
Royal Mint
Encyclopedia
The Royal Mint is the body permitted to manufacture, or mint, coins in the United Kingdom
. The Mint originated over 1,100 years ago, but since 2009 it operates as Royal Mint Ltd, a company which has an exclusive contract with HM Treasury
to supply all coinage for the UK. Royal Mint Ltd is 100% owned by HM Treasury
, though the latter delegates shareholder responsibilities to the Shareholder Executive
.
As well as minting coins for the UK, it also mints and exports coins to many other countries, and produces military medal
s, commemorative medals and other such items for governments, schools and business
es, being known as the world's leading exporting Mint. Responsibility for the security of the site falls to the Ministry of Defence Police
, who provide an armed contingent.
The Royal Mint began to move its operations from Tower Hill
, London
to Llantrisant
, South Wales
in 1968 and has operated on a single site in Llantrisant since 1980.
At Llantrisant it holds an extensive collection of coins dating from the 16th century onwards, housed in eighty cabinets made by Elizabeth II's
cabinet maker, Hugh Swann
. The site occupies 38 acres (15.4 ha) and employs 765 people.
The annual Trial of the Pyx
assay
s coins produced for the UK government for size, weight and chemical composition.
, but was only one of many mints throughout the kingdom. By 1279 it had moved to the Tower of London
, and remained there the next 500 years, achieving a monopoly
on the production of coin of the realm in the 16th century. Sir Isaac Newton
took up the post of Warden of the Mint
, responsible for investigating cases of counterfeiting, in 1696, and subsequently held the office of Master of the Royal Mint
from 1699 until his death in 1727. He unofficially moved the Pound Sterling
to the gold standard
from silver
in 1717.
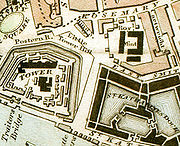 By the time Newton arrived, the Mint had expanded to fill several rickety wooden buildings ranged around the outside of the Tower. In the seventeenth century the processes for minting coins were mechanised and rolling mills and coining presses were installed. The new machinery and the demand on space in the Tower of London following the outbreak of war with France
By the time Newton arrived, the Mint had expanded to fill several rickety wooden buildings ranged around the outside of the Tower. In the seventeenth century the processes for minting coins were mechanised and rolling mills and coining presses were installed. The new machinery and the demand on space in the Tower of London following the outbreak of war with France
led to a decision to move the Mint to an adjacent site in East Smithfield
. The new building, designed by James Johnson and Robert Smirke
, was completed in 1809, and included space for the new machinery, and accommodation for the officers and staff of the Mint.
The building was rebuilt in the 1880s to accommodate new machinery which increased the capacity of the Mint. As technology changed with the introduction of electricity and demand grew, the process of rebuilding continued so that by the 1960s little of the original mint remained, apart from Smirke's 1809 building and the gatehouse in the front.
During WWII, the Royal Mint was bombed by the Germans. The Mint was hit on several different occasions and was put out of commission for three weeks at one point.
The Tower Hill site finally reached capacity ahead of decimalisation in 1971, with the need to strike hundreds of millions of new decimal coins, while at the same time not neglecting overseas customers. In 1967 it was announced that the Mint would move away from London to new buildings in Llantrisant, ten miles (16 km) north west of Cardiff. The first phase was opened by Queen Elizabeth II on 17 December 1968, and production gradually shifted to the new site over the next seven years until the last coin, a gold sovereign, was struck in London in November 1975. Smirke's 1809 Building is now used as commercial offices by Barclays Global Investors
.
On 1 April 1975 the Royal Mint became a trading fund
to help improve its efficiency by requiring it to become self financing.
