
Robot Odyssey
Encyclopedia
Robot Odyssey is an adventure game
, published by The Learning Company
in 1984. It was released for the Apple II
, TRS-80 Color Computer
, and DOS
.
s, Robotropolis. The player begins in the sewers of the city with three programmable robots, and must make his way to the top of the city to try to find his way home again.
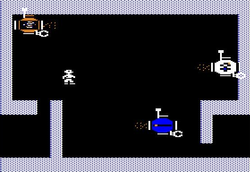 Except for their initial programming, the three robots are identical inside. They are equipped with four thrusters and bumper sensors, a grabber, a radio antenna
Except for their initial programming, the three robots are identical inside. They are equipped with four thrusters and bumper sensors, a grabber, a radio antenna
(for basic communication with other robots), a battery
, and a periscope
to use while riding inside a robot.
Throughout the game, the player is presented with various challenges which require programming
the three robots to accomplish various tasks. This is done by wiring a synchronous digital circuit
, consisting of logic gate
s and flip-flop
s, inside of the robots. Tasks and puzzles range from navigating a simple maze and retrieving items to complex tasks requiring interaction and communication between two or more robots. Though the player can ride inside the robots, most challenges involve the robots acting autonomously and cannot be completed with the player inside (and perhaps simply rewiring their robot on the fly).
The robots can also be wired up to chip
s, which provide a convenient and reproducible way to program the robots. Various pre-programmed chips are scattered throughout the city and range from complex circuits such as a wall-hugging chip which can be used to navigate through mazes and corridors (one of which is wired to a robot at the beginning) to clocks and counters. The player must find out how these chips work themselves, as the only information about each chip is a short, and sometimes cryptic, description. Additionally, there are predesigned chip files stored on the various disks containing the game that can be loaded into the in-game chips. The available chips stored in this fashion, vary depending one which port or version.
The Innovation Lab can be used to test out circuit designs in the robots or create new chips. Chips created in the lab can then be loaded into and used in the main game. Loading a chip in the main game will erase the previous programming in the chip used.
Although the game is recommended for ages 10 and up, it can prove to be quite challenging even for adults. In terms of educational value, the game teaches the basic concepts of electrical engineering
and digital logic in general.
, who wrote the animation utility underlying the game. The room has a lock for a key in it though placing the key in the lock does not do anything.
, and variants of it were used in many of The Learning Company's graphical adventure games of the time, including Rocky's Boots
, Gertrude's Secrets
, Gertrude's Puzzles, and Think Quick!, all of which are similar but easier logic puzzle games. The gameplay and visual design were derived from Robinett's influential Atari 2600
video game, Adventure
.
Carnage Heart
involves programming mechas that then fight without any user input.
Cognitoy's MindRover
is a relatively recent game which is similar in spirit to Robot Odyssey, but uses different programming concepts in its gameplay.
ChipWits
by Doug Sharp
and Mike Johnston, a game for the Apple II
, Macintosh, and Commodore 64
computers is similar in both theme and implementation, although the interface to program your robot differed.
Epsitec Games created Colobot
and Ceebot in recent years for Windows machines which are in many ways spiritual successors to Robot Odyssey. In these games the player program machines to accomplish puzzle tasks. Instead of using logic flops, switches, etc., these two games instead teach the player the fundamentals of object oriented programming like Java
, C++
, or C#.
One Girl One Laptop productions created a spiritual successor called Gate which uses the same digital logic puzzles as Robot Odyssey.
There is also a clone written in Java, Droidquest, which contains all of the original levels and an additional secret level.
Adventure game
An adventure game is a video game in which the player assumes the role of protagonist in an interactive story driven by exploration and puzzle-solving instead of physical challenge. The genre's focus on story allows it to draw heavily from other narrative-based media such as literature and film,...
, published by The Learning Company
The Learning Company
The Learning Company is an American educational software company, founded in 1980. It produced a grade-based system similar to Knowledge Adventure's JumpStart series. The products for preschoolers through second graders feature Reader Rabbit, and software for more advanced students features The...
in 1984. It was released for the Apple II
Apple II series
The Apple II series is a set of 8-bit home computers, one of the first highly successful mass-produced microcomputer products, designed primarily by Steve Wozniak, manufactured by Apple Computer and introduced in 1977 with the original Apple II...
, TRS-80 Color Computer
TRS-80 Color Computer
The Radio Shack TRS-80 Color Computer was a home computer launched in 1980. It was one of the earliest of the first generation of computers marketed for home use in English-speaking markets...
