
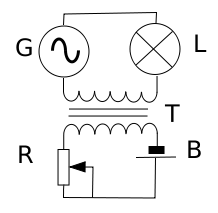
Saturable reactor
Encyclopedia
Electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is a field of engineering that generally deals with the study and application of electricity, electronics and electromagnetism. The field first became an identifiable occupation in the late nineteenth century after commercialization of the electric telegraph and electrical...
is a special form of inductor
Inductor
An inductor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in a magnetic field. An inductor's ability to store magnetic energy is measured by its inductance, in units of henries...
where the magnetic core
Magnetic core
A magnetic core is a piece of magnetic material with a high permeability used to confine and guide magnetic fields in electrical, electromechanical and magnetic devices such as electromagnets, transformers, electric motors, inductors and magnetic assemblies. It is made of ferromagnetic metal such...
can be deliberately saturated
Saturation (magnetic)
Seen in some magnetic materials, saturation is the state reached when an increase in applied external magnetizing field H cannot increase the magnetization of the material further, so the total magnetic field B levels off...
by means of a direct electric current
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
in a control winding. Once saturated, the inductance
Inductance
In electromagnetism and electronics, inductance is the ability of an inductor to store energy in a magnetic field. Inductors generate an opposing voltage proportional to the rate of change in current in a circuit...
of the saturable reactor drops dramatically.
Saturable reactors provide a very simple means to remotely and proportionally control the alternating current
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
(AC) through a load such as an incandescent lamp; the AC is roughly proportional to the direct current
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
(DC) in the control winding. In addition, because of the particular arrangement of the power windings, the control winding, and the core, the control winding is well isolated from the AC power. The AC power windings are also usually configured so that they cancel out AC voltages that would otherwise be induced into the control winding.
Because the required inductance to achieve dimming varies with the size of the load, saturable reactors often have multiple taps, allowing a small inductance to be used with a large load or a larger inductance to be used with a smaller load. In this way, the required magnitude of the control current can be also held roughly constant, no matter what the load.
Saturable reactors at mains frequency are larger, heavier, and more expensive than electronic power controllers developed after the introduction of semiconductor electronic components, and have largely been replaced by thyristor
Thyristor
A thyristor is a solid-state semiconductor device with four layers of alternating N and P-type material. They act as bistable switches, conducting when their gate receives a current trigger, and continue to conduct while they are forward biased .Some sources define silicon controlled rectifiers and...
dimmer
Dimmer
Dimmers are devices used to vary the brightness of a light. By decreasing or increasing the RMS voltage and, hence, the mean power to the lamp, it is possible to vary the intensity of the light output...
s using triac
Triac
Triac may refer to:* TRIAC , an electronics component* Triac , a green vehicle* Tiratricol, a common thyroid hormone analogue used for treating thyroid hormone resistance syndrome...
s or SCRs
Thyristor
A thyristor is a solid-state semiconductor device with four layers of alternating N and P-type material. They act as bistable switches, conducting when their gate receives a current trigger, and continue to conduct while they are forward biased .Some sources define silicon controlled rectifiers and...
. However, they are still used in switch-mode power supplies, where the high operating frequency considerably reduces the cost, size, and weight of the saturable inductor.

