
Robot end effector
Encyclopedia
In robotics, an end effector is the device at the end of a robotic arm, designed to interact with the environment. The exact nature of this device depends on the application of the robot.
In the strict definition, which originates from serial robotic manipulator
s, the end effector means the last link (or end) of the robot. At this endpoint the tool
s are attached. In a wider sense, an end effector can be seen as the part of a robot that interacts with the work environment. This does not refer to the wheels of a mobile robot
or the feet of a humanoid robot
which are also not end effectors—they are part of the robot's mobility.
End effectors may consist of a gripper or a tool. The gripper can be of two fingers, three fingers or even five fingers.
The end effectors that can be used as tools serves various purposes. Such as, Spot welding in an assembly, spray painting where uniformity of painting is necessary and for other purposes where the working conditions are dangerous for human beings.
There are two mechanisms of gripping the object in between the fingers (due to simplicity in the two finger grippers, in the following explanations, two finger grippers are considered).
The shape of the gripping surface on the fingers can be chosen according to the shape of the objects that are lifted by the grippers. For example, if the robot is designated a task to lift a round object, the gripper surface shape can be a negative impression of the object to make the grip efficient, or for a square shape the surface can be plane.
Though there are numerous forces acting over the body that has been lifted by the robotic arm, the main force acting there is the frictional force. The gripping surface can be made of a soft material with high coefficient of friction so that the surface of the object is not damaged. The robotic gripper must withstand not only the weight of the object but also acceleration and the motion that is caused due to frequent movement of the object. To find out the force required to grip the object, the following formula is used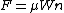
where:
But the above equation is incomplete. The direction of the movement also plays an important role over the gripping of the object. For example, when the body is moved upwards, against the gravitational force, the force required will be more than towards the gravitational force. Hence, another term is introduced and the formula becomes:
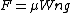
Here, the value of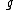 should not be taken as the acceleration due to gravity. In fact, here
should not be taken as the acceleration due to gravity. In fact, here 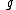 stands for multiplication factor. The value of
stands for multiplication factor. The value of 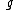 ranges from 1 to 3. When the body is moved in the horizontal direction then the value is taken to be 2, when moved against the gravitational force then 3 and along the gravitational force, i.e., downwards, 1.
ranges from 1 to 3. When the body is moved in the horizontal direction then the value is taken to be 2, when moved against the gravitational force then 3 and along the gravitational force, i.e., downwards, 1.
, or a paint spray gun
. A surgical robot's end effector could be a scalpel
or others tools used in surgery. Other possible end effectors are machine tools, like a drill
or milling cutter
s. The end effector on the space shuttle’s robotic arm uses a pattern of wires which close like the aperture
of a camera around a handle or other grasping point.
When referring to robotic prehension there are four general categories of robot grippers, these are:
In the strict definition, which originates from serial robotic manipulator
Manipulator
In robotics a manipulator is a device used to manipulate materials without direct contact. The applications were originally for dealing with radioactive or biohazardous materials, using robotic arms, or they were used in inaccessible places. In more recent developments they have been used in...
s, the end effector means the last link (or end) of the robot. At this endpoint the tool
Tool
A tool is a device that can be used to produce an item or achieve a task, but that is not consumed in the process. Informally the word is also used to describe a procedure or process with a specific purpose. Tools that are used in particular fields or activities may have different designations such...
s are attached. In a wider sense, an end effector can be seen as the part of a robot that interacts with the work environment. This does not refer to the wheels of a mobile robot
Mobile robot
A mobile robot is an automatic machine that is capable of movement in a given environment.-Overview:Mobile robots have the capability to move around in their environment and are not fixed to one physical location...
or the feet of a humanoid robot
Humanoid robot
A humanoid robot or an anthropomorphic robot is a robot with its overall appearance, based on that of the human body, allowing interaction with made-for-human tools or environments. In general humanoid robots have a torso with a head, two arms and two legs, although some forms of humanoid robots...
which are also not end effectors—they are part of the robot's mobility.
End effectors may consist of a gripper or a tool. The gripper can be of two fingers, three fingers or even five fingers.
The end effectors that can be used as tools serves various purposes. Such as, Spot welding in an assembly, spray painting where uniformity of painting is necessary and for other purposes where the working conditions are dangerous for human beings.
