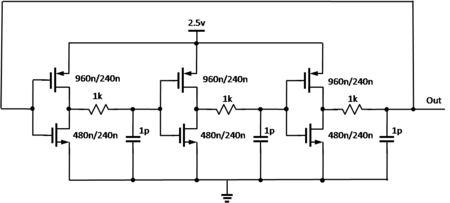
The ring oscillator is a distributed version of the delay oscillator. The ring oscillator uses an odd number of inverters to give the effect of a single inverting amplifier with a gain of greater than one. Rather than having a single delay element, each inverter contributes to the delay of the signal around the ring of inverters, hence the name ring oscillator. Adding pairs of inverters to the ring increases the total delay and thereby decreases the oscillator frequency. Changing the supply voltage changes the delay through each inverter, with higher voltages typically decreasing the delay and increasing the oscillator frequency.
Applications
- The voltage-controlled oscillatorVoltage-controlled oscillatorA voltage-controlled oscillator or VCO is an electronic oscillator designed to be controlled in oscillation frequency by a voltage input. The frequency of oscillation is varied by the applied DC voltage, while modulating signals may also be fed into the VCO to cause frequency modulation or phase...
in most phase-locked loopPhase-locked loopA phase-locked loop or phase lock loop is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input "reference" signal. It is an electronic circuit consisting of a variable frequency oscillator and a phase detector...
s is built from a ring oscillator. - A ring oscillator is often used to demonstrate a new hardware technology, analogous to the way a hello world programHello world programA "Hello world" program is a computer program that outputs "Hello world" on a display device. Because it is typically one of the simplest programs possible in most programming languages, it is by tradition often used to illustrate to beginners the most basic syntax of a programming language, or to...
is often used to demonstrate a new software technology. - Many waferWafer (electronics)A wafer is a thin slice of semiconductor material, such as a silicon crystal, used in the fabrication of integrated circuits and other microdevices...
s include a ring oscillator as part of the scribe line test structures. They are used during wafer testingWafer testingWafer testing is a step performed during semiconductor device fabrication. During this step, performed before a wafer is sent to die preparation, all individual integrated circuits that are present on the wafer are tested for functional defects by applying special test patterns to them. The wafer...
to measure the effects of manufacturing process variations. - Ring oscillators can also be used to measure the effects of voltage and temperature on a chip.