In March 2009, the then Chancellor of the Exchequer
, Alistair Darling
began planning to sell off of the Royal Mint and on 31 December 2009 its assets were vested in a limited company, Royal Mint Ltd. The trading fund continued to exist as a holding entity of the new company, itself owned by HM Treasury
.
coins for circulation in the UK. However, it also manufactures and circulates coins for over 60 other countries (http://www.royalmint.com/Corporate/TheRoyalMint.aspx), mints collectors' coins
, and produces military medals
and civilian decorations for the British armed forces
and orders of chivalry
. The Royal Mint in London also produced coins for Canada
until a branch was opened in Ottawa, Canada in 1908. In the year 1931, control of the Canadian branch mint was passed to the Canadian government and it then became the Royal Canadian Mint
.
is the procedure in the United Kingdom for ensuring that newly-minted
coins
conform to required standards. The trials have been held since the twelfth century, normally once per calendar year, and continue to the present day. The form of the ceremony has been essentially the same since 1282. They are trials
in the full judicial sense, presided over by a judge
with an expert jury
of assayer
s. Trials are now held at the Hall of the Worshipful Company of Goldsmiths
, having previously taken place at the Palace of Westminster
Given modern production methods, it is unlikely that coins would not conform, although this has been a problem in the past as it would have been tempting for the Master of the Mint
to steal precious metals.
The term "Pyx" refers to the boxwood chest (in Greek
, πυξίς, pyxis) in which coins were placed for presentation to the jury. There is also a Pyx Chapel (or Pyx Chamber) in Westminster Abbey
, which was once used for secure storage of the Pyx and related articles.
Coins to be tested are drawn from the regular production of the Royal Mint. The Deputy Master of the Mint must, throughout the year, randomly select several thousand sample coins and place them aside for the Trial. These must be in a certain fixed proportion to the number of coins produced. For example, for every 5,000 bimetallic coins issued, one must be set aside, but for silver Maundy money
the proportion is one in 150.
The jury is composed of Freemen of the Company of Goldsmiths
, who assay
the coins provided to decide whether they have been minted within the criteria determined by the relevant Coinage Acts.
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
. The Mint originated over 1,100 years ago, but since 2009 it operates as Royal Mint Ltd, a company which has an exclusive contract with HM Treasury
HM Treasury
HM Treasury, in full Her Majesty's Treasury, informally The Treasury, is the United Kingdom government department responsible for developing and executing the British government's public finance policy and economic policy...
to supply all coinage for the UK. Royal Mint Ltd is 100% owned by HM Treasury
HM Treasury
HM Treasury, in full Her Majesty's Treasury, informally The Treasury, is the United Kingdom government department responsible for developing and executing the British government's public finance policy and economic policy...
, though the latter delegates shareholder responsibilities to the Shareholder Executive
Shareholder executive
The Shareholder Executive is the body within the British Government responsible for managing the government's financial interest in a range of public companies. Originally established within the Cabinet Office, it has since 2004 been part of the Department for Business...
.
As well as minting coins for the UK, it also mints and exports coins to many other countries, and produces military medal
Medal
A medal, or medallion, is generally a circular object that has been sculpted, molded, cast, struck, stamped, or some way rendered with an insignia, portrait, or other artistic rendering. A medal may be awarded to a person or organization as a form of recognition for athletic, military, scientific,...
s, commemorative medals and other such items for governments, schools and business
Business
A business is an organization engaged in the trade of goods, services, or both to consumers. Businesses are predominant in capitalist economies, where most of them are privately owned and administered to earn profit to increase the wealth of their owners. Businesses may also be not-for-profit...
es, being known as the world's leading exporting Mint. Responsibility for the security of the site falls to the Ministry of Defence Police
Ministry of Defence Police
The Ministry of Defence Police is a civilian police force which is part of the United Kingdom's Ministry of Defence. The force is part of the larger government agency, the Ministry of Defence Police and Guarding Agency , together with the Ministry of Defence Guard Service...
, who provide an armed contingent.
The Royal Mint began to move its operations from Tower Hill
Tower Hill
Tower Hill is an elevated spot northwest of the Tower of London, just outside the limits of the City of London, in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. Formerly it was part of the Tower Liberty under the direct administrative control of Tower...
