
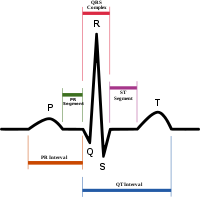
QT interval
Encyclopedia
Cardiology
Cardiology is a medical specialty dealing with disorders of the heart . The field includes diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease and electrophysiology...
, the QT interval is a measure of the time between the start of the Q wave and the end of the T wave in the heart's electrical cycle
Electrical conduction system of the heart
The normal intrinsic electrical conduction of the heart allows electrical propagation to be transmitted from the Sinoatrial Node through both atria and forward to the Atrioventricular Node. Normal/baseline physiology allows further propagation from the AV node to the ventricle or Purkinje Fibers...
. In general, the QT interval represents electrical depolarization and repolarization of the left and right ventricles. A prolonged QT interval is a biomarker for ventricular tachyarrhythmias like torsades de pointes
Torsades de pointes
Torsades de pointes, or simply torsades, is a French term that literally means "twisting of the points". It was first described by Dessertenne in 1966 and refers to a specific, rare variety of ventricular tachycardia that exhibits distinct characteristics on the electrocardiogram .- Presentation...
and a risk factor for sudden death.
Correction for heart rate
The QT interval is dependent on the heart rateHeart rate
Heart rate is the number of heartbeats per unit of time, typically expressed as beats per minute . Heart rate can vary as the body's need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide changes, such as during exercise or sleep....
in an obvious way (the faster the heart rate the shorter the QT interval) and may be adjusted to improve the detection of patients at increased risk of ventricular arrhythmia. Modern computer-based ECG machines can easily calculate a corrected QT, but this correction may not aid in the detection of patients at increased risk of arrhythmia.
The standard clinical correction is to use Bazett's formula, named after physiologist Henry Cuthbert Bazett, calculating the heart rate-corrected QT interval QTc.
Bazett's formula is as follows:
QTcB=
where QTc is the QT interval corrected for heart rate, and RR is the interval from the onset of one QRS complex
QRS complex
The QRS complex is a name for the combination of three of the graphical deflections seen on a typical electrocardiogram . It is usually the central and most visually obvious part of the tracing. It corresponds to the depolarization of the right and left ventricles of the human heart...
to the onset of the next QRS complex, measured in seconds, often derived from the heart rate (HR) as 60/HR (here QT is measured in milliseconds). However, this nonlinear formula, obtained from data in only 39 young men, is not accurate, and over-corrects at high heart rates and under-corrects at low heart rates.
Fridericia
Louis Sigurd Fridericia
Louis Sigurd Fridericia was a Danish hygienist born in Copenhagen.Louis Fridericia's family had come to Denmark in the 1750s and took the name of the Jutland town where they settled...
has published an alternative correction using the cuberoot of RR.
QTcF=
There are several other methods as well. For example a regression-based approach that had been developed by Sagie et al., as follows:
QTcL= QT + 0.154(1000-RR)
Definitions of normal QTc varies around being equal to or less than 0.40 s (≤400ms), 0.41s (≤410ms), 0.42s (≤420ms) or 0.44s (≤440ms). For risk of sudden cardiac death
Sudden Cardiac Death
Sudden cardiac death is natural death from cardiac causes, heralded by abrupt loss of consciousness within one hour of the onset of acute symptoms. Other forms of sudden death may be noncardiac in origin...
"Borderline QTc" in males is 431-450 ms, and in females 451-470 ms. An "abnormal" QTc in males is a QTc above 450 ms, and in females, above 470 ms.
If there is not a very high or low heart rate, the upper limits of QT can roughly be estimated by taking QT=QTc at a heart rate of 60 beats per minute (bpm), and subtracting 0.02s from QT for every 10bpm increase in heart rate. For example, taking normal QTc ≤ 0.42s, QT would be expected to be 0.42s or less at a heart rate of 60bpm. For a heart rate of 70 bpm, QT would roughly be expected to be equal to or below 0.40s. Likewise, for 80 bpm, QT would roughly be expected to be equal to or below 0.38s.
