
Simulation
Encyclopedia

Simulation is used in many contexts, such as simulation of technology
Technology
Technology is the making, usage, and knowledge of tools, machines, techniques, crafts, systems or methods of organization in order to solve a problem or perform a specific function. It can also refer to the collection of such tools, machinery, and procedures. The word technology comes ;...
for performance optimization, safety engineering
Safety engineering
Safety engineering is an applied science strongly related to systems engineering / industrial engineering and the subset System Safety Engineering...
, testing
Experiment
An experiment is a methodical procedure carried out with the goal of verifying, falsifying, or establishing the validity of a hypothesis. Experiments vary greatly in their goal and scale, but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results...
, training
Training
The term training refers to the acquisition of knowledge, skills, and competencies as a result of the teaching of vocational or practical skills and knowledge that relate to specific useful competencies. It forms the core of apprenticeships and provides the backbone of content at institutes of...
, education
Education
Education in its broadest, general sense is the means through which the aims and habits of a group of people lives on from one generation to the next. Generally, it occurs through any experience that has a formative effect on the way one thinks, feels, or acts...
, and video games. Training simulators include flight simulator
Flight simulator
A flight simulator is a device that artificially re-creates aircraft flight and various aspects of the flight environment. This includes the equations that govern how aircraft fly, how they react to applications of their controls and other aircraft systems, and how they react to the external...
s for training aircraft pilots in order to provide them with a lifelike experience
Lifelike experience
Lifelike is an adjective that relates to anything that simulates real life, in accordance with its laws. Its goal is to immerse individuals into what is called a lifelike experience. It gets as close as possible to real life behavior, appearance, senses, etc. therefore enabling its subject to...
. Simulation is also used for scientific modeling of natural systems or human systems in order to gain insight into their functioning. Simulation can be used to show the eventual real effects of alternative conditions and courses of action. Simulation is also used when the real system cannot be engaged, because it may not be accessible, or it may be dangerous or unacceptable to engage, or it is being designed but not yet built, or it may simply not exist .
Key issues in simulation include acquisition of valid source information about the relevant selection of key characteristics and behaviours, the use of simplifying approximations and assumptions within the simulation, and fidelity and validity of the simulation outcomes.
Classification and terminology

Systems theory
Systems theory is the transdisciplinary study of systems in general, with the goal of elucidating principles that can be applied to all types of systems at all nesting levels in all fields of research...
and Cybernetics
Cybernetics
Cybernetics is the interdisciplinary study of the structure of regulatory systems. Cybernetics is closely related to information theory, control theory and systems theory, at least in its first-order form...
combined with spreading use of computers across all those fields have led to some unification and a more systematic view of the concept.
Physical simulation refers to simulation in which physical objects are substituted for the real thing (some circles use the term for computer simulations modelling selected laws of physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, but this article doesn't). These physical objects are often chosen because they are smaller or cheaper than the actual object or system.
Interactive simulation is a special kind of physical simulation, often referred to as a human in the loop
Human-in-the-Loop
Human-in-the-Loop is defined as a model that requires human interaction. HITL is associated with Virtual Modeling & Simulation in the Live, Virtual, and Constructive taxonomy. HITL models may conform to Human factors requirements as is the case of a Mockup...
simulation, in which physical simulations include human operators, such as in a flight simulator or a driving simulator
Driving simulator
Driving simulators are used for entertainment as well as in training of driver's education courses taught in educational institutions and private businesses...
.
Human in the loop simulations can include a computer simulation as a so-called synthetic environment.
Computer simulation
A computer simulation (or "sim") is an attempt to model a real-life or hypothetical situation on a computer so that it can be studied to see how the system works. By changing variables in the simulation, predictionPrediction
A prediction or forecast is a statement about the way things will happen in the future, often but not always based on experience or knowledge...
s may be made about the behaviour of the system. It is a tool to virtually investigate the behaviour of the system under study.
Computer simulation has become a useful part of modeling many natural systems in physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
and biology
Biology
Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Biology is a vast subject containing many subdivisions, topics, and disciplines...
, and human systems in economics
Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
and social science (the computational sociology
Computational sociology
Computational sociology is a branch of sociology that uses computationally intensive methods to analyze and model social phenomena. Using computer simulations, artificial intelligence, complex statistical methods, and new analytic approaches like social network analysis, computational sociology...
) as well as in engineering
Engineering
Engineering is the discipline, art, skill and profession of acquiring and applying scientific, mathematical, economic, social, and practical knowledge, in order to design and build structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes that safely realize improvements to the lives of...
to gain insight into the operation of those systems. A good example of the usefulness of using computers to simulate can be found in the field of network traffic simulation
Network traffic simulation
Network traffic simulation is a process used in telecommunications engineering to measure the efficiency of a communications network.-Overview:...
. In such simulations, the model behaviour will change each simulation according to the set of initial parameters assumed for the environment.
Traditionally, the formal modeling of systems has been via a mathematical model
Mathematical model
A mathematical model is a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed mathematical modeling. Mathematical models are used not only in the natural sciences and engineering disciplines A mathematical model is a...
, which attempts to find analytical solutions enabling the prediction of the behaviour of the system from a set of parameters and initial conditions. Computer simulation is often used as an adjunct to, or substitution for, modeling systems for which simple closed form analytic solutions are not possible. There are many different types of computer simulation, the common feature they all share is the attempt to generate a sample of representative scenario
Scenario
A scenario is a synoptical collage of an event or series of actions and events. In the Commedia dell'arte it was an outline of entrances, exits, and action describing the plot of a play that was literally pinned to the back of the scenery...
s for a model in which a complete enumeration of all possible states would be prohibitive or impossible.
Several software packages exist for running computer-based simulation modeling (e.g. Monte Carlo
Monte Carlo method
Monte Carlo methods are a class of computational algorithms that rely on repeated random sampling to compute their results. Monte Carlo methods are often used in computer simulations of physical and mathematical systems...
simulation, stochastic modeling
Stochastic
Stochastic refers to systems whose behaviour is intrinsically non-deterministic. A stochastic process is one whose behavior is non-deterministic, in that a system's subsequent state is determined both by the process's predictable actions and by a random element. However, according to M. Kac and E...
, multimethod modeling) that makes all the modeling almost effortless.
Modern usage of the term "computer simulation" may encompass virtually any computer-based representation.
Computer science
In computer scienceComputer science
Computer science or computing science is the study of the theoretical foundations of information and computation and of practical techniques for their implementation and application in computer systems...
, simulation has some specialized meanings: Alan Turing
Alan Turing
Alan Mathison Turing, OBE, FRS , was an English mathematician, logician, cryptanalyst, and computer scientist. He was highly influential in the development of computer science, providing a formalisation of the concepts of "algorithm" and "computation" with the Turing machine, which played a...
used the term "simulation" to refer to what happens when a universal machine
Universal Turing machine
In computer science, a universal Turing machine is a Turing machine that can simulate an arbitrary Turing machine on arbitrary input. The universal machine essentially achieves this by reading both the description of the machine to be simulated as well as the input thereof from its own tape. Alan...
executes a state transition table (in modern terminology, a computer runs a program) that describes the state transitions, inputs and outputs of a subject discrete-state machine. The computer simulates the subject machine. Accordingly, in theoretical computer science
Theoretical computer science
Theoretical computer science is a division or subset of general computer science and mathematics which focuses on more abstract or mathematical aspects of computing....
the term simulation
Simulation preorder
In theoretical computer science a simulation preorder is a relation between state transition systems associating systems which behave in the same way in the sense that one system simulates the other....
is a relation between state transition system
State transition system
In theoretical computer science, a state transition system is an abstract machine used in the study of computation. The machine consists of a set of states and transitions between states, which may be labeled with labels chosen from a set; the same label may appear on more than one transition...
s, useful in the study of operational semantics
Operational semantics
In computer science, operational semantics is a way to give meaning to computer programs in a mathematically rigorous way. Operational semantics are classified into two categories: structural operational semantics formally describe how the individual steps of a computation take place in a...
.
