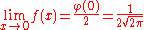
Slash distribution
Encyclopedia
In probability theory
, the slash distribution is the probability distribution
of a standard normal variate divided by an independent standard uniform variate. In other words, if the random variable
Z has a normal distribution with zero mean and unit variance
, the random variable U has a uniform distribution on [0,1] and Z and U are statistically independent, then the random variable X = Z / U has a slash distribution. The slash distribution is an example of a ratio distribution
. The distribution was named by William H. Rogers
and John Tukey
in a paper published in 1972.
The probability density function
is
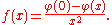
where φ(x) is the probability density function of the standard normal distribution. This is undefined at x = 0, but the discontinuity is removable:
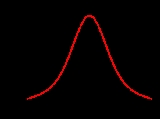
The most common use of the slash distribution is in simulation
studies. It is a useful distribution in this context because it has heavier tails than a normal distribution, but it is not as pathological
as the Cauchy distribution
.
Probability theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with analysis of random phenomena. The central objects of probability theory are random variables, stochastic processes, and events: mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic events or measured quantities that may either be single...
, the slash distribution is the probability distribution
Probability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
of a standard normal variate divided by an independent standard uniform variate. In other words, if the random variable
Random variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
Z has a normal distribution with zero mean and unit variance
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
, the random variable U has a uniform distribution on [0,1] and Z and U are statistically independent, then the random variable X = Z / U has a slash distribution. The slash distribution is an example of a ratio distribution
Ratio distribution
A ratio distribution is a probability distribution constructed as the distribution of the ratio of random variables having two other known distributions....
. The distribution was named by William H. Rogers
William H. Rogers
William H. Rogers was an English architect. His most notable building was 20 Fenchurch Street in the City of London, which was occupied by Kleinwort Benson from 1968 to 2006....
and John Tukey
John Tukey
John Wilder Tukey ForMemRS was an American statistician.- Biography :Tukey was born in New Bedford, Massachusetts in 1915, and obtained a B.A. in 1936 and M.Sc. in 1937, in chemistry, from Brown University, before moving to Princeton University where he received a Ph.D...
in a paper published in 1972.
The probability density function
Probability density function
In probability theory, a probability density function , or density of a continuous random variable is a function that describes the relative likelihood for this random variable to occur at a given point. The probability for the random variable to fall within a particular region is given by the...
is
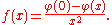
where φ(x) is the probability density function of the standard normal distribution. This is undefined at x = 0, but the discontinuity is removable:
The most common use of the slash distribution is in simulation
Simulation
Simulation is the imitation of some real thing available, state of affairs, or process. The act of simulating something generally entails representing certain key characteristics or behaviours of a selected physical or abstract system....
studies. It is a useful distribution in this context because it has heavier tails than a normal distribution, but it is not as pathological
Pathological (mathematics)
In mathematics, a pathological phenomenon is one whose properties are considered atypically bad or counterintuitive; the opposite is well-behaved....
as the Cauchy distribution
Cauchy distribution
The Cauchy–Lorentz distribution, named after Augustin Cauchy and Hendrik Lorentz, is a continuous probability distribution. As a probability distribution, it is known as the Cauchy distribution, while among physicists, it is known as the Lorentz distribution, Lorentz function, or Breit–Wigner...
.