, London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
to Llantrisant
Llantrisant
Llantrisant is a town in the county borough of Rhondda Cynon Taf in Wales, within the historic county boundaries of Glamorgan, Wales, lying on the River Ely and the Afon Clun. The town's name translates as The Parish of the Three Saints. The three saints in question are St Illtyd, St Gwynno and St...
, South Wales
Wales
Wales is a country that is part of the United Kingdom and the island of Great Britain, bordered by England to its east and the Atlantic Ocean and Irish Sea to its west. It has a population of three million, and a total area of 20,779 km²...
in 1968 and has operated on a single site in Llantrisant since 1980.
At Llantrisant it holds an extensive collection of coins dating from the 16th century onwards, housed in eighty cabinets made by Elizabeth II's
Elizabeth II of the United Kingdom
Elizabeth II is the constitutional monarch of 16 sovereign states known as the Commonwealth realms: the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Jamaica, Barbados, the Bahamas, Grenada, Papua New Guinea, the Solomon Islands, Tuvalu, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Belize,...
cabinet maker, Hugh Swann
Hugh Swann
Hugh Sinclair Swann , otherwise known as Tim Swann, became the cabinet maker to Elizabeth II of the United Kingdom. His work was inspired by his admiration for Barnsley, Gimson and Russell...
. The site occupies 38 acres (15.4 ha) and employs 765 people.
The annual Trial of the Pyx
Trial of the Pyx
The Trial of the Pyx is the procedure in the United Kingdom for ensuring that newly minted coins conform to required standards. Trials have been held from the twelfth century to the present day, normally once per calendar year; the form of the ceremony has been essentially the same since 1282 AD...
assay
Metallurgical assay
A metallurgical assay is a compositional analysis of an ore, metal, or alloy.Some assay methods are suitable for raw materials; others are more appropriate for finished goods. Raw precious metals are assayed by an assay office...
s coins produced for the UK government for size, weight and chemical composition.
History
The London Mint first became a single institution in 886, during the reign of Alfred the GreatAlfred the Great
Alfred the Great was King of Wessex from 871 to 899.Alfred is noted for his defence of the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of southern England against the Vikings, becoming the only English monarch still to be accorded the epithet "the Great". Alfred was the first King of the West Saxons to style himself...
, but was only one of many mints throughout the kingdom. By 1279 it had moved to the Tower of London
Tower of London
Her Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress, more commonly known as the Tower of London, is a historic castle on the north bank of the River Thames in central London, England. It lies within the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, separated from the eastern edge of the City of London by the open space...
, and remained there the next 500 years, achieving a monopoly
Monopoly
A monopoly exists when a specific person or enterprise is the only supplier of a particular commodity...
on the production of coin of the realm in the 16th century. Sir Isaac Newton
Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton PRS was an English physicist, mathematician, astronomer, natural philosopher, alchemist, and theologian, who has been "considered by many to be the greatest and most influential scientist who ever lived."...
took up the post of Warden of the Mint
Warden of the Mint
The Warden of the Mint was in principle the highest ranking officer of the Royal Mint of Great Britain, having oversight over its operations and physical plant by virtue of a royal warrant. The office received a yearly emolument of £500. Technically subordinate to the Warden was the Master of the...
, responsible for investigating cases of counterfeiting, in 1696, and subsequently held the office of Master of the Royal Mint
Master of the Mint
Master of the Mint was an important office in the governments of Scotland and England, and later Great Britain, between the 16th and 19th centuries. The Master was the highest officer in the Royal Mint. Until 1699, appointment was usually for life. Its holder occasionally sat in the cabinet...
from 1699 until his death in 1727. He unofficially moved the Pound Sterling
Pound sterling
The pound sterling , commonly called the pound, is the official currency of the United Kingdom, its Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, British Antarctic Territory and Tristan da Cunha. It is subdivided into 100 pence...
to the gold standard
Gold standard
The gold standard is a monetary system in which the standard economic unit of account is a fixed mass of gold. There are distinct kinds of gold standard...
from silver
Silver standard
The silver standard is a monetary system in which the standard economic unit of account is a fixed weight of silver. The silver specie standard was widespread from the fall of the Byzantine Empire until the 19th century...
in 1717.

