
Shock polar
Encyclopedia
The term shock polar is generally used with the graphical representation of the Rankine-Hugoniot equation
s in either the hodograph
plane or the pressure ratio-flow deflection angle plane. The polar itself is the locus of all possible states after an oblique shock
.
Shock Polar in the
The minimum angle,  , which an oblique shock can have is the Mach angle
, which an oblique shock can have is the Mach angle  , where
, where  is the initial Mach number before the shock and the greatest angle corresponds to a normal shock. The range of shock angles is therefore
is the initial Mach number before the shock and the greatest angle corresponds to a normal shock. The range of shock angles is therefore  . To calculate the pressures for this range of angles,the Rankine-Hugoniot equation
. To calculate the pressures for this range of angles,the Rankine-Hugoniot equation
s are solved for pressure:

To calculate the possible flow deflection angles, the relationship between shock angle and
and  is used:
is used:

Where is the ratio of specific heats and
is the ratio of specific heats and  is the flow deflection angle.
is the flow deflection angle.
Rankine-Hugoniot equation
The Rankine–Hugoniot conditions, also referred to as Rankine–Hugoniot jump conditions or Rankine–Hugoniot relations, relate to the behaviour of shock waves traveling normal to the prevailing flow. They are named in recognition of the work carried out by Scottish engineer and physicist William John...
s in either the hodograph
Hodograph
A hodograph is a diagram that gives a vectorial visual representation of the movement of a body or a fluid. It is the locus of one end of a variable vector, with the other end fixed. The position of any plotted data on such a diagram is proportional to the velocity of the moving particle. It is...
plane or the pressure ratio-flow deflection angle plane. The polar itself is the locus of all possible states after an oblique shock
Oblique shock
An oblique shock wave, unlike a normal shock, is inclined with respect to the incident upstream flow direction. It will occur when a supersonic flow encounters a corner that effectively turns the flow into itself and compresses. The upstream streamlines are uniformly deflected after the shock wave...
.
Shock Polar in the 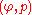 Plane
Plane
The minimum angle,  , which an oblique shock can have is the Mach angle
, which an oblique shock can have is the Mach angle  , where
, where  is the initial Mach number before the shock and the greatest angle corresponds to a normal shock. The range of shock angles is therefore
is the initial Mach number before the shock and the greatest angle corresponds to a normal shock. The range of shock angles is therefore  . To calculate the pressures for this range of angles,the Rankine-Hugoniot equation
. To calculate the pressures for this range of angles,the Rankine-Hugoniot equationRankine-Hugoniot equation
The Rankine–Hugoniot conditions, also referred to as Rankine–Hugoniot jump conditions or Rankine–Hugoniot relations, relate to the behaviour of shock waves traveling normal to the prevailing flow. They are named in recognition of the work carried out by Scottish engineer and physicist William John...
s are solved for pressure:

To calculate the possible flow deflection angles, the relationship between shock angle
 and
and  is used:
is used:
Where
 is the ratio of specific heats and
is the ratio of specific heats and  is the flow deflection angle.
is the flow deflection angle.
