Robin Hood effect
Encyclopedia
The Robin Hood effect is an economic occurrence where income
is redistributed so that economic inequality
is reduced. The effect is named after Robin Hood
, said to have stolen from the rich to give to the poor.
Simon Kuznets
argued that one major factor behind levels of economic inequality is the stage of economic development
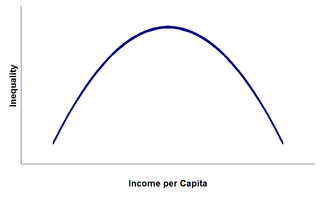
of a country. Kuznets described a curve-like relationship between level of income and inequality, as shown. That theory prescribes that countries with very low levels of development will have relatively equal distributions of wealth.
As a country develops, it necessarily acquires more capital, and the owners of this capital will then have more wealth and income, which introduces inequality. However, eventually various possible redistribution mechanisms such as trickle down effects and social welfare programs will lead to a Robin Hood effect, with wealth redistributed to the poor. Therefore, more developed countries move back to lower levels of inequality.
system where the first part of a worker's salary is taxed very little or not at all, while those on higher salaries must pay a higher tax rate on earnings over a certain threshold, known as progressive taxation. This has the effect of the better-off population paying a higher proportion of their salary in tax, effectively subsidising the less-well off, leading to a Robin Hood effect.
Specifically, a progressive tax is a tax
by which the tax rate increases as the taxable base amount increases. "Progressive" describes a distribution effect on income
or expenditure
, referring to the way the rate progresses from low to high, where the average tax rate is less than the marginal tax rate. It can be applied to individual taxes or to a tax system as a whole; a year, multi-year, or lifetime. Progressive taxes attempt to reduce the tax incidence
of people with a lower ability-to-pay, as they shift the incidence increasingly to those with a higher ability-to-pay.
tend to experience a large network externality
, which regulators and operators seek to correct by subsiding subscriptions through increased prices for call termination
. That then allows the less-well off in that country to gain access to communications services, often for free (on a prepay tariff). The additional cost is then levied on subscribers who make calls to these new subscribers; the call originators tend to be better-off. Therefore, despite there being no direct transfer of money, there is a strong Robin Hood effect, with the better-off subsidising the less well-off.
Income
Income is the consumption and savings opportunity gained by an entity within a specified time frame, which is generally expressed in monetary terms. However, for households and individuals, "income is the sum of all the wages, salaries, profits, interests payments, rents and other forms of earnings...
is redistributed so that economic inequality
Economic inequality
Economic inequality comprises all disparities in the distribution of economic assets and income. The term typically refers to inequality among individuals and groups within a society, but can also refer to inequality among countries. The issue of economic inequality is related to the ideas of...
is reduced. The effect is named after Robin Hood
Robin Hood
Robin Hood was a heroic outlaw in English folklore. A highly skilled archer and swordsman, he is known for "robbing from the rich and giving to the poor", assisted by a group of fellow outlaws known as his "Merry Men". Traditionally, Robin Hood and his men are depicted wearing Lincoln green clothes....
, said to have stolen from the rich to give to the poor.
Causes of a Robin Hood effect
A Robin Hood effect can be caused by a large number of different policies or economic decisions, not all of which are specifically aimed at reducing inequality. This article lists only some of these.Natural national development

Simon Kuznets
Simon Kuznets
Simon Smith Kuznets was a Russian American economist at the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania who won the 1971 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences "for his empirically founded interpretation of economic growth which has led to new and deepened insight into the economic and...
argued that one major factor behind levels of economic inequality is the stage of economic development
Economic development
Economic development generally refers to the sustained, concerted actions of policymakers and communities that promote the standard of living and economic health of a specific area...
of a country. Kuznets described a curve-like relationship between level of income and inequality, as shown. That theory prescribes that countries with very low levels of development will have relatively equal distributions of wealth.
As a country develops, it necessarily acquires more capital, and the owners of this capital will then have more wealth and income, which introduces inequality. However, eventually various possible redistribution mechanisms such as trickle down effects and social welfare programs will lead to a Robin Hood effect, with wealth redistributed to the poor. Therefore, more developed countries move back to lower levels of inequality.