France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
led to a decision to move the Mint to an adjacent site in East Smithfield
East Smithfield
East Smithfield is the name of a road in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets in east London, part of the A1203 road. It was historically an alternative name for the liberty and parish of St Botolph without Aldgate....
. The new building, designed by James Johnson and Robert Smirke
Robert Smirke (architect)
Sir Robert Smirke was an English architect, one of the leaders of Greek Revival architecture his best known building in that style is the British Museum, though he also designed using other architectural styles...
, was completed in 1809, and included space for the new machinery, and accommodation for the officers and staff of the Mint.
The building was rebuilt in the 1880s to accommodate new machinery which increased the capacity of the Mint. As technology changed with the introduction of electricity and demand grew, the process of rebuilding continued so that by the 1960s little of the original mint remained, apart from Smirke's 1809 building and the gatehouse in the front.
During WWII, the Royal Mint was bombed by the Germans. The Mint was hit on several different occasions and was put out of commission for three weeks at one point.
The Tower Hill site finally reached capacity ahead of decimalisation in 1971, with the need to strike hundreds of millions of new decimal coins, while at the same time not neglecting overseas customers. In 1967 it was announced that the Mint would move away from London to new buildings in Llantrisant, ten miles (16 km) north west of Cardiff. The first phase was opened by Queen Elizabeth II on 17 December 1968, and production gradually shifted to the new site over the next seven years until the last coin, a gold sovereign, was struck in London in November 1975. Smirke's 1809 Building is now used as commercial offices by Barclays Global Investors
BlackRock
BlackRock, Inc. is an American multinational investment management corporation and the world's largest asset manager. BlackRock is headquartered in Manhattan, New York City, New York, United States and is the leading provider of investment, advisory, and risk management solutions...
.
On 1 April 1975 the Royal Mint became a trading fund
Trading Fund
A trading fund is a UK executive agency, government department or part of a department, which has been established as such by means of a Trading Fund Order made under the Government Trading Funds Act 1973....
to help improve its efficiency by requiring it to become self financing.
In March 2009, the then Chancellor of the Exchequer
Chancellor of the Exchequer
The Chancellor of the Exchequer is the title held by the British Cabinet minister who is responsible for all economic and financial matters. Often simply called the Chancellor, the office-holder controls HM Treasury and plays a role akin to the posts of Minister of Finance or Secretary of the...
, Alistair Darling
Alistair Darling
Alistair Maclean Darling is a Scottish Labour Party politician who has been a Member of Parliament since 1987, currently for Edinburgh South West. He served as the Chancellor of the Exchequer from 2007 to 2010...
began planning to sell off of the Royal Mint and on 31 December 2009 its assets were vested in a limited company, Royal Mint Ltd. The trading fund continued to exist as a holding entity of the new company, itself owned by HM Treasury
HM Treasury
HM Treasury, in full Her Majesty's Treasury, informally The Treasury, is the United Kingdom government department responsible for developing and executing the British government's public finance policy and economic policy...
.
Role of the Royal Mint
The Royal Mint exists principally to mintMint (coin)
A mint is an industrial facility which manufactures coins for currency.The history of mints correlates closely with the history of coins. One difference is that the history of the mint is usually closely tied to the political situation of an era...
coins for circulation in the UK. However, it also manufactures and circulates coins for over 60 other countries (http://www.royalmint.com/Corporate/TheRoyalMint.aspx), mints collectors' coins
Coin collecting
Coin collecting is the collecting or trading of coins or other forms of minted legal tender.Coins of interest to collectors often include those that circulated for only a brief time, coins with mint errors and especially beautiful or historically significant pieces. Coin collecting can be...