, and DOS
MS-DOS
MS-DOS is an operating system for x86-based personal computers. It was the most commonly used member of the DOS family of operating systems, and was the main operating system for IBM PC compatible personal computers during the 1980s to the mid 1990s, until it was gradually superseded by operating...
.
Story
The player is readying himself for bed when, suddenly, he falls through the floor into an underground city of robotRobot
A robot is a mechanical or virtual intelligent agent that can perform tasks automatically or with guidance, typically by remote control. In practice a robot is usually an electro-mechanical machine that is guided by computer and electronic programming. Robots can be autonomous, semi-autonomous or...
s, Robotropolis. The player begins in the sewers of the city with three programmable robots, and must make his way to the top of the city to try to find his way home again.
Gameplay
In Robot Odyssey, the player pilots their robots through each level of the labyrinthine city of Robotropolis, where various puzzles and tasks need to be solved in order to advance through each level of the city and on to the next. A tutorial and robot testing laboratory (the Innovation lab) are also provided with the game.
Antenna (radio)
An antenna is an electrical device which converts electric currents into radio waves, and vice versa. It is usually used with a radio transmitter or radio receiver...
(for basic communication with other robots), a battery
Battery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
, and a periscope
Periscope
A periscope is an instrument for observation from a concealed position. In its simplest form it consists of a tube with mirrors at each end set parallel to each other at a 45-degree angle....
to use while riding inside a robot.
Throughout the game, the player is presented with various challenges which require programming
Computer programming
Computer programming is the process of designing, writing, testing, debugging, and maintaining the source code of computer programs. This source code is written in one or more programming languages. The purpose of programming is to create a program that performs specific operations or exhibits a...
the three robots to accomplish various tasks. This is done by wiring a synchronous digital circuit
Digital circuit
Digital electronics represent signals by discrete bands of analog levels, rather than by a continuous range. All levels within a band represent the same signal state...
, consisting of logic gate
Logic gate
A logic gate is an idealized or physical device implementing a Boolean function, that is, it performs a logical operation on one or more logic inputs and produces a single logic output. Depending on the context, the term may refer to an ideal logic gate, one that has for instance zero rise time and...
s and flip-flop
Flip-flop (electronics)
In electronics, a flip-flop or latch is a circuit that has two stable states and can be used to store state information. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will have one or two outputs. It is the basic storage element in sequential logic...
s, inside of the robots. Tasks and puzzles range from navigating a simple maze and retrieving items to complex tasks requiring interaction and communication between two or more robots. Though the player can ride inside the robots, most challenges involve the robots acting autonomously and cannot be completed with the player inside (and perhaps simply rewiring their robot on the fly).
The robots can also be wired up to chip
Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
s, which provide a convenient and reproducible way to program the robots. Various pre-programmed chips are scattered throughout the city and range from complex circuits such as a wall-hugging chip which can be used to navigate through mazes and corridors (one of which is wired to a robot at the beginning) to clocks and counters. The player must find out how these chips work themselves, as the only information about each chip is a short, and sometimes cryptic, description. Additionally, there are predesigned chip files stored on the various disks containing the game that can be loaded into the in-game chips. The available chips stored in this fashion, vary depending one which port or version.
The Innovation Lab can be used to test out circuit designs in the robots or create new chips. Chips created in the lab can then be loaded into and used in the main game. Loading a chip in the main game will erase the previous programming in the chip used.
Although the game is recommended for ages 10 and up, it can prove to be quite challenging even for adults. In terms of educational value, the game teaches the basic concepts of electrical engineering
Electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is a field of engineering that generally deals with the study and application of electricity, electronics and electromagnetism. The field first became an identifiable occupation in the late nineteenth century after commercialization of the electric telegraph and electrical...
and digital logic in general.
Easter eggs
In level 2, The Subway, there is a room called the "Secret Room of Public Knowledge" which dedicates Robot Odyssey to Warren RobinettWarren Robinett
Joseph Warren Robinett, Jr. is a designer of interactive computer graphics software, notable as the developer of the Atari 2600's Adventure — the first graphical adventure video game — and as a founder of The Learning Company, where he designed Rocky's Boots and Robot Odyssey...
, who wrote the animation utility underlying the game. The room has a lock for a key in it though placing the key in the lock does not do anything.