Mechanism of gripping
Generally, the gripping mechanism is done by the grippers or mechanical fingers. The number of fingers can be two, three or even as high as five. Though in the industrial robotics due to less complications, two finger grippers are used. The fingers are also replaceable. Due to gradual wearing, the fingers can be replaced without actually replacing the grippers.There are two mechanisms of gripping the object in between the fingers (due to simplicity in the two finger grippers, in the following explanations, two finger grippers are considered).
Shape of the gripping surface
The shape of the gripping surface on the fingers can be chosen according to the shape of the objects that are lifted by the grippers. For example, if the robot is designated a task to lift a round object, the gripper surface shape can be a negative impression of the object to make the grip efficient, or for a square shape the surface can be plane.
Force required to grip the object
Though there are numerous forces acting over the body that has been lifted by the robotic arm, the main force acting there is the frictional force. The gripping surface can be made of a soft material with high coefficient of friction so that the surface of the object is not damaged. The robotic gripper must withstand not only the weight of the object but also acceleration and the motion that is caused due to frequent movement of the object. To find out the force required to grip the object, the following formula is used
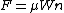
where:
-
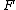
is the force required to grip the object, 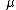
is the coeffecient of friction, 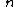
is the number of fingers in the gripper and 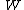
is the weight of the object.
But the above equation is incomplete. The direction of the movement also plays an important role over the gripping of the object. For example, when the body is moved upwards, against the gravitational force, the force required will be more than towards the gravitational force. Hence, another term is introduced and the formula becomes:
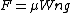
Here, the value of
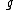 should not be taken as the acceleration due to gravity. In fact, here
should not be taken as the acceleration due to gravity. In fact, here 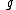 stands for multiplication factor. The value of
stands for multiplication factor. The value of  ranges from 1 to 3. When the body is moved in the horizontal direction then the value is taken to be 2, when moved against the gravitational force then 3 and along the gravitational force, i.e., downwards, 1.
ranges from 1 to 3. When the body is moved in the horizontal direction then the value is taken to be 2, when moved against the gravitational force then 3 and along the gravitational force, i.e., downwards, 1.Examples
The end effector of an assembly line robot would typically be a welding headWelding
Welding is a fabrication or sculptural process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by causing coalescence. This is often done by melting the workpieces and adding a filler material to form a pool of molten material that cools to become a strong joint, with pressure sometimes...
, or a paint spray gun
Spray painting
Spray painting is a painting technique where a device sprays a coating through the air onto a surface. The most common types employ compressed gas—usually air—to atomize and direct the paint particles. Spray guns evolved from airbrushes, and the two are usually distinguished by their size and the...
. A surgical robot's end effector could be a scalpel
Scalpel
A scalpel, or lancet, is a small and extremely sharp bladed instrument used for surgery, anatomical dissection, and various arts and crafts . Scalpels may be single-use disposable or re-usable. Re-usable scalpels can have attached, resharpenable blades or, more commonly, non-attached, replaceable...
or others tools used in surgery. Other possible end effectors are machine tools, like a drill
Drill
A drill or drill motor is a tool fitted with a cutting tool attachment or driving tool attachment, usually a drill bit or driver bit, used for drilling holes in various materials or fastening various materials together with the use of fasteners. The attachment is gripped by a chuck at one end of...
or milling cutter
Milling cutter
Milling cutters are cutting tools typically used in milling machines or machining centres . They remove material by their movement within the machine or directly from the cutter's shape .-Features of a milling cutter:Milling cutters come in several shapes and many sizes...
s. The end effector on the space shuttle’s robotic arm uses a pattern of wires which close like the aperture
Aperture
In optics, an aperture is a hole or an opening through which light travels. More specifically, the aperture of an optical system is the opening that determines the cone angle of a bundle of rays that come to a focus in the image plane. The aperture determines how collimated the admitted rays are,...
of a camera around a handle or other grasping point.
When referring to robotic prehension there are four general categories of robot grippers, these are:
- Impactive – jaws or claws which physically grasp by direct impact upon the object.
- Ingressive – pins, needles or hackles which physically penetrate the surface of the object (used in textile, carbon and glass fibre handling).
- Astrictive – suction forces applied to the objects surface (whether by vacuum, magneto– or electroadhesion).
- Contigutive – requiring direct contact for adhesion to take place (such as glue, surface tension or freezing).