, and produces military medals
Medal
A medal, or medallion, is generally a circular object that has been sculpted, molded, cast, struck, stamped, or some way rendered with an insignia, portrait, or other artistic rendering. A medal may be awarded to a person or organization as a form of recognition for athletic, military, scientific,...
and civilian decorations for the British armed forces
British Armed Forces
The British Armed Forces are the armed forces of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.Also known as Her Majesty's Armed Forces and sometimes legally the Armed Forces of the Crown, the British Armed Forces encompasses three professional uniformed services, the Royal Navy, the...
and orders of chivalry
Chivalric order
Chivalric orders are societies and fellowships of knights that have been created by European monarchs in imitation of the military orders of the Crusades...
. The Royal Mint in London also produced coins for Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
until a branch was opened in Ottawa, Canada in 1908. In the year 1931, control of the Canadian branch mint was passed to the Canadian government and it then became the Royal Canadian Mint
Royal Canadian Mint
The Royal Canadian Mint produces all of Canada's circulation coins, and manufactures circulation coins on behalf of other nations. The Mint also designs and manufactures: precious and base metal collector coins; gold, silver, palladium, and platinum bullion coins; medals, as well as medallions and...
.
Trial of the Pyx
The Trial of the PyxTrial of the Pyx
The Trial of the Pyx is the procedure in the United Kingdom for ensuring that newly minted coins conform to required standards. Trials have been held from the twelfth century to the present day, normally once per calendar year; the form of the ceremony has been essentially the same since 1282 AD...
is the procedure in the United Kingdom for ensuring that newly-minted
Mint (coin)
A mint is an industrial facility which manufactures coins for currency.The history of mints correlates closely with the history of coins. One difference is that the history of the mint is usually closely tied to the political situation of an era...
coins
British coinage
The standard circulating coinage of the United Kingdom is denominated in pounds sterling , and, since the introduction of the two-pound coin in 1998, ranges in value from one penny to two pounds. Since decimalisation, on 15 February 1971, the pound has been divided into 100 pence...
conform to required standards. The trials have been held since the twelfth century, normally once per calendar year, and continue to the present day. The form of the ceremony has been essentially the same since 1282. They are trials
Trial (law)
In law, a trial is when parties to a dispute come together to present information in a tribunal, a formal setting with the authority to adjudicate claims or disputes. One form of tribunal is a court...
in the full judicial sense, presided over by a judge
Judge
A judge is a person who presides over court proceedings, either alone or as part of a panel of judges. The powers, functions, method of appointment, discipline, and training of judges vary widely across different jurisdictions. The judge is supposed to conduct the trial impartially and in an open...
with an expert jury
Jury
A jury is a sworn body of people convened to render an impartial verdict officially submitted to them by a court, or to set a penalty or judgment. Modern juries tend to be found in courts to ascertain the guilt, or lack thereof, in a crime. In Anglophone jurisdictions, the verdict may be guilty,...
of assayer
Assayer
An assayer is a person who tests ores and minerals and analyzes them to determine their composition and value. They may use spectrographic analysis, chemical solutions, and chemical or laboratory equipment, such as furnaces, beakers, graduates, pipettes, and crucibles.An assayer separates metals...
s. Trials are now held at the Hall of the Worshipful Company of Goldsmiths
Worshipful Company of Goldsmiths
The Worshipful Company of Goldsmiths is one of the Livery Companies of the City of London. The Company, which has origins in the twelfth century, received a Royal Charter in 1327. It ranks fifth in the order of precedence of Livery Companies. Its motto is Justitia Virtutum Regina, Latin for Justice...
, having previously taken place at the Palace of Westminster
Palace of Westminster
The Palace of Westminster, also known as the Houses of Parliament or Westminster Palace, is the meeting place of the two houses of the Parliament of the United Kingdom—the House of Lords and the House of Commons...
