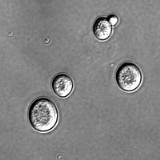
Saccharomyces
Overview
Saccharomyces is a genus
in the kingdom of fungi
that includes many species of yeast
. Saccharomyces is from Greek
σάκχαρ (sugar) and μύκης (mushroom) and means sugar fungus. Many members of this genus are considered very important in food production. One example is Saccharomyces cerevisiae
, which is used in making wine
, bread
, and beer
. Other members of this genus include Saccharomyces bayanus
, used in making wine, and Saccharomyces boulardii
, used in medicine.
Colonies
of Saccharomyces grow rapidly and mature in three days.
Genus
In biology, a genus is a low-level taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms, which is an example of definition by genus and differentia...
in the kingdom of fungi
Fungus
A fungus is a member of a large group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds , as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, Fungi, which is separate from plants, animals, and bacteria...
that includes many species of yeast
Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic micro-organisms classified in the kingdom Fungi, with 1,500 species currently described estimated to be only 1% of all fungal species. Most reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by an asymmetric division process called budding...
. Saccharomyces is from Greek
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
σάκχαρ (sugar) and μύκης (mushroom) and means sugar fungus. Many members of this genus are considered very important in food production. One example is Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a species of yeast. It is perhaps the most useful yeast, having been instrumental to baking and brewing since ancient times. It is believed that it was originally isolated from the skin of grapes...
, which is used in making wine
Wine
Wine is an alcoholic beverage, made of fermented fruit juice, usually from grapes. The natural chemical balance of grapes lets them ferment without the addition of sugars, acids, enzymes, or other nutrients. Grape wine is produced by fermenting crushed grapes using various types of yeast. Yeast...
, bread
Bread
Bread is a staple food prepared by cooking a dough of flour and water and often additional ingredients. Doughs are usually baked, but in some cuisines breads are steamed , fried , or baked on an unoiled frying pan . It may be leavened or unleavened...
, and beer
Beer
Beer is the world's most widely consumed andprobably oldest alcoholic beverage; it is the third most popular drink overall, after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of sugars, mainly derived from malted cereal grains, most commonly malted barley and malted wheat...
. Other members of this genus include Saccharomyces bayanus
Saccharomyces bayanus
Saccharomyces bayanus is a yeast of the genus Saccharomyces, and is used in winemaking and cider fermentation. It is closely related to Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Both Saccharomyces bayanus and Saccharomyces pastorianus contain diverse strains, with different genetic and metabolic characteristics,...
, used in making wine, and Saccharomyces boulardii
Saccharomyces boulardii
Saccharomyces boulardii is a tropical strain of yeast first isolated from lychee and mangosteen fruit in 1923 by French scientist Henri Boulard. It is related to, but distinct from, Saccharomyces cerevisiae in several taxonomic, metabolic, and genetic properties. S...
, used in medicine.
Colonies
Colony (biology)
In biology, a colony reference to several individual organisms of the same species living closely together, usually for mutual benefit, such as stronger defense or the ability to attack bigger prey. Some insects live only in colonies...
of Saccharomyces grow rapidly and mature in three days.
Unanswered Questions

