Short QT syndrome
Encyclopedia
Short QT syndrome is a genetic
disease of the electrical system of the heart
. It consists of a constellation of signs and symptoms, consisting of a short QT interval
on an EKG (≤ 300 ms
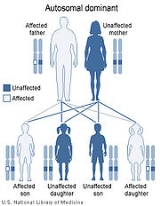
) that does not significantly change with heart rate, tall and peaked T waves, and a structurally normal heart. Short QT syndrome appears to be inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, and a few affected families have been identified.
 Some individuals with short QT syndrome frequently complain of palpitations and may have unexplained syncope
Some individuals with short QT syndrome frequently complain of palpitations and may have unexplained syncope
(loss of consciousness). Mutations in the KCNH2, KCNJ2
, and KCNQ1 genes cause short QT syndrome. These genes provide instructions for making proteins that act as channels across the cell membrane. These channels transport positively charged atoms (ions) of potassium into and out of cells. In cardiac muscle
, these ion channels play critical roles in maintaining the heart's normal rhythm. Mutations in the KCNH2, KCNJ2, or KCNQ1 gene increase the activity of the channels, which changes the flow of potassium ions between cells. This disruption in ion transport alters the way the heart beats, leading to the abnormal heart rhythm characteristic of short QT syndrome. Short QT syndrome appears to have an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance.
Short QT syndrome is associated with an increased risk of sudden cardiac death, most likely due to ventricular fibrillation
.
from Drs. Michael H Gollob and Jason D Roberts.
The Short QT Syndrome diagnostic criteria is based on a point system as follows:
QTc in milliseconds
<370 1
<350 2
<330 3
Jpoint-Tpeak interval
<120 1
Clinical History
Sudden cardiac arrest 2
Polymorphic VT or VF 2
Unexplained syncope 1
Atrial fibrillation 1
Family History
1st or 2nd degree relative with SQTS 2
1st or 2nd degree relative with sudden death 1
Sudden infant death syndrome 1
Genotype
Genotype positive 2
Mutation of undetermined significance 1
in a culprit gene
Patients are deemed high-probability (> or equal to 4 points), intermediate probability (3 points) or low probability (2 or less points).
is that short QT syndrome is due to increased activity of outward potassium currents in phase 2 and 3 of the cardiac action potential
. This would cause a shortening of the plateau phase of the action potential (phase 2), causing a shortening of the overall action potential, leading to an overall shortening of refractory periods and the QT interval.
In the families afflicted by short QT syndrome, mutation
s have been described in three genes, KvLQT1
, the human ether-a-go-go gene
(HERG
), and KCNJ2.
(ICD) as a preventive action, although it has not been demonstrated that cardiac problems have occurred before deciding to implant an ICD.
A recent study has suggested the use of certain antiarrhythmic agents, particularly quinidine
, may be of benefit in individuals with short QT syndrome due to their effects on prolonging the action potential and by their action on the IK channels. Some Trial are currently under way but do not show a longer QT statistically.
Genetics
Genetics , a discipline of biology, is the science of genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms....
disease of the electrical system of the heart
Heart
The heart is a myogenic muscular organ found in all animals with a circulatory system , that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions...
. It consists of a constellation of signs and symptoms, consisting of a short QT interval
QT interval
In cardiology, the QT interval is a measure of the time between the start of the Q wave and the end of the T wave in the heart's electrical cycle. In general, the QT interval represents electrical depolarization and repolarization of the left and right ventricles...
on an EKG (≤ 300 ms
Millisecond
A millisecond is a thousandth of a second.10 milliseconds are called a centisecond....
) that does not significantly change with heart rate, tall and peaked T waves, and a structurally normal heart. Short QT syndrome appears to be inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, and a few affected families have been identified.
Symptoms and signs

Syncope (medicine)
Syncope , the medical term for fainting, is precisely defined as a transient loss of consciousness and postural tone characterized by rapid onset, short duration, and spontaneous recovery due to global cerebral hypoperfusion that most often results from hypotension.Many forms of syncope are...
(loss of consciousness). Mutations in the KCNH2, KCNJ2
KCNJ2
The Kir2.1 inward-rectifier potassium ion channel is encoded by the gene.- Clinical significance :A defect in this gene is associated with Andersen-Tawil syndrome.A mutation in the KCNJ2 gene has also been shown to cause short QT syndrome....