Less theoretically, an interesting application of computer simulation is to simulate computers using computers. In computer architecture
Computer architecture
In computer science and engineering, computer architecture is the practical art of selecting and interconnecting hardware components to create computers that meet functional, performance and cost goals and the formal modelling of those systems....
, a type of simulator, typically called an emulator
Emulator
In computing, an emulator is hardware or software or both that duplicates the functions of a first computer system in a different second computer system, so that the behavior of the second system closely resembles the behavior of the first system...
, is often used to execute a program that has to run on some inconvenient type of computer (for example, a newly designed computer that has not yet been built or an obsolete computer that is no longer available), or in a tightly controlled testing environment (see Computer architecture simulator
Computer architecture simulator
In computer science, a computer architecture simulator, or an architectural simulator, is a piece of software to model computer devices to predict outputs and performance metrics on a given input...
and Platform virtualization). For example, simulators have been used to debug a microprogram or sometimes commercial application programs, before the program is downloaded to the target machine. Since the operation of the computer is simulated, all of the information about the computer's operation is directly available to the programmer, and the speed and execution of the simulation can be varied at will.
Simulators may also be used to interpret fault trees, or test VLSI logic designs before they are constructed. Symbolic simulation
Symbolic simulation
In computer science, a simulation is a computation of the execution of some appropriately modelled state-transition system. Typically this process models the complete state of the system at individual points in a discrete linear time frame, computing each state sequentially from its predecessor...
uses variables to stand for unknown values.
In the field of optimization
Optimization (mathematics)
In mathematics, computational science, or management science, mathematical optimization refers to the selection of a best element from some set of available alternatives....
, simulations of physical processes are often used in conjunction with evolutionary computation
Evolutionary computation
In computer science, evolutionary computation is a subfield of artificial intelligence that involves combinatorial optimization problems....
to optimize control strategies...
Simulation in education and training
Simulation is extensively used for educational purposes. It is frequently used by way of adaptive hypermediaAdaptive hypermedia
In contrast to traditional e-learning/electronic learning, e-business, and e-government systems, whereby all users are offered or even directed a standard series of hyperlinks, adaptive hypermedia tailors what the user sees to the learner's goals, abilities, interests, knowledge, etc...
.
Simulation is often used in the training
Training
The term training refers to the acquisition of knowledge, skills, and competencies as a result of the teaching of vocational or practical skills and knowledge that relate to specific useful competencies. It forms the core of apprenticeships and provides the backbone of content at institutes of...
of civilian and military personnel. This usually occurs when it is prohibitively expensive or simply too dangerous to allow trainees to use the real equipment in the real world. In such situations they will spend time learning valuable lessons in a "safe" virtual environment yet living a lifelike experience
Lifelike experience
Lifelike is an adjective that relates to anything that simulates real life, in accordance with its laws. Its goal is to immerse individuals into what is called a lifelike experience. It gets as close as possible to real life behavior, appearance, senses, etc. therefore enabling its subject to...
(or at least it is the goal). Often the convenience is to permit mistakes during training for a safety-critical system. For example, in simSchool teachers practice classroom management and teaching techniques on simulated students, which avoids "learning on the job" that can damage real students. There is a distinction, though, between simulations used for training and Instructional simulation
Instructional Simulation
- Instructional simulation or virtual learning environment :An instructional simulation, also called an educational simulation, is a simulation of some type of reality but which also includes instructional elements that help a learner explore, navigate or obtain more information about that system...
.
Training simulations
Training simulation
A training simulation is a virtual medium through which various types of skills can be acquired. Training simulations can be used in a wide variety of genres; however they are most commonly used in corporate situations to improve business awareness and management skills...
typically come in one of three categories:
- "live" simulation (where actual players use genuine systems in a real environment);
- "virtual" simulation (where actual players use simulated systems in a synthetic environment ), or
- "constructive" simulation (where simulated players use simulated systems in a synthetic environment). Constructive simulation is often referred to as "wargaming" since it bears some resemblance to table-top war gamesWargamingA wargame is a strategy game that deals with military operations of various types, real or fictional. Wargaming is the hobby dedicated to the play of such games, which can also be called conflict simulations, or consims for short. When used professionally to study warfare, it is generally known as...
in which players command armies of soldiers and equipment that move around a board.
In standardized test
Standardized test
A standardized test is a test that is administered and scored in a consistent, or "standard", manner. Standardized tests are designed in such a way that the questions, conditions for administering, scoring procedures, and interpretations are consistent and are administered and scored in a...
s, "live" simulations are sometimes called "high-fidelity", producing "samples of likely performance", as opposed to "low-fidelity", "pencil-and-paper" simulations producing only "signs of possible performance", but the distinction between high, moderate and low fidelity remains relative, depending on the context of a particular comparison.
Simulations in education are somewhat like training simulations. They focus on specific tasks. The term 'microworld' is used to refer to educational simulations which model some abstract concept rather than simulating a realistic object or environment, or in some cases model a real world environment in a simplistic way so as to help a learner develop an understanding of the key concepts. Normally, a user can create some sort of construction within the microworld that will behave in a way consistent with the concepts being modeled. Seymour Papert
Seymour Papert
Seymour Papert is an MIT mathematician, computer scientist, and educator. He is one of the pioneers of artificial intelligence, as well as an inventor of the Logo programming language....
was one of the first to advocate the value of microworlds, and the Logo
Logo (programming language)
Logo is a multi-paradigm computer programming language used in education. It is an adaptation and dialect of the Lisp language; some have called it Lisp without the parentheses. It was originally conceived and written as functional programming language, and drove a mechanical turtle as an output...
programming environment developed by Papert is one of the most famous microworlds. As another example, the Global Challenge Award
Global Challenge Award
The is an online science and engineering design program for pre-college school students from all over the world...
online STEM learning web site uses microworld simulations to teach science concepts related to global warming and the future of energy. Other projects for simulations in educations are Open Source Physics
Open Source Physics
Open Source Physics, or OSP, is a project sponsored by the National Science Foundation and Davidson College, whose mission is to spread the use of open source code libraries, tools, and compiled simulations for physics and other numerical simulations. The OSP collection provides curriculum...
, NetSim
NetSim
NetSim is a popular network simulation tool used by the academic community for teaching, network lab experimentation and research. Various technologies such as Ethernet, Wireless LAN, Wi Max, TCP, IP, etc are covered in NetSim.-History:...
etc.
Management games (or business simulations) have been finding favour in business education in recent years. Business simulations that incorporate a dynamic model enable experimentation with business strategies in a risk free environment and provide a useful extension to case study
Case study
A case study is an intensive analysis of an individual unit stressing developmental factors in relation to context. The case study is common in social sciences and life sciences. Case studies may be descriptive or explanatory. The latter type is used to explore causation in order to find...
discussions.
Social simulations may be used in social science classrooms to illustrate social and political processes in anthropology, economics, history, political science, or sociology courses, typically at the high school or university level. These may, for example, take the form of civics simulations, in which participants assume roles in a simulated society, or international relations simulations in which participants engage in negotiations, alliance formation, trade, diplomacy, and the use of force. Such simulations might be based on fictitious political systems, or be based on current or historical events. An example of the latter would be Barnard College
Barnard College
Barnard College is a private women's liberal arts college and a member of the Seven Sisters. Founded in 1889, Barnard has been affiliated with Columbia University since 1900. The campus stretches along Broadway between 116th and 120th Streets in the Morningside Heights neighborhood in the borough...
's "Reacting to the Past" series of educational simulations. The "Reacting to the Past" series also includes simulation games that address science education.
In recent years, there has been increasing use of social simulations for staff training in aid and development agencies. The Carana simulation, for example, was first developed by the United Nations Development Programme
United Nations Development Programme
The United Nations Development Programme is the United Nations' global development network. It advocates for change and connects countries to knowledge, experience and resources to help people build a better life. UNDP operates in 177 countries, working with nations on their own solutions to...
, and is now used in a very revised form by the World Bank
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans to developing countries for capital programmes.The World Bank's official goal is the reduction of poverty...
for training staff to deal with fragile and conflict-affected countries.
