SDHA
Encyclopedia
Succinate dehydrogenase complex, subunit A, flavoprotein variant is a protein
that in humans is encoded by the SDHA gene
.
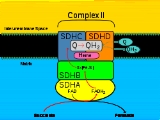
The succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) protein complex catalyzes the oxidation of succinate (succinate + ubiquinone => fumarate + ubiquinol). The SDHA subunit is connected to the SDHB
subunit on the hydrophilic, catalytic end of the complex, and weighs 72.7 kDA. Electrons removed from succinate transfer to SDHA, transfer across SDHB to the SDHC/SDHD
subunits on the hydrophobic end of the complex anchored in the mitochondrial membrane.
and Respiratory chain.
SDHA acts as an intermediate in the basic SDH enzyme action:
at p15. The gene
is partitioned in 15 exon
s.
The expressed protein has 664 amino acids.
mutations (i.e. both copies of the gene are mutated) have been described in Leigh syndrome.
Mutation
s in the SDHA subunit have a distinct pathology from mutations in the SDHB/SDHC/SDHD subunits; it is the only subunit to never have shown tumor suppressor behaviour. Heterozygous carriers of an SDHA mutation do not develop paraganglioma
s as has been seen for mutations in the other subunits. This appears to be due to the expression of two similar SDHA genes (Types I and II) in the paraganglia system. This would require the improbable event of inactivation of all four alleles to trigger a paraganglioma.
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
that in humans is encoded by the SDHA gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
.
The succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) protein complex catalyzes the oxidation of succinate (succinate + ubiquinone => fumarate + ubiquinol). The SDHA subunit is connected to the SDHB
SDHB
Succinate dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur subunit, mitochondrial also known as iron-sulfur subunit of complex II is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SDHB gene....
subunit on the hydrophilic, catalytic end of the complex, and weighs 72.7 kDA. Electrons removed from succinate transfer to SDHA, transfer across SDHB to the SDHC/SDHD
SDHD
Succinate dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] cytochrome b small subunit, mitochondrial , also known as succinate dehydrogenase complex subunit D , is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SDHD gene....
subunits on the hydrophobic end of the complex anchored in the mitochondrial membrane.
Function of the SDHA Protein
The SDH complex is located on the inner membrane of the mitochondria and participates in both the Citric Acid CycleCitric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle — also known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle , the Krebs cycle, or the Szent-Györgyi-Krebs cycle — is a series of chemical reactions which is used by all aerobic living organisms to generate energy through the oxidization of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and...
and Respiratory chain.
SDHA acts as an intermediate in the basic SDH enzyme action:
- SDHA converts succinate to fumarate as part of the Citric Acid CycleCitric acid cycleThe citric acid cycle — also known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle , the Krebs cycle, or the Szent-Györgyi-Krebs cycle — is a series of chemical reactions which is used by all aerobic living organisms to generate energy through the oxidization of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and...
. This reaction also converts FADFADIn biochemistry, flavin adenine dinucleotide is a redox cofactor involved in several important reactions in metabolism. FAD can exist in two different redox states, which it converts between by accepting or donating electrons. The molecule consists of a riboflavin moiety bound to the phosphate...
to FADH2. - Electrons from the FADH2 are transferred to the SDHB subunit iron clusters [2Fe-2S],[4Fe-4S],[3Fe-4S]. This function is part of the Respiratory chain
- Finally the electrons are transferred to the Ubiquinone (Q) pool via the SDHC/SDHDSDHDSuccinate dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] cytochrome b small subunit, mitochondrial , also known as succinate dehydrogenase complex subunit D , is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SDHD gene....
subunits.
Gene that Codes for SDHA
The gene that codes for the SDHA protein is nuclear, even though the protein is located in the inner membrane of the mitochondria. The location of the gene in humans is on the fifth chromosomeChromosome 5 (human)
Chromosome 5 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 5 spans about 181 million base pairs and represents almost 6% of the total DNA in cells. Chromosome 5 is one of the largest human chromosomes, yet has one of the lowest gene...
at p15. The gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
is partitioned in 15 exon
Exon
An exon is a nucleic acid sequence that is represented in the mature form of an RNA molecule either after portions of a precursor RNA have been removed by cis-splicing or when two or more precursor RNA molecules have been ligated by trans-splicing. The mature RNA molecule can be a messenger RNA...
s.
The expressed protein has 664 amino acids.
Role in Disease
Bi-allelicAllele
An allele is one of two or more forms of a gene or a genetic locus . "Allel" is an abbreviation of allelomorph. Sometimes, different alleles can result in different observable phenotypic traits, such as different pigmentation...
mutations (i.e. both copies of the gene are mutated) have been described in Leigh syndrome.
Mutation
Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
s in the SDHA subunit have a distinct pathology from mutations in the SDHB/SDHC/SDHD subunits; it is the only subunit to never have shown tumor suppressor behaviour. Heterozygous carriers of an SDHA mutation do not develop paraganglioma
Paraganglioma
A paraganglioma is a rare neuroendocrine neoplasm that may develop at various body sites . About 97% are benign and cured by surgical removal; the remaining 3% are malignant because they are able to produce distant metastases...
s as has been seen for mutations in the other subunits. This appears to be due to the expression of two similar SDHA genes (Types I and II) in the paraganglia system. This would require the improbable event of inactivation of all four alleles to trigger a paraganglioma.

