
SUMO enzymes
Encyclopedia
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
the dynamic posttranslational modification
Posttranslational modification
Posttranslational modification is the chemical modification of a protein after its translation. It is one of the later steps in protein biosynthesis, and thus gene expression, for many proteins....
process of sumoylation (i.e. transfer of SUMO protein
SUMO protein
Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier or SUMO proteins are a family of small proteins that are covalently attached to and detached from other proteins in cells to modify their function...
to other proteins). The Small Ubiquitin-related Modifier, SUMO-1, is a ubiquitin
Ubiquitin
Ubiquitin is a small regulatory protein that has been found in almost all tissues of eukaryotic organisms. Among other functions, it directs protein recycling.Ubiquitin can be attached to proteins and label them for destruction...
-like family member that is conjugated to its substrate
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
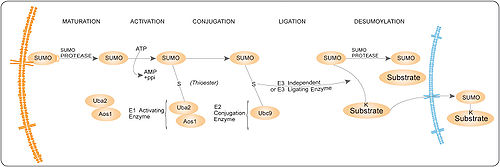
s through three discrete enzymatic steps (see the figure on the right): activation, involving the E1 enzyme (SAE1/SAE2); conjugation, involving the E2 enzyme (UBC9); substrate modification, through the cooperation of the E2 and E3 protein ligases.
SUMO pathway modifies hundreds of proteins that participate in diverse cellular processes. SUMO pathway is the most studied ubiquitin
Ubiquitin
Ubiquitin is a small regulatory protein that has been found in almost all tissues of eukaryotic organisms. Among other functions, it directs protein recycling.Ubiquitin can be attached to proteins and label them for destruction...
-like pathway that regulates a wide range of cellular events, evidenced by a large number of sumoylated proteins identified in more than ten large-scale studies.