, and KCNQ1 genes cause short QT syndrome. These genes provide instructions for making proteins that act as channels across the cell membrane. These channels transport positively charged atoms (ions) of potassium into and out of cells. In cardiac muscle
Cardiac muscle
Cardiac muscle is a type of involuntary striated muscle found in the walls and histologic foundation of the heart, specifically the myocardium. Cardiac muscle is one of three major types of muscle, the others being skeletal and smooth muscle...
, these ion channels play critical roles in maintaining the heart's normal rhythm. Mutations in the KCNH2, KCNJ2, or KCNQ1 gene increase the activity of the channels, which changes the flow of potassium ions between cells. This disruption in ion transport alters the way the heart beats, leading to the abnormal heart rhythm characteristic of short QT syndrome. Short QT syndrome appears to have an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance.
Short QT syndrome is associated with an increased risk of sudden cardiac death, most likely due to ventricular fibrillation
Ventricular fibrillation
Ventricular fibrillation is a condition in which there is uncoordinated contraction of the cardiac muscle of the ventricles in the heart, making them quiver rather than contract properly. Ventricular fibrillation is a medical emergency and most commonly identified arrythmia in cardiac arrest...
.
Diagnosis
Recent diagnostic criteria have been published out of the Arrhythmia Research Laboratory at the University of Ottawa Heart InstituteUniversity of Ottawa Heart Institute
The University of Ottawa Heart Institute is Canada’s largest and foremost cardiovascular health centre. It began as a department in The Ottawa Hospital, and since has evolved into Canada’s only complete cardiac centre, encompassing prevention, diagnosis, treatment, rehabilitation, research, and...
from Drs. Michael H Gollob and Jason D Roberts.
The Short QT Syndrome diagnostic criteria is based on a point system as follows:
QTc in milliseconds
<370 1
<350 2
<330 3
Jpoint-Tpeak interval
<120 1
Clinical History
Sudden cardiac arrest 2
Polymorphic VT or VF 2
Unexplained syncope 1
Atrial fibrillation 1
Family History
1st or 2nd degree relative with SQTS 2
1st or 2nd degree relative with sudden death 1
Sudden infant death syndrome 1
Genotype
Genotype positive 2
Mutation of undetermined significance 1
in a culprit gene
Patients are deemed high-probability (> or equal to 4 points), intermediate probability (3 points) or low probability (2 or less points).
Etiology
The etiology of short QT syndrome is unclear at this time. A current hypothesisHypothesis
A hypothesis is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. The term derives from the Greek, ὑποτιθέναι – hypotithenai meaning "to put under" or "to suppose". For a hypothesis to be put forward as a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it...
is that short QT syndrome is due to increased activity of outward potassium currents in phase 2 and 3 of the cardiac action potential
Cardiac action potential
In electrocardiography, the cardiac action potential is a specialized action potential in the heart, necessary for the electrical conduction system of the heart....
. This would cause a shortening of the plateau phase of the action potential (phase 2), causing a shortening of the overall action potential, leading to an overall shortening of refractory periods and the QT interval.
In the families afflicted by short QT syndrome, mutation
Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
s have been described in three genes, KvLQT1
KvLQT1
Kv7.1 is a potassium channel protein coded for by the gene KCNQ1. Kv7.1 is present in the cell membranes of cardiac muscle tissue and in inner ear neurons among other tissues...
, the human ether-a-go-go gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
(HERG
HERG
hERG is a gene that codes for a protein known as Kv11.1 potassium ion channel...
), and KCNJ2.
Treatment
Currently, some individuals with short QT syndrome have had implantation of an implantable cardioverter-defibrillatorImplantable cardioverter-defibrillator
An implantable cardioverter-defibrillator is a small battery-powered electrical impulse generator which is implanted in patients who are at risk of sudden cardiac death due to ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia. The device is programmed to detect cardiac arrhythmia and correct it...
(ICD) as a preventive action, although it has not been demonstrated that cardiac problems have occurred before deciding to implant an ICD.
A recent study has suggested the use of certain antiarrhythmic agents, particularly quinidine
Quinidine
Quinidine is a pharmaceutical agent that acts as a class I antiarrhythmic agent in the heart. It is a stereoisomer of quinine, originally derived from the bark of the cinchona tree.-Mechanism:...
, may be of benefit in individuals with short QT syndrome due to their effects on prolonging the action potential and by their action on the IK channels. Some Trial are currently under way but do not show a longer QT statistically.