Common User Interaction Systems for Virtual Simulations
Virtual Simulations represent a specific category of simulation that utilizes simulation equipment to create a simulated world for the user. Virtual Simulations allow users to interact with a virtual world. Virtual worlds operate on platforms of integrated software and hardware components. In this manner, the system can accept input from the user (e.g., body tracking, voice/sound recognition, physical controllers) and produce output to the user (e.g., visual display, aural display, haptic display) . Virtual Simulations use the aforementioned modes of interaction to produce a sense of immersion for the user.Virtual Simulation Input Hardware
There is a wide variety of input hardware available to accept user input for virtual simulations. The following list briefly describes several of them:Body Tracking The motion capture method is often used to record the user’s movements and translate the captured data into inputs for the virtual simulation. For example, if a user physically turns their head, the motion would be captured by the simulation hardware in some way and translated to a corresponding shift in view within the simulation.
- Capture Suits and/or gloves may be used to capture movements of users body parts. The systems may have sensors incorporated inside them to sense movements of different body parts (e.g., fingers). Alternatively, these systems may have exterior tracking devices or marks that can be detected by external ultrasound, optical receivers or electromagnetic sensors. Internal inertial sensors are also available on some systems. The units may transmit data either wirelessly or through cables.
- Eye trackers can also be used to detect eye movements so that the system can determine precisely where a user is looking at any given instant.
Physical Controllers Physical controllers provide input to the simulation only through direct manipulation by the user. In virtual simulations, tactile feedback from physical controllers is highly desirable in a number of simulation environments.
- Omni directional treadmills can be used to capture the users locomotion as they walk or run.
- High fidelity instrumentation such as instrument panels in virtual aircraft cockpits provides users with actual controls to raise the level of immersion. For example, pilots can use the actual global positioning system controls from the real device in a simulated cockpit to help them practice procedures with the actual device in the context of the integrated cockpit system.
Voice/Sound Recognition This form of interaction may be used either to interact with agents within the simulation (e.g., virtual people) or to manipulate objects in the simulation (e.g., information). Voice interaction presumably increases the level of immersion for the user.
- Users may use headsets with boom microphones, lapel microphones or the room may be equipped with strategically located microphones.
Current Research into User Input Systems
Research in future input systems hold a great deal of promise for virtual simulations. Systems such as brain-computer interfaces (BCIs)Brain-computer interface
Brain-computer interface
A brain–computer interface , sometimes called a direct neural interface or a brain–machine interface , is a direct communication pathway between the brain and an external device...
offer the ability to further increase the level of immersion for virtual simulation users. Lee, Keinrath, Scherer, Bischof, Pfurtscheller proved that naïve subjects could be trained to use a BCI to navigate a virtual apartment with relative ease. Using the BCI, the authors found that subjects were able to freely navigate the virtual environment with relatively minimal effort. It is possible that these types of systems will become standard input modalities in future virtual simulation systems.
Virtual Simulation Output Hardware
There is a wide variety of output hardware available to deliver stimulus to users in virtual simulations. The following list briefly describes several of them:Visual Display Visual displays provide the visual stimulus to the user.
- Stationary displays can vary from a conventional desktop display to 360-degree wrap around screens to stereo three-dimensional screens. Conventional desktop displays can vary in size from 15 to 60+ inches. Wrap around screens are typically utilized in what is known as a Cave Automatic Virtual Environment (CAVE) Cave Automatic Virtual EnvironmentCave Automatic Virtual EnvironmentA Cave Automatic Virtual Environment is an immersive virtual reality environment where projectors are directed to three, four, five or six of the walls of a room-sized cube...
. Stereo three-dimensional screens produce three-dimensional images either with or without special glasses—depending on the design. - Head mounted displays (HMDs) have small displays that are mounted on headgear worn by the user. These systems are connected directly into the virtual simulation to provide the user with a more immersive experience. Weight, update rates and field of view are some of the key variables that differentiate HMDs. Naturally, heavier HMDs are undesirable as they cause fatigue over time. If the update rate is too slow, the system is unable to update the displays fast enough to correspond with a quick head turn by the user. Slower update rates tend to cause simulation sickness and disrupt the sense of immersion. Field of view or the angular extent of the world that is seen at a given moment Field of viewField of viewThe field of view is the extent of the observable world that is seen at any given moment....
can vary from system to system and has been found to affect the users sense of immersion.
Aural Display Several different types of audio systems exist to help the user hear and localize sounds spatially. Special software can be used to produce 3D audio effects 3D audio to create the illusion that sound sources are placed within a defined three-dimensional space around the user.
- Stationary conventional speaker systems may be used provide dual or multi-channel surround sound. However, external speakers are not as effective as headphones in producing 3D audio effects.
- Conventional headphones offer a portable alternative to stationary speakers. They also have the added advantages of masking real world noise and facilitate more effective 3D audio sound effects.
Haptic Display These displays provide sense of touch to the user Haptic technology. This type of output is sometimes referred to as force feedback.
- Tactile Tile Displays use different types of actuators such as inflatable bladders, vibrators, low frequency sub-woofers, pin actuators and/or thermo-actuators to produce sensations for the user.
- End Effector Displays can respond to users inputs with resistance and force. These systems are often used in medical applications for remote surgeries that employ robotic instruments.
Vestibular Display These displays provide a sense of motion to the user Motion simulator
Motion simulator
A motion simulator or motion platform is a mechanism that encapsulates occupants and creates the effect/feelings of being in a moving vehicle...
. They often manifest as motion bases for virtual vehicle simulation such as driving simulators or flight simulators. Motion bases are fixed in place but use actuators to move the simulator in ways that can produce the sensations pitching, yawing or rolling. The simulators can also move in such a way as to produce a sense of acceleration on all axes (e.g., the motion base can produce the sensation of falling).
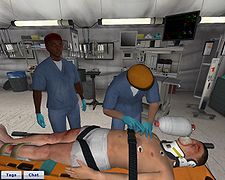
Clinical healthcare simulators
Medical simulators are increasingly being developed and deployed to teach therapeutic and diagnostic procedures as well as medical concepts and decision making to personnel in the health professions. Simulators have been developed for training procedures ranging from the basics such as blood draw, to laparoscopic surgery and trauma care. They are also important to help on prototyping new devices for biomedical engineering problems. Currently, simulators are applied to research and development of tools for new therapies, treatments and early diagnosis in medicine.Many medical simulators involve a computer connected to a plastic simulation of the relevant
anatomy. Sophisticated simulators of this type employ a life size mannequin that responds to injected drugs and can be programmed to create simulations of life-threatening emergencies.
In other simulations, visual components of the procedure are reproduced by computer graphics
Computer graphics
Computer graphics are graphics created using computers and, more generally, the representation and manipulation of image data by a computer with help from specialized software and hardware....
techniques, while touch-based components are reproduced by haptic feedback devices combined with physical simulation routines computed in response to the user's actions. Medical simulations of this sort will often use 3D CT
Computed tomography
X-ray computed tomography or Computer tomography , is a medical imaging method employing tomography created by computer processing...
or MRI scans of patient data to enhance realism. Some medical simulations are developed to be widely distributed (such as web-enabled simulations that can be viewed via standard web browsers) and can be interacted with using standard computer interfaces, such as the keyboard
Computer keyboard
In computing, a keyboard is a typewriter-style keyboard, which uses an arrangement of buttons or keys, to act as mechanical levers or electronic switches...
and mouse.
Another important medical application of a simulator — although, perhaps, denoting a slightly different meaning of simulator — is the use of a placebo
Placebo
A placebo is a simulated or otherwise medically ineffectual treatment for a disease or other medical condition intended to deceive the recipient...
drug, a formulation that simulates the active drug in trials of drug efficacy (see Placebo (origins of technical term)).