Non-proportional income tax
Many countries have an income taxIncome tax
An income tax is a tax levied on the income of individuals or businesses . Various income tax systems exist, with varying degrees of tax incidence. Income taxation can be progressive, proportional, or regressive. When the tax is levied on the income of companies, it is often called a corporate...
system where the first part of a worker's salary is taxed very little or not at all, while those on higher salaries must pay a higher tax rate on earnings over a certain threshold, known as progressive taxation. This has the effect of the better-off population paying a higher proportion of their salary in tax, effectively subsidising the less-well off, leading to a Robin Hood effect.
Specifically, a progressive tax is a tax
Tax
To tax is to impose a financial charge or other levy upon a taxpayer by a state or the functional equivalent of a state such that failure to pay is punishable by law. Taxes are also imposed by many subnational entities...
by which the tax rate increases as the taxable base amount increases. "Progressive" describes a distribution effect on income
Income
Income is the consumption and savings opportunity gained by an entity within a specified time frame, which is generally expressed in monetary terms. However, for households and individuals, "income is the sum of all the wages, salaries, profits, interests payments, rents and other forms of earnings...
or expenditure
Consumption (economics)
Consumption is a common concept in economics, and gives rise to derived concepts such as consumer debt. Generally, consumption is defined in part by comparison to production. But the precise definition can vary because different schools of economists define production quite differently...
, referring to the way the rate progresses from low to high, where the average tax rate is less than the marginal tax rate. It can be applied to individual taxes or to a tax system as a whole; a year, multi-year, or lifetime. Progressive taxes attempt to reduce the tax incidence
Tax incidence
In economics, tax incidence is the analysis of the effect of a particular tax on the distribution of economic welfare. Tax incidence is said to "fall" upon the group that, at the end of the day, bears the burden of the tax...
of people with a lower ability-to-pay, as they shift the incidence increasingly to those with a higher ability-to-pay.
Cross-subsidisation of mobile telephony
In many developing countries, mobile communications networksCellular network
A cellular network is a radio network distributed over land areas called cells, each served by at least one fixed-location transceiver known as a cell site or base station. When joined together these cells provide radio coverage over a wide geographic area...
tend to experience a large network externality
Network effect
In economics and business, a network effect is the effect that one user of a good or service has on the value of that product to other people. When network effect is present, the value of a product or service is dependent on the number of others using it.The classic example is the telephone...
, which regulators and operators seek to correct by subsiding subscriptions through increased prices for call termination
Call termination
Call termination, also known as voice termination, refers to the routing of telephone calls from one telephone company, also known as a carrier or provider, to another.The terminating point is the called party or end point...
. That then allows the less-well off in that country to gain access to communications services, often for free (on a prepay tariff). The additional cost is then levied on subscribers who make calls to these new subscribers; the call originators tend to be better-off. Therefore, despite there being no direct transfer of money, there is a strong Robin Hood effect, with the better-off subsidising the less well-off.
Examples
- A Robin Hood effect caused by affirmative action
- International roaming charges argued to make the rich subsidise the poor
See also
- Income redistribution
- Distribution of wealthDistribution of wealthThe distribution of wealth is a comparison of the wealth of various members or groups in a society. It differs from the distribution of income in that it looks at the distribution of ownership of the assets in a society, rather than the current income of members of that society.-Definition of...
- Economic inequalityEconomic inequalityEconomic inequality comprises all disparities in the distribution of economic assets and income. The term typically refers to inequality among individuals and groups within a society, but can also refer to inequality among countries. The issue of economic inequality is related to the ideas of...
- Robin HoodRobin HoodRobin Hood was a heroic outlaw in English folklore. A highly skilled archer and swordsman, he is known for "robbing from the rich and giving to the poor", assisted by a group of fellow outlaws known as his "Merry Men". Traditionally, Robin Hood and his men are depicted wearing Lincoln green clothes....
- Robin Hood taxRobin Hood taxThe Robin Hood tax commonly refers to a package of financial transaction taxes , proposed by a campaigning group of civil society NGOs. Campaigners have suggested the tax could be implemented globally, regionally or unilaterally by individual nations...