Given modern production methods, it is unlikely that coins would not conform, although this has been a problem in the past as it would have been tempting for the Master of the Mint
Master of the Mint
Master of the Mint was an important office in the governments of Scotland and England, and later Great Britain, between the 16th and 19th centuries. The Master was the highest officer in the Royal Mint. Until 1699, appointment was usually for life. Its holder occasionally sat in the cabinet...
to steal precious metals.
The term "Pyx" refers to the boxwood chest (in Greek
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
, πυξίς, pyxis) in which coins were placed for presentation to the jury. There is also a Pyx Chapel (or Pyx Chamber) in Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey
The Collegiate Church of St Peter at Westminster, popularly known as Westminster Abbey, is a large, mainly Gothic church, in the City of Westminster, London, United Kingdom, located just to the west of the Palace of Westminster. It is the traditional place of coronation and burial site for English,...
, which was once used for secure storage of the Pyx and related articles.
Coins to be tested are drawn from the regular production of the Royal Mint. The Deputy Master of the Mint must, throughout the year, randomly select several thousand sample coins and place them aside for the Trial. These must be in a certain fixed proportion to the number of coins produced. For example, for every 5,000 bimetallic coins issued, one must be set aside, but for silver Maundy money
Maundy money
Royal Maundy is a religious service in the Church of England held on Maundy Thursday, the day before Good Friday. At the service, the British Monarch or a royal official ceremonially distributes small silver coins known as "Maundy money" as symbolic alms to elderly recipients...
the proportion is one in 150.
The jury is composed of Freemen of the Company of Goldsmiths
Worshipful Company of Goldsmiths
The Worshipful Company of Goldsmiths is one of the Livery Companies of the City of London. The Company, which has origins in the twelfth century, received a Royal Charter in 1327. It ranks fifth in the order of precedence of Livery Companies. Its motto is Justitia Virtutum Regina, Latin for Justice...
, who assay
Assay
An assay is a procedure in molecular biology for testing or measuring the activity of a drug or biochemical in an organism or organic sample. A quantitative assay may also measure the amount of a substance in a sample. Bioassays and immunoassays are among the many varieties of specialized...
the coins provided to decide whether they have been minted within the criteria determined by the relevant Coinage Acts.
See also
- British coinageBritish coinageThe standard circulating coinage of the United Kingdom is denominated in pounds sterling , and, since the introduction of the two-pound coin in 1998, ranges in value from one penny to two pounds. Since decimalisation, on 15 February 1971, the pound has been divided into 100 pence...
- British banknotes
- Pound SterlingPound sterlingThe pound sterling , commonly called the pound, is the official currency of the United Kingdom, its Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, British Antarctic Territory and Tristan da Cunha. It is subdivided into 100 pence...
- George Frederick AnsellGeorge Frederick AnsellGeorge Frederick Ansell was an English scientific inventor, chemist and assayer, and author of a standard work on the Royal Mint.-Biography:...
- William John HockingWilliam John HockingWilliam John Hocking, CVO, CBE was born at Sennen Cove, Cornwall into a Congregational church family in 1864 and died in Danbury in April 1953.-Royal Mint:...
- Joseph Harris (British astronomer)Joseph Harris (British astronomer)Joseph Harris was a British blacksmith, astronomer, navigator, economist, natural philosopher, government adviser and King's Assay Master at the Royal Mint....
- List of Mints
- Mints of ScotlandMints of ScotlandThere were a number of mints in Scotland, for the production of the Scottish coinage. The most important mint was that in the capital, Edinburgh, which was active from the reign of David I , and was the last to close, in the 19th century....
External links
- The Royal Mint - official website
- Royal Mint privatisation plan halted - BBC News, 9 July 1999
- Coin Designs 2005- Royal Mint Competition Designs
- Royal Mint Coins Designed by John W Mills