Improving Patient Safety through New Innovations
Patient safety is a concern in the medical industry. Patients have been known to suffer injuries and even death due to management error, and lack of using best standards of care and training. According to Building a National Agenda for Simulation-Based Medical Education (Eder-Van Hook, Jackie, 2004) , “A health care provider’s ability to react prudently in an unexpected situation is one of the most critical factors in creating a positive outcome in medical emergency, regardless of whether it occurs on the battlefield, freeway, or hospital emergency room.” simulation. Eder-Van Hook (2004) also noted that medical errors kill up to 98,000 with an estimated cost between $37 and $50 million and $17 to $29 billion for preventable adverse events dollars per year. “Deaths due to preventable adverse events exceed deaths attributable to motor vehicle accidents, breast cancer, or AIDS” Eder-Van Hook (2004). With these types of statistics it is no wonder that improving patient safety is a prevalent concern in the industry.New innovative simulation training solutions are now being used to train medical professionals in an attempt to reduce the number of safety concerns that have adverse effects on the patients. However, according to the article Does Simulation Improve Patient Safety? Self-efficacy, Competence, Operational Performance, and Patient Safety (Nishisaki A., Keren R., and Nadkarni, V., 2007), the jury is still out. Nishisaki states that “There is good evidence that simulation training improves provider and team self-efficacy and competence on manikins. There is also good evidence that procedural simulation improves actual operational performance in clinical settings. However, no evidence yet shows that crew resource management training through simulation, despite its promise, improves team operational performance at the bedside. Also, no evidence to date proves that simulation training actually improves patient outcome. Even so, confidence is growing in the validity of medical simulation as the training tool of the future.” This could be because there are not enough research studies yet conducted to effectively determine the success of simulation initiatives to improve patient safety. Examples of [recently implemented] research simulations used to improve patient care [and its funding] can be found at Improving Patient Safety through Simulation Research (US Department of Human Health Services) http://www.ahrq.gov/qual/simulproj.htm.
One such attempt to improve patient safety through the use of simulations training is pediatric care to deliver just-in-time service or/and just-in-place. This training consists of 20 minutes of simulated training just before workers report to shift. It is hoped that the recentness of the training will increase the positive and reduce the negative results that have generally been associated with the procedure. The purpose of this study is to determine if just-in-time training improves patient safety and operational performance of orotracheal intubation and decrease occurrences of undesired associated events and “to test the hypothesis that high fidelity simulation may enhance the training efficacy and patient safety in simulation settings.” The conclusion as reported in Abstract P38: Just-In-Time Simulation Training Improves ICU Physician Trainee Airway Resuscitation Participation without Compromising Procedural Success or Safety (Nishisaki A., 2008), were that simulation training improved resident participation in real cases; but did not sacrifice the quality of service. It could be therefore hypothesized that by increasing the number of highly trained residents through the use of simulation training, that the simulation training does in fact increase patient safety. This hypothesis would have to be researched for validation and the results may or may not generalize to other situations.
History of simulation in healthcare
The first medical simulators were simple models of human patients.Since antiquity, these representations in clay and stone were used to demonstrate clinical features of disease states and their effects on humans. Models have been found from many cultures and continents. These models have been used in some cultures (e.g., Chinese culture) as a "diagnostic
Medical diagnosis
Medical diagnosis refers both to the process of attempting to determine or identify a possible disease or disorder , and to the opinion reached by this process...
" instrument, allowing women to consult male physicians while maintaining social laws of modesty. Models are used today to help students learn the anatomy
Anatomy
Anatomy is a branch of biology and medicine that is the consideration of the structure of living things. It is a general term that includes human anatomy, animal anatomy , and plant anatomy...
of the musculoskeletal system and organ systems.
Type of models
Active models- Active models that attempt to reproduce living anatomy or physiology are recent developments. The famous “Harvey” mannequin was developed at the University of MiamiUniversity of MiamiThe University of Miami is a private, non-sectarian university founded in 1925 with its main campus in Coral Gables, Florida, a medical campus in Miami city proper at Civic Center, and an oceanographic research facility on Virginia Key., the university currently enrolls 15,629 students in 12...
and is able to recreate many of the physical findings of the cardiologyCardiologyCardiology is a medical specialty dealing with disorders of the heart . The field includes diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease and electrophysiology...
examination, including palpationPalpationPalpation is used as part of a physical examination in which an object is felt to determine its size, shape, firmness, or location...
, auscultationAuscultationAuscultation is the term for listening to the internal sounds of the body, usually using a stethoscope...
, and electrocardiography.
Interactive models
- More recently, interactive models have been developed that respond to actions taken by a student or physician. Until recently, these simulations were two dimensional computer programs that acted more like a textbook than a patient. Computer simulations have the advantage of allowing a student to make judgements, and also to make errors. The process of iterative learning through assessment, evaluation, decision making, and error correction creates a much stronger learning environment than passive instruction.
Computer simulators
- Simulators have been proposed as an ideal tool for assessment of students for clinical skills. For patients, "cybertherapy" can be used for sessions simulating traumatic expericences, from fear of heights to social anxiety.
- Programmed patients and simulated clinical situations, including mock disaster drills, have been used extensively for education and evaluation. These “lifelike” simulations are expensive, and lack reproducibility. A fully functional "3Di" simulator would be the most specific tool available for teaching and measurement of clinical skills. Gaming platformsGame engineA game engine is a system designed for the creation and development of video games. There are many game engines that are designed to work on video game consoles and personal computers...
have been applied to create these virtual medical environments to create an interactive method for learning and application of information in a clinical context.
- Immersive disease state simulations allow a doctor or HCP to experience what a disease actually feels like. Using sensors and transducers symptomatic effects can be delivered to a participant allowing them to experience the patients disease state.
- Such a simulator meets the goals of an objective and standardized examination for clinical competence. This system is superior to examinations that use "standard patientsSimulated patientA simulated patient, standardized patient or sample patient , in health care, is an individual who is trained to act as a real patient in order to simulate a set of symptoms or problems. Simulated patients have been successfully used in medical education, nursing education, evaluation, and...
" because it permits the quantitative measurement of competence, as well as reproducing the same objective findings.
Simulation in entertainment
Entertainment simulation is a term that encompasses many large and popular industries such as filmFilm
A film, also called a movie or motion picture, is a series of still or moving images. It is produced by recording photographic images with cameras, or by creating images using animation techniques or visual effects...
, television
Television
Television is a telecommunication medium for transmitting and receiving moving images that can be monochrome or colored, with accompanying sound...
, video games (including serious game
Serious game
A serious game is a game designed for a primary purpose other than pure entertainment. The "serious" adjective is generally prepended to refer to products used by industries like defense, education, scientific exploration, health care, emergency management, city planning, engineering, religion,...
s) and rides in theme parks. Although modern simulation is thought to have its roots in training and the military, in the 20th century it also became a conduit for enterprises which were more hedonistic in nature. Advances in technology in the 1980s and 1990s caused simulation to become more widely used and it began to appear in movies such as Jurassic Park
Jurassic Park (film)
Jurassic Park is a 1993 American science fiction adventure film directed by Steven Spielberg. The film is based on the novel of the same name by Michael Crichton. It stars Sam Neill, Laura Dern, Jeff Goldblum, Richard Attenborough, Martin Ferrero, and Bob Peck...
(1993) and in computer-based games such as Atari’s Battlezone
Battlezone
Battlezone is an arcade game from Atari released in 1980. It displays a wireframe view on a horizontal black and white vector monitor...
.
Early History (1940’s and 50’s)
The first simulation game may have been created as early as 1947 by Thomas T. Goldsmith Jr. and Estle Ray Mann. This was a straightforward game that simulated a missile being fired at a target. The curve of the missile and its speed could be adjusted using several knobs. In 1958 a computer game called “Tennis for TwoTennis for Two
Tennis for Two was a game developed in 1958 on an analog computer, which simulates a game of tennis or ping pong on an oscilloscope. Created by American physicist William Higinbotham, it is important in the history of video games as one of the first electronic games to use a graphical...
” was created by Willy Higginbotham which simulated a tennis game between two players who could both play at the same time using hand controls and was displayed on an oscilloscope. This was one of the first electronic video games to use a graphical display.
