
ST elevation
Encyclopedia
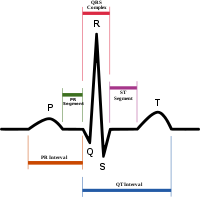

Electrocardiogram
Electrocardiography is a transthoracic interpretation of the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time, as detected by electrodes attached to the outer surface of the skin and recorded by a device external to the body...
, wherein the trace in the ST segment
ST segment
In electrocardiography, the ST segment connects the QRS complex and the T wave and has a duration of 0.08 to 0.12 sec .It starts at the J point and ends at the beginning of the T wave...
is abnormally high above the isoelectric line.
Measurement
An ST elevation is considered significant if the vertical distance between the ECG trace and the isoelectric line at a point 0.04 seconds after the J-point is at least 0.1 mV (usually representing 1 mmMillimetre
The millimetre is a unit of length in the metric system, equal to one thousandth of a metre, which is the SI base unit of length....
) in a limb lead or 0.2 mV (2 mm) in a precordial lead. This measure has a false positive rate of 15-20% (which is slightly higher in women than men) and a false negative rate of 20-30%.
Physiology
The ST segmentST segment
In electrocardiography, the ST segment connects the QRS complex and the T wave and has a duration of 0.08 to 0.12 sec .It starts at the J point and ends at the beginning of the T wave...
corresponds to a period of ventricle systolic
Systole (medicine)
Systole is the contraction of the heart. Used alone, it usually means the contraction of the left ventricle.In all mammals, the heart has 4 chambers. The left and right ventricles pump together. The atria and ventricles pump in sequence...
depolarization
Depolarization
In biology, depolarization is a change in a cell's membrane potential, making it more positive, or less negative. In neurons and some other cells, a large enough depolarization may result in an action potential...
, when the cardiac muscle is contracted. Subsequent relaxation occurs during the diastolic
Diastole
Diastole is the period of time when the heart fills with blood after systole . Ventricular diastole is the period during which the ventricles are relaxing, while atrial diastole is the period during which the atria are relaxing...
repolarization
Repolarization
In neuroscience, repolarization refers to the change in membrane potential that returns the membrane potential to a negative value after the depolarization phase of an action potential has just previously changed the membrane potential to a positive value. Repolarization results from the movement...
phase. The normal course of ST segment
ST segment
In electrocardiography, the ST segment connects the QRS complex and the T wave and has a duration of 0.08 to 0.12 sec .It starts at the J point and ends at the beginning of the T wave...
reflects a certain sequence of muscular layers undergoing repolarization and certain timing of this activity. When the cardiac muscle is damaged or undergoes a pathological process (e.g. inflammation
Inflammation
Inflammation is part of the complex biological response of vascular tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. Inflammation is a protective attempt by the organism to remove the injurious stimuli and to initiate the healing process...
), its contractile and electrical properties change. Usually, this leads to early repolarization, or premature ending of the systole
Systole (medicine)
Systole is the contraction of the heart. Used alone, it usually means the contraction of the left ventricle.In all mammals, the heart has 4 chambers. The left and right ventricles pump together. The atria and ventricles pump in sequence...
.
Associated conditions
The exact topology and distribution of the affected areas depend on the underlying condition. Thus, ST elevation may be present on all or some leads of ECG.It can be associated with:
- Myocardial infarctionMyocardial infarctionMyocardial infarction or acute myocardial infarction , commonly known as a heart attack, results from the interruption of blood supply to a part of the heart, causing heart cells to die...
(see also ECG in myocardial infarctionElectrocardiography in myocardial infarctionElectrocardiography in suspected myocardial infarction has the main purpose of detecting ischemia or acute coronary injury in emergency department populations coming for symptoms of myocardial infarction . Also, it can distinguish clinically different types of myocardial infarction.-Technical...
). ST elevation in select leads is more common with MI. - Acute pericarditisAcute pericarditisAcute pericarditis is a type of pericarditis usually lasting 1.5 µg/L. Coronary angiography in those patients should indicated normal vascular perfusion. The elevation of these biomarkers are typically transient and should return to normal within a week. Persistence may indicated...
. ST elevation in all leads is more common with acute pericarditis. - Left ventricular aneurysm
- Blunt traumaBlunt traumaIn medical terminology, blunt trauma, blunt injury, non-penetrating trauma or blunt force trauma refers to a type of physical trauma caused to a body part, either by impact, injury or physical attack; the latter usually being referred to as blunt force trauma...
to the chest resulting in a cardiac contusion