Measurement
The QT interval is an important ECG parameter and the identification of ECGs with long QT syndrome is of clinical importance. Considering the required standards for precision, the measurement of QT interval is subjective. This is because the end of the T wave is not always clearly defined and usually merges gradually with the baseline. QT interval in an ECG complex can be measured manually by different methods such as the threshold method, in which the end of the T wave is determined by the point at which the component of the T wave merges with the isoelectric baseline or the tangent method, in which the end of the T wave is determined by the intersection of a line extrapolated from the isoelectric baseline and the tangent line, which touches the terminal part of the T wave at the point of maximum downslope.With the increased availability of digital ECGs with simultaneous 12-channel recording, QT measurement may also done by the 'superimposed median beat' method. In the superimposed median beat method, a median ECG complex is constructed for each of the 12 leads. The 12 median beats are superimposed on each other and the QT interval is measured either from the earliest onset of the Q wave to the latest offset of the T wave or from the point of maximum convergence for the Q wave onset to the T wave offset...
Abnormal intervals
If abnormally prolonged or shortened, there is a risk of developing ventricularVentricle (heart)
In the heart, a ventricle is one of two large chambers that collect and expel blood received from an atrium towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The Atria primes the Pump...
arrhythmias.
Genetic causes
An abnormal prolonged QT interval could be due to Long QT syndromeLong QT syndrome
The long QT syndrome is a rare inborn heart condition in which delayed repolarization of the heart following a heartbeat increases the risk of episodes of torsade de pointes . These episodes may lead to palpitations, fainting and sudden death due to ventricular fibrillation...
, whereas an abnormal shortened QT interval could be due to Short QT syndrome
Short QT syndrome
Short QT syndrome is a genetic disease of the electrical system of the heart. It consists of a constellation of signs and symptoms, consisting of a short QT interval on an EKG that does not significantly change with heart rate, tall and peaked T waves, and a structurally normal heart...
.
The length of the interval was found to associate with variations in NOS1AP
NOS1AP
Nitric oxide synthase 1 adaptor protein also known as carboxyl-terminal PDZ ligand of neuronal nitric oxide synthase protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NOS1AP gene....
gene.
Due to adverse drug reactions
Prolongation of the QT interval may be due to an adverse drug reactionAdverse drug reaction
An adverse drug reaction is an expression that describes harm associated with the use of given medications at a normal dosage. ADRs may occur following a single dose or prolonged administration of a drug or result from the combination of two or more drugs...
. Many drugs such as haloperidol
Haloperidol
Haloperidol is a typical antipsychotic. It is in the butyrophenone class of antipsychotic medications and has pharmacological effects similar to the phenothiazines....
and methadone
Methadone
Methadone is a synthetic opioid, used medically as an analgesic and a maintenance anti-addictive for use in patients with opioid dependency. It was developed in Germany in 1937...
can prolong the QT interval. Some antiarrhythmic drugs, like amiodarone
Amiodarone
Amiodarone is an antiarrhythmic agent used for various types of tachyarrhythmias , both ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmias. Discovered in 1961, it was not approved for use in the United States until 1985...
or sotalol
Sotalol
Sotalol is a drug used in individuals with rhythm disturbances of the heart, and to treat hypertension in some individuals. It is a non-selective competitive β-adrenergic receptor blocker that also exhibits Class III antiarrhythmic properties by its inhibition of potassium channels...
work by getting a pharmacological QT prolongation. Additionally, some second generation of antihistamines, such as astemizole
Astemizole
Astemizole was a second generation antihistamine drug which has a long duration of action. Astemizole was discovered by Janssen Pharmaceutica in 1977...
, have this effect. Additionally, alcohol in high blood concentrations prolong the QT interval.
Due to pathological conditions
HypothyroidismHypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Iodine deficiency is the most common cause of hypothyroidism worldwide but it can be caused by other causes such as several conditions of the thyroid gland or, less commonly, the pituitary gland or...
, a condition of low function of the thyroid
Thyroid
The thyroid gland or simply, the thyroid , in vertebrate anatomy, is one of the largest endocrine glands. The thyroid gland is found in the neck, below the thyroid cartilage...
gland, can give QTc prolongation at the electrocardiogram
Electrocardiogram
Electrocardiography is a transthoracic interpretation of the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time, as detected by electrodes attached to the outer surface of the skin and recorded by a device external to the body...
. Acute hypocalcemia causes prolongation of the QT interval, which may lead to ventricular dysrhythmias.
A shortened QT can be associated with hypercalcemia.