Modern Simulation (1980’s-present)
Advances in technology in the 1980s made the computer more affordable and more capable than they were in previous decades which facilitated the rise of computer gaming. The first video game consoleVideo game console
A video game console is an interactive entertainment computer or customized computer system that produces a video display signal which can be used with a display device to display a video game...
s released in the 1970s and early 1980s fell prey to the industry crash in 1983, but in 1985, Nintendo
Nintendo
is a multinational corporation located in Kyoto, Japan. Founded on September 23, 1889 by Fusajiro Yamauchi, it produced handmade hanafuda cards. By 1963, the company had tried several small niche businesses, such as a cab company and a love hotel....
released the Nintendo Entertainment System (NES) which became the best selling console in video game history. In the 1990s, computer games became widely popular with the release of such game as The Sims
The Sims
The Sims is a strategic life-simulation computer game developed by Maxis and published by Electronic Arts. Its development was led by game designer Will Wright, also known for developing SimCity...
and Command and Conquer and the still increasing power of desktop computers. Today, computer simulation games such as World of Warcraft
World of Warcraft
World of Warcraft is a massively multiplayer online role-playing game by Blizzard Entertainment. It is the fourth released game set in the fantasy Warcraft universe, which was first introduced by Warcraft: Orcs & Humans in 1994...
are played by millions of people around the world.
Computer-generated imagery
Computer-generated imagery
Computer-generated imagery is the application of the field of computer graphics or, more specifically, 3D computer graphics to special effects in art, video games, films, television programs, commercials, simulators and simulation generally, and printed media...
was used in film to simulate objects as early as 1976, though in 1982, the film Tron
Tron
-Film:*Tron , a franchise that began in 1982 with the Walt Disney Pictures film Tron** Tron , a 1982 science fiction film by Disney, starring Jeff Bridges, Bruce Boxleitner, Cindy Morgan, Dan Shor and David Warner...
was the first film to use computer-generated imagery for more than a couple of minutes. However, the commercial failure of the movie may have caused the industry to step away from the technology. In 1993, the film Jurassic Park
Jurassic Park (film)
Jurassic Park is a 1993 American science fiction adventure film directed by Steven Spielberg. The film is based on the novel of the same name by Michael Crichton. It stars Sam Neill, Laura Dern, Jeff Goldblum, Richard Attenborough, Martin Ferrero, and Bob Peck...
became the first popular film to use computer-generated graphics extensively, integrating the simulated dinosaurs almost seamlessly into live action scenes. This event transformed the film industry; in 1995, the film Toy Story
Toy Story
Toy Story is a 1995 American computer-animated film released by Walt Disney Pictures. It is Pixar's first feature film as well as the first ever feature film to be made entirely with CGI. The film was directed by John Lasseter and featuring the voices of Tom Hanks and Tim Allen...
was the first film to use only computer-generated images and by the new millennium computer generated graphics were the leading choice for special effects in films.
Simulators have been used for entertainment since the Link Trainer
Link Trainer
The term Link Trainer, also known as the "Blue box" and "Pilot Trainer" is commonly used to refer to a series of flight simulators produced between the early 1930s and early 1950s by Ed Link, based on technology he pioneered in 1929 at his family's business in Binghamton, New York...
in the 1930s. The first modern simulator ride to open at a theme park was Disney’s Star Tours
Star Tours
Star Tours is a motion simulator attraction currently operating at Tokyo Disneyland and Disneyland Park at Disneyland Paris. The ride is based on the successful Star Wars film series created by George Lucas, making it the first Disney attraction based on a non-Disney produced film.The first...
in 1987 soon followed by Universal’s The Funtastic World of Hanna-Barbera
The Funtastic World of Hanna-Barbera
The Funtastic World of Hanna-Barbera was a syndicated block of animated television programming and new original shows produced by Hanna-Barbera Productions.-Format:...
in 1990 which was the first ride to be done entirely with computer graphics.
Computer and video games
Simulation games, as opposed to other genres of video and computer games, represent or simulate an environment accurately. Moreover, they represent the interactions between the playable characters and the environment realistically. These kinds of games are usually more complex in terms of game play. Simulation games have become incredibly popular among people of all ages. Popular simulation games include SimCitySimCity
SimCity is a critically acclaimed city-building simulation video game, first released in 1989, and designed by Will Wright. SimCity was Maxis' first product, which has since been ported into various personal computers and game consoles, and spawned several sequels including SimCity 2000 in 1994,...
, Tiger Woods PGA Tour
Tiger Woods PGA Tour
Tiger Woods PGA TOUR is a series of video games developed and published by Electronic Arts featuring professional golfer Tiger Woods, among other pros on the PGA Tour....
and Virtonomics
Virtonomics
Virtonomics is a browser-based multiplayer economic game. Virtonomics is a business simulation, simulating economics. It allows users to study the basics of management. The game is turn-based and the conversion of a game situation occurs once a day.-Gameplay:The game resembles the game Capitalism 2...
.
Film
Computer-generated imagery is “the application of the field of 3D computer graphics to special effects”. This technology is used for visual effects because they are high in quality, controllable, and can create effects that would not be feasible using any other technology either because of cost, resources or safety. Computer-generated graphics can be seen in many live action movies today, especially those of the action genre. Further, computer generated imagery has almost completely supplanted hand-drawn animation in children's movies which are increasingly computer-generated only. Examples of movies that use computer-generated imagery include Finding NemoFinding Nemo
Finding Nemo is a 2003 American comi-drama animated film written by Andrew Stanton, directed by Andrew Stanton and Lee Unkrich and produced by Pixar. It tells the story of the overly protective clownfish Marlin who, along with a regal tang called Dory , searches for his abducted son Nemo...
, 300
300 (film)
300 is a 2007 American fantasy action film based on the 1998 comic series of the same name by Frank Miller. It is a fictionalized retelling of the Battle of Thermopylae. The film was directed by Zack Snyder, while Miller served as executive producer and consultant...
and Iron Man
Iron Man (film)
Iron Man is a 2008 American superhero film based on the Marvel Comics character of the same name. Directed by Jon Favreau, the film stars Robert Downey, Jr. as Tony Stark, an industrialist and master engineer who builds a powered exoskeleton and becomes the technologically advanced superhero, Iron...
.
Theme park rides
Simulator rides are the progeny of military training simulators and commercial simulators, but they are different in a fundamental way. While military training simulators react realistically to the input of the trainee in real time, ride simulators only feel like they move realistically and move according to prerecorded motion scripts. One of the first simulator rides, Star Tours, which cost $32 million, used a hydraulic motion based cabin. The movement was programmed by a joystick. Today’s simulator rides, such as The Amazing Adventures of Spider-ManThe Amazing Adventures of Spider-Man
The Amazing Adventures of Spider-Man is a theme park ride located in Islands of Adventure, in Orlando, Florida and Universal Studios Japan. Built for Islands of Adventure's opening in 1999, the attraction is a hybrid ride combining special roving motion vehicles with 3-D projection, elaborate...
include elements to increase the amount of immersion experienced by the riders such as: 3D imagery, physical effects (spraying water or producing scents), and movement through an environment. Examples of simulation rides include
Mission Space and The Simpsons Ride
The Simpsons Ride
The Simpsons Ride is a simulator ride featured at the Universal Studios Florida and Universal Studios Hollywood theme parks. The ride is based on the animated television series The Simpsons. It was first announced in 2007 and replaced the Back to the Future: The Ride at both locations...
. There are many simulation rides at themeparks like Disney, Universal etc., Examples are Flint Stones, Earth Quake, Time Machine
Time Machine
A time machine is a fictional/hypothetical device used to achieve time travel. The term may also refer to:-Novels and films:* The Time Machine, an 1895 novel by H. G...
, King Kong
King Kong
King Kong is a fictional character, a giant movie monster resembling a gorilla, that has appeared in several movies since 1933. These include the groundbreaking 1933 movie, the film remakes of 1976 and 2005, as well as various sequels of the first two films...
.
Simulation and Manufacturing
Manufacturing represents one of the most important applications of Simulation. This technique represents a valuable tool used by engineers when evaluating the effect of capital investment in equipments and physical facilities like factory plants, warehouses, and distribution centers. Simulation can be used to predict the performance of an existing or planned system and to compare alternative solutions for a particular design problem.Another important goal of manufacturing-simulations is to quantify system performance. Common measures of system performance include the following:
- Throughput under average and peak loads;
- System cycle time (how long it take to produce one part);
- Utilization of resource, labor, and machines;
- Bottlenecks and choke points;
- Queuing at work locations;
- Queuing and delays caused by material-handling devices and systems;
- WIP storage needs;
- Staffing requirements;
- Effectiveness of scheduling systems;
- Effectiveness of control systems.
