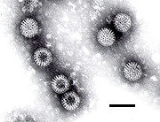
Rotavirus
Overview
Rotavirus is the most common cause of severe diarrhoea
among infants and young children, and is one of several viruses that cause infections often called stomach flu, despite having no relation to influenza
. It is a genus
of double-stranded RNA virus in the family
Reoviridae
. By the age of five, nearly every child in the world has been infected with rotavirus at least once. However, with each infection, immunity
develops, and subsequent infections are less severe; adults are rarely affected.
Diarrhea
Diarrhea , also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having three or more loose or liquid bowel movements per day. It is a common cause of death in developing countries and the second most common cause of infant deaths worldwide. The loss of fluids through diarrhea can cause dehydration and...
among infants and young children, and is one of several viruses that cause infections often called stomach flu, despite having no relation to influenza
Influenza
Influenza, commonly referred to as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by RNA viruses of the family Orthomyxoviridae , that affects birds and mammals...
. It is a genus
Genus
In biology, a genus is a low-level taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms, which is an example of definition by genus and differentia...
of double-stranded RNA virus in the family
Family (biology)
In biological classification, family is* a taxonomic rank. Other well-known ranks are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, genus, and species, with family fitting between order and genus. As for the other well-known ranks, there is the option of an immediately lower rank, indicated by the...
Reoviridae
Reoviridae
Reoviridae is a family of viruses that can affect the gastrointestinal system and respiratory tract. Viruses in the family Reoviridae have genomes consisting of segmented, double-stranded RNA...
. By the age of five, nearly every child in the world has been infected with rotavirus at least once. However, with each infection, immunity
Immunity (medical)
Immunity is a biological term that describes a state of having sufficient biological defenses to avoid infection, disease, or other unwanted biological invasion. Immunity involves both specific and non-specific components. The non-specific components act either as barriers or as eliminators of wide...
develops, and subsequent infections are less severe; adults are rarely affected.
Unanswered Questions