Similar games
The engine for the game was written by Warren RobinettWarren Robinett
Joseph Warren Robinett, Jr. is a designer of interactive computer graphics software, notable as the developer of the Atari 2600's Adventure — the first graphical adventure video game — and as a founder of The Learning Company, where he designed Rocky's Boots and Robot Odyssey...
, and variants of it were used in many of The Learning Company's graphical adventure games of the time, including Rocky's Boots
Rocky's Boots
Rocky's Boots is an educational logic puzzle game by Warren Robinett and Leslie Grimm, published by The Learning Company in 1982. It was released for the Apple II, the CoCo, the Commodore 64 and the IBM PC. It was followed by a more difficult sequel, Robot Odyssey...
, Gertrude's Secrets
Gertrude's secrets
Gertrude's Secrets is a 1984 children's computer game by The Learning Company. The goal of the game is to solve puzzles and find secrets....
, Gertrude's Puzzles, and Think Quick!, all of which are similar but easier logic puzzle games. The gameplay and visual design were derived from Robinett's influential Atari 2600
Atari 2600
The Atari 2600 is a video game console released in October 1977 by Atari, Inc. It is credited with popularizing the use of microprocessor-based hardware and cartridges containing game code, instead of having non-microprocessor dedicated hardware with all games built in...
video game, Adventure
Adventure (Atari 2600)
Adventure is a video game for the Atari 2600 video game console and is considered the first action-adventure game. Its creator, Warren Robinett, also introduced the first widely-known Easter egg to the gaming world.-History and design:...
.
Carnage Heart
Carnage Heart
Carnage Heart is a video game for the PlayStation, developed by Artdink. Its gameplay is a mecha-based, turn-based strategy game, where the player takes the role of a commander in a war fought by robots...
involves programming mechas that then fight without any user input.
Cognitoy's MindRover
MindRover
Mind Rover is a video game, developed by CogniToy. The game, which can be thought of as an successor to the Learning Company's Robot Odyssey, revolves around two activities:* Assemble a virtual robots from a library of stock parts....
is a relatively recent game which is similar in spirit to Robot Odyssey, but uses different programming concepts in its gameplay.
ChipWits
ChipWits
ChipWits is a 1984 game for the Apple Macintosh, programmed by Doug Sharp and Mike Johnston, and published by BrainPower software.-Summary:The player uses an iconic programming language to teach a virtual robot how to navigate various mazes. The gameplay straddled the line between entertainment and...
by Doug Sharp
Doug Sharp
Doug Sharp is an American bobsledder who has competed from the late 1990s to the early 2000s. He won the bronze medal in the four-man event at the 2002 Winter Olympics in Salt Lake City....
and Mike Johnston, a game for the Apple II
Apple II series
The Apple II series is a set of 8-bit home computers, one of the first highly successful mass-produced microcomputer products, designed primarily by Steve Wozniak, manufactured by Apple Computer and introduced in 1977 with the original Apple II...
, Macintosh, and Commodore 64
Commodore 64
The Commodore 64 is an 8-bit home computer introduced by Commodore International in January 1982.Volume production started in the spring of 1982, with machines being released on to the market in August at a price of US$595...
computers is similar in both theme and implementation, although the interface to program your robot differed.
Epsitec Games created Colobot
Colobot
Colobot is an educational real-time strategy video game featuring 3D graphics. The objective of the game is to find a planet for colonization by the human race by establishing basic a infrastructure on the surface and eliminating any alien life forms endangering the expedition. The game takes...
and Ceebot in recent years for Windows machines which are in many ways spiritual successors to Robot Odyssey. In these games the player program machines to accomplish puzzle tasks. Instead of using logic flops, switches, etc., these two games instead teach the player the fundamentals of object oriented programming like Java
Java (programming language)
Java is a programming language originally developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems and released in 1995 as a core component of Sun Microsystems' Java platform. The language derives much of its syntax from C and C++ but has a simpler object model and fewer low-level facilities...
, C++
C++
C++ is a statically typed, free-form, multi-paradigm, compiled, general-purpose programming language. It is regarded as an intermediate-level language, as it comprises a combination of both high-level and low-level language features. It was developed by Bjarne Stroustrup starting in 1979 at Bell...
, or C#.
One Girl One Laptop productions created a spiritual successor called Gate which uses the same digital logic puzzles as Robot Odyssey.
There is also a clone written in Java, Droidquest, which contains all of the original levels and an additional secret level.
External links
- droidquest.com - A reimplementation in Java.
- A binary patch for running Robot Odyssey on modern computers
- Robot Odyssey chip disassembler