Automobile simulator

The simulator provides a constructive experience for the novice driver and enables more complex exercises to be undertaken by the more mature driver. For novice drivers, truck simulators provide an opportunity to begin their career by applying best practice. For mature drivers, simulation provides the ability to enhance good driving or to detect poor practice and to suggest the necessary steps for remedial action. For companies, it provides an opportunity to educate staff in the driving skills that achieve reduced maintenance costs, improved productivity and, most importantly, to ensure the safety of their actions in all possible situations.
Biomechanics simulators
A biomechanics simulator is used to analyze walking dynamics, study sports performance, simulate surgical procedures, analyze joint loads, design medical devices, and animate human and animal movement.A neuromechanical simulator that combines biomechanical and biologically realistic neural network simulation. It allows the user to test hypotheses on the neural basis of behavior in a physically accurate 3-D virtual environment.
City and urban simulation
A city simulator can be a city-building gameCity-building game
City-building games are a genre of strategy computer game where players act as the overall planner and leader of a city, looking down on it from above, and being responsible for its growth and management...
but can also be a tool used by urban planners to understand how cities are likely to evolve in response to various policy decisions. AnyLogic
AnyLogic
-History of AnyLogic:In the beginning of 1990s there was a big interest in the mathematical approach to modeling and simulation of parallel processes. This approach may be applied to the analysis of correctness of parallel and distributed programs...
is an example of modern, large-scale urban simulators designed for use by urban planners. City simulators are generally agent
Agent (economics)
In economics, an agent is an actor and decision maker in a model. Typically, every agent makes decisions by solving a well or ill defined optimization/choice problem. The term agent can also be seen as equivalent to player in game theory....
-based simulations with explicit representations for land use and transportation. UrbanSim
UrbanSim
UrbanSim is an Open Source urban simulation system designed by Paul Waddell and developed with numerous collaborators to support metropolitan land use, transportation, and environmental planning. It has been distributed on the web since 1998, with regular revisions and updates, from...
and LEAM
Leam
Leam is a hamlet in the English county of Derbyshire. There are a number of buildings, which once formed a single estate.Leam is due south of Hathersage, close to Grindleford. There are several inhabitants....
are examples of large-scale urban simulation models that are used by metropolitan planning agencies and military bases for land use and transportation planning.
Classroom of the future
The "classroom of the future" will probably contain several kinds of simulators, in addition to textual and visual learning tools. This will allow students to enter the clinical years better prepared, and with a higher skill level. The advanced student or postgraduate will have a more concise and comprehensive method of retraining — or of incorporating new clinical procedures into their skill set — and regulatory bodies and medical institutions will find it easier to assess the proficiency and competencyCompetence (human resources)
Competence is the ability of an individual to perform a job properly. A competency is a set of defined behaviors that provide a structured guide enabling the identification, evaluation and development of the behaviors in individual employees. As defined, the term "competence" first appeared in...
of individuals.
The classroom of the future will also form the basis of a clinical skills unit for continuing education of medical personnel; and in the same way that the use of periodic flight training assists airline pilots, this technology will assist practitioners throughout their career.
The simulator will be more than a "living" textbook, it will become an integral a part of the practice of medicine. The simulator environment will also provide a standard platform for curriculum development in institutions of medical education.
Communication Satellite Simulation
Modern satellite communications systems (SatComSATCOM
SATCOM or Satcom may refer to:* Short for Satellite Communications and used frequently in the context of VSAT * Communications satellites or comsats...
) are often large and complex with many interacting parts and elements. In addition, the need for broadband connectivity on a moving vehicle has increased dramatically in the past few years for both commercial and military applications. To accurately predict and deliver high quality of service, satcom
SATCOM
SATCOM or Satcom may refer to:* Short for Satellite Communications and used frequently in the context of VSAT * Communications satellites or comsats...
system designers have to factor in terrain as well as atmospheric and meteorological conditions in their planning. To deal with such complexity, system designers and operators increasingly turn towards computer models of their systems to simulate real world operational conditions and gain insights in to usability and requirements prior to final product sign-off. Modeling improves the understanding of the system by enabling the SatCom system designer or planner to simulate real world performance by injecting the models with multiple hypothetical atmospheric and environmental conditions.
Digital Lifecycle Simulation
The research firm Aberdeen Group has found that nearly all best-in-class manufacturers use simulation early in the design process as compared to 3 or 4 laggards who do not.
The successful use of Simulation, early in the lifecycle, has been largely driven by increased integration of simulation tools with the entire CAD, CAM and PLM solution-set. Simulation solutions can now function across the extended enterprise in a multi-CAD environment, and include solutions for managing simulation data and processes and ensuring that simulation results are made part of the product lifecycle history. The ability to use simulation across the entire lifecycle has been enhanced through improved user interfaces such as tailorable user interfaces and "wizards" which allow all appropriate PLM participants to take part in the simulation process.
Disaster Preparedness and Simulation Training
Simulation training has become a method for preparing people for disasters. Simulations can replicate emergency situations and track how learners respond thanks to a lifelike experienceLifelike experience
Lifelike is an adjective that relates to anything that simulates real life, in accordance with its laws. Its goal is to immerse individuals into what is called a lifelike experience. It gets as close as possible to real life behavior, appearance, senses, etc. therefore enabling its subject to...
. Disaster preparedness simulations can involve training on how to handle terrorism
Terrorism
Terrorism is the systematic use of terror, especially as a means of coercion. In the international community, however, terrorism has no universally agreed, legally binding, criminal law definition...
attacks, natural disasters, pandemic
Pandemic
A pandemic is an epidemic of infectious disease that is spreading through human populations across a large region; for instance multiple continents, or even worldwide. A widespread endemic disease that is stable in terms of how many people are getting sick from it is not a pandemic...
outbreaks, or other life-threatening emergencies.
One organization that has used simulation training for disaster preparedness is CADE (Center for Advancement of Distance Education). CADE has used a video game to prepare emergency workers for multiple types of attacks. As reported by News-Medical.Net, ”The video game is the first in a series of simulations to address bioterrorism, pandemic flu, smallpox and other disasters that emergency personnel must prepare for.” Developed by a team from the University of Illinois at Chicago
University of Illinois at Chicago
The University of Illinois at Chicago, or UIC, is a state-funded public research university located in Chicago, Illinois, United States. Its campus is in the Near West Side community area, near the Chicago Loop...
(UIC), the game allows learners to practice their emergency skills in a safe, controlled environment.
The Emergency Simulation Program (ESP) at the British Columbia Institute of Technology (BCIT), Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada is another example of an organization that uses simulation to train for emergency situations. ESP uses simulation to train on the following situations: forest fire fighting, oil or chemical spill response, earthquake response, law enforcement, municipal fire fighting, hazardous material handling, military training, and response to terrorist attack One feature of the simulation system is the implementation of “Dynamic Run-Time Clock,” which allows simulations to run a 'simulated' time frame, 'speeding up' or 'slowing down' time as desired” Additionally, the system allows session recordings, picture-icon based navigation, file storage of individual simulations, multimedia components, and launch external applications.
At the University of Québec in Chicoutimi, a research team at the outdoor research and expertise laboratory (Laboratoire d'Expertise et de Recherche en Plein Air - LERPA) specializes in using wilderness backcountry accident simulations to verify emergency response coordination.
Instructionally, the benefits of emergency training through simulations are that learner performance can be tracked through the system. This allows the developer to make adjustments as necessary or alert the educator on topics that may require additional attention. Other advantages are that the learner can be guided or trained on how to respond appropriately before continuing to the next emergency segment—this is an aspect that may not be available in the live-environment. Some emergency training simulators also allows for immediate feedback, while other simulations may provide a summary and instruct the learner to engage in the learning topic again.
In a live-emergency situation, emergency responders do not have time to waste. Simulation-training in this environment provides an opportunity for learners to gather as much information as they can and practice their knowledge in a safe environment. They can make mistakes without risk of endangering lives and be given the opportunity to correct their errors to prepare for the real-life emergency.
Engineering, technology or process simulation
Simulation is an important feature in engineering systems or any system that involves many processes. For example in electrical engineeringElectrical engineering
Electrical engineering is a field of engineering that generally deals with the study and application of electricity, electronics and electromagnetism. The field first became an identifiable occupation in the late nineteenth century after commercialization of the electric telegraph and electrical...
, delay lines may be used to simulate propagation delay
Propagation delay
Propagation delay is a technical term that can have a different meaning depending on the context. It can relate to networking, electronics or physics...
and phase shift caused by an actual transmission line
Transmission line
In communications and electronic engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable designed to carry alternating current of radio frequency, that is, currents with a frequency high enough that its wave nature must be taken into account...
. Similarly, dummy load
Dummy load
A dummy load is a device used to simulate an electrical load, usually for testing purposes.-Radio:In radio this device is also known as a dummy antenna or a radio frequency termination. It is a device used in place of an antenna to aid in testing a radio transmitter...
s may be used to simulate impedance
Electrical impedance
Electrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
without simulating propagation, and is used in situations where propagation is unwanted. A simulator may imitate only a few of the operations and functions of the unit it simulates. Contrast with: emulate
Emulator
In computing, an emulator is hardware or software or both that duplicates the functions of a first computer system in a different second computer system, so that the behavior of the second system closely resembles the behavior of the first system...
.
Most engineering simulations entail mathematical modeling and computer assisted investigation. There are many cases, however, where mathematical modeling is not reliable. Simulation of fluid dynamics problems often require both mathematical and physical simulations. In these cases the physical models require dynamic similitude
Similitude (model)
Similitude is a concept applicable to the testing of engineering models. A model is said to have similitude with the real application if the two share geometric similarity, kinematic similarity and dynamic similarity...
. Physical and chemical simulations have also direct realistic uses, rather than research uses; in chemical engineering
Chemical engineering
Chemical engineering is the branch of engineering that deals with physical science , and life sciences with mathematics and economics, to the process of converting raw materials or chemicals into more useful or valuable forms...
, for example, process simulation
Process simulation
Process simulation is used for the design, development, analysis, and optimization of technical processes and is mainly applied to chemical plants and chemical processes, but also to power stations, and similar technical facilities.- Main principle :...
s are used to give the process parameters immediately used for operating chemical plants, such as oil refineries.
Economics simulation
In economicsEconomics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
and especially macroeconomics
Macroeconomics
Macroeconomics is a branch of economics dealing with the performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of the whole economy. This includes a national, regional, or global economy...
, the effects of proposed policy actions, such as fiscal policy
Fiscal policy
In economics and political science, fiscal policy is the use of government expenditure and revenue collection to influence the economy....
changes or monetary policy
Monetary policy
Monetary policy is the process by which the monetary authority of a country controls the supply of money, often targeting a rate of interest for the purpose of promoting economic growth and stability. The official goals usually include relatively stable prices and low unemployment...
changes, are simulated in order to judge their desirability. A mathematical model of the economy, having been fitted to historical economic data, is used as a proxy for the actual economy; proposed values of government spending
Government spending
Government spending includes all government consumption, investment but excludes transfer payments made by a state. Government acquisition of goods and services for current use to directly satisfy individual or collective needs of the members of the community is classed as government final...
, taxation, open market operations, etc. are used as inputs to the simulation of the model, and various variables of interest such as the inflation rate
Inflation rate
In economics, the inflation rate is a measure of inflation, the rate of increase of a price index . It is the percentage rate of change in price level over time. The rate of decrease in the purchasing power of money is approximately equal.The inflation rate is used to calculate the real interest...
, the unemployment rate, the balance of trade
Balance of trade
The balance of trade is the difference between the monetary value of exports and imports of output in an economy over a certain period. It is the relationship between a nation's imports and exports...
deficit, the government budget deficit, etc. are the outputs of the simulation. The simulated values of these variables of interest are compared for different proposed policy inputs to determine which set of outcomes is most desirable.
Finance simulation
In financeFinance
"Finance" is often defined simply as the management of money or “funds” management Modern finance, however, is a family of business activity that includes the origination, marketing, and management of cash and money surrogates through a variety of capital accounts, instruments, and markets created...
, computer simulations are often used for scenario planning. Risk
Risk
Risk is the potential that a chosen action or activity will lead to a loss . The notion implies that a choice having an influence on the outcome exists . Potential losses themselves may also be called "risks"...
-adjusted net present value
Net present value
In finance, the net present value or net present worth of a time series of cash flows, both incoming and outgoing, is defined as the sum of the present values of the individual cash flows of the same entity...
, for example, is computed from well-defined but not always known (or fixed) inputs. By imitating the performance of the project under evaluation, simulation can provide a distribution of NPV over a range of discount rates
Discount
Discounting is a financial mechanism in which a debtor obtains the right to delay payments to a creditor, for a defined period of time, in exchange for a charge or fee. Essentially, the party that owes money in the present purchases the right to delay the payment until some future date...
and other variables.
Simulations are frequently used in financial training to engage participants in experiencing various historical as well as fictional situations. There are stock market simulations, portfolio simulations, risk management simulations or models and forex simulations. Such simulations are typically based on stochastic asset models. Using these simulations in a training program allows for the application of theory into a something akin to real life. As with other industries, the use of simulations can be technology or case-study driven.
Flight simulation
Flight Simulation Training Devices (FSTD) are used to train pilotsAviator
An aviator is a person who flies an aircraft. The first recorded use of the term was in 1887, as a variation of 'aviation', from the Latin avis , coined in 1863 by G. de la Landelle in Aviation Ou Navigation Aérienne...
on the ground. In comparison to training in an actual aircraft
Aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air, or, in general, the atmosphere of a planet. An aircraft counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines.Although...
, simulation based training allows for the training of maneuvers or situations that may be impractical (or even dangerous) to perform in the aircraft, while keeping the pilot and instructor in a relatively low-risk environment on the ground. For example, electrical system failures, instrument failures, hydraulic system failures, and even flight control failures can be simulated without risk to the pilots or an aircraft.
Instructors can also provide students with a higher concentration of training tasks in a given period of time than is usually possible in the aircraft. For example, conducting multiple instrument approach
Instrument approach
For aircraft operating under instrument flight rules , an instrument approach or instrument approach procedure is a series of predetermined maneuvers for the orderly transfer of an aircraft under instrument flight conditions from the beginning of the initial approach to a landing, or to a point...
es in the actual aircraft may require significant time spent repositioning the aircraft, while in a simulation, as soon as one approach has been completed, the instructor can immediately preposition the simulated aircraft to an ideal (or less than ideal) location from which to begin the next approach.
Flight simulation also provides an economic advantage over training in an actual aircraft. Once fuel, maintenance, and insurance costs are taken into account, the operating costs of an FSTD are usually substantially lower than the operating costs of the simulated aircraft. For some large transport category airplanes, the operating costs may be several times lower for the FSTD than the actual aircraft.
Some people who use simulator software, especially flight simulator software, build their own simulator at home. Some people — in order to further the realism of their homemade simulator — buy used cards and racks that run the same software used by the original machine. While this involves solving the problem of matching hardware and software — and the problem that hundreds of cards plug into many different racks — many still find that solving these problems is well worthwhile. Some are so serious about realistic simulation that they will buy real aircraft parts, like complete nose sections of written-off aircraft
Aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air, or, in general, the atmosphere of a planet. An aircraft counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines.Although...
, at aircraft boneyard
Aircraft boneyard
Aircraft boneyard is a term for a storage area for aircraft that are retired from service. Most aircraft at boneyards are either kept for storage or turned into scrap metal...
s. This permits people to simulate a hobby that they are unable to pursue in real life.
Marine simulators
Bearing resemblance to flight simulators, marine simulators train ships' personnel. The most common marine simulators include:- Ship's bridge simulators
- Engine room simulators
- Cargo handling simulators
- Communication / GMDSS simulators
- ROV simulators
Simulators like these are mostly used within maritime colleges, training institutions and navies. They often consist of a replication of a ships' bridge, with operating console(s), and a number of screens on which the virtual surroundings are projected.
Military simulations
MilitaryMilitary
A military is an organization authorized by its greater society to use lethal force, usually including use of weapons, in defending its country by combating actual or perceived threats. The military may have additional functions of use to its greater society, such as advancing a political agenda e.g...
simulations, also known informally as war games, are models in which theories of warfare can be tested and refined without the need for actual hostilities. They exist in many different forms, with varying degrees of realism. In recent times, their scope has widened to include not only military but also political and social factors (for example, the NationLab
Nationlab
The Center for Hemispheric Defense studies conducts NationLab, a computer-assisted simulation exercise that engages senior policy makers and senior students at superior studies institutes throughout Latin America and the Caribbean. It consists of a series of complex exercises designed to develop...
series of strategic exercises in Latin America. Whilst many governments make use of simulation, both individually and collaboratively, little is known about the model's specifics outside professional circles.
Robotics simulators
A robotics simulator is used to create embedded applications for a specific (or not) robot without being dependent on the 'real' robot. In some cases, these applications can be transferred to the real robot (or rebuilt) without modifications. Robotics simulators allow reproducing situations that cannot be 'created' in the real world because of cost, time, or the 'uniqueness' of a resource. A simulator also allows fast robot prototyping. Many robot simulators feature physics enginePhysics engine
A physics engine is computer software that provides an approximate simulation of certain physical systems, such as rigid body dynamics , soft body dynamics, and fluid dynamics, of use in the domains of computer graphics, video games and film. Their main uses are in video games , in which case the...
s to simulate a robot's dynamics.
Production simulation
Simulations of production systems is mainly a used to examine improvements or investments in a production system. Most often is this done using a static spreadsheet with process times and transportation times. For more sophisticated simulations Discrete Event SimulationDiscrete Event Simulation
In discrete-event simulation, the operation of a system is represented as a chronological sequence of events. Each event occurs at an instant in time and marks a change of state in the system...
(DES) is used with the advantages to simulate dynamics in the production system. A production system is very much dynamic depending on variations in manufacturing processes, assembly times, machine set-ups, breaks, breakdowns and small stoppages. There are lots of programs commonly used for discrete event simulation. They differ in usability and markets but do often share the same foundation.
There is an academic project investigating the possibilities to use production simulation software for ecology labeling, named EcoProIT
EcoProIT
EcoProIT is a project initiated at Chalmers University of Technology at the department of Product and Production Development. It was set up in the context of ecological footprint analyses, which are becoming more important in terms of marketing and legislation...
.
Sales process simulators
Simulations are useful in modeling the flow of transactions through business processes, such as in the field of sales process engineeringSales process engineering
Sales process engineering has been described as “the systematic application of scientific and mathematical principles to achieve the practical goals of a particular sales process". Selden pointed out that in this context, sales referred to the output of a process involving a variety of functions...
, to study and improve the flow of customer orders through various stages of completion (say, from an initial proposal for providing goods/services through order acceptance and installation). Such simulations can help predict the impact of how improvements in methods might impact variability, cost, labor time, and the quantity of transactions at various stages in the process. A full-featured computerized process simulator can be used to depict such models, as can simpler educational demonstrations using spreadsheet software, pennies being transferred between cups based on the roll of a die, or dipping into a tub of colored beads with a scoop.
Payment and Securities Settlement System Simulations
Simulation techniques have also been applied to payment and securities settlement systems. Among the main users are central banks who are generally responsible for the oversight of market infrastructure and entitled to contribute to the smooth functioning of the payment systems.Central Banks have been using payment system simulations to evaluate things such as the adequacy or sufficiency of liquidity available ( in the form of account balances and intraday credit limits) to participants (mainly banks) to allow efficient settlement of payments. The need for liquidity is also dependent on the availability and the type of netting procedures in the systems, thus some of the studies have a focus on system comparisons.
Another application is to evaluate risks related to events such as communication network breakdowns or the inability of participants to send payments (e.g. in case of possible bank failure). This kind of analysis falls under the concepts of Stress testing
Stress testing
Stress testing is a form of testing that is used to determine the stability of a given system or entity. It involves testing beyond normal operational capacity, often to a breaking point, in order to observe the results...
or scenario analysis
Scenario analysis
Scenario analysis is a process of analyzing possible future events by considering alternative possible outcomes . Thus, the scenario analysis, which is a main method of projections, does not try to show one exact picture of the future. Instead, it presents consciously several alternative future...
.
A common way to conduct these simulations is to replicate the settlement logics of the real payment or securities settlement systems under analysis and then use real observed payment data. In case of system comparison or system development, naturally also the other settlement logics need to be implemented.
To perform stress testing and scenario analysis, the observed data needs to be altered, e.g. some payments delayed or removed. To analyze the levels of liquidity, initial liquidity levels are varried. System comparisons (benchmarking)or evaluations of new netting algorithms or rules are performed by running simulations with a fixed set of data and varying only the system setups.
Inference is usually done by comparing the benchmark simulation results to the results of altered simulation setups by comparing indicators such as unsettled transactions or settlement delays
Space Shuttle Countdown Simulation

Kennedy Space Center
The John F. Kennedy Space Center is the NASA installation that has been the launch site for every United States human space flight since 1968. Although such flights are currently on hiatus, KSC continues to manage and operate unmanned rocket launch facilities for America's civilian space program...
(KSC) to train and certify Space Shuttle
Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle was a manned orbital rocket and spacecraft system operated by NASA on 135 missions from 1981 to 2011. The system combined rocket launch, orbital spacecraft, and re-entry spaceplane with modular add-ons...
engineers during simulated launch countdown operations. The Space Shuttle engineering community participates in a launch countdown integrated simulation before each shuttle flight. This simulation is a virtual simulation where real people interact with simulated Space Shuttle vehicle and Ground Support Equipment (GSE) hardware. The Shuttle Final Countdown Phase Simulation, also known as S0044, involves countdown processes that integrate many of the Space Shuttle vehicle and GSE systems. Some of the Shuttle systems integrated in the simulation are the Main Propulsion System, Main Engines
Space Shuttle main engine
The RS-25, otherwise known as the Space Shuttle Main Engine , is a reusable liquid-fuel rocket engine built by Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne for the Space Shuttle, running on liquid hydrogen and oxygen. Each Space Shuttle was propelled by three SSMEs mated to one powerhead...
, Solid Rocket Boosters
Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Booster
The Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Boosters were the pair of large solid rockets used by the United States' NASA Space Shuttle during the first two minutes of powered flight. Together they provided about 83% of liftoff thrust for the Space Shuttle. They were located on either side of the rusty or...
, ground Liquid Hydrogen and Liquid Oxygen, External Tank, Flight Controls, Navigation, and Avionics. The high-level objectives of the Shuttle Final Countdown Phase Simulation are:
- To demonstrate Firing Room final countdown phase operations.
- To provide training for system engineers in recognizing, reporting and evaluating system problems in a time critical environment.
- To exercise the launch teams ability to evaluate, prioritize and respond to problems in an integrated manner within a time critical environment.
- To provide procedures to be used in performing failure/recovery testing of the operations performed in the final countdown phase.
The Shuttle Final Countdown Phase Simulation takes place at the Kennedy Space Center
Kennedy Space Center
The John F. Kennedy Space Center is the NASA installation that has been the launch site for every United States human space flight since 1968. Although such flights are currently on hiatus, KSC continues to manage and operate unmanned rocket launch facilities for America's civilian space program...
Launch Control Center
Launch Control Center
The Launch Control Center is a four-story building located at NASA's Kennedy Space Center on Merritt Island, Florida used for the supervision of launches from Launch Complex 39. In practice, this means that the LCC handles all American manned space flights...
Firing Rooms. The firing room used during the simulation is the same control room where real launch countdown operations are executed. As a result, equipment used for real launch countdown operations is engaged. Command and control computers, application software, engineering plotting and trending tools, launch countdown procedure documents, launch commit criteria documents, hardware requirement documents, and any other items used by the engineering launch countdown teams during real launch countdown operations are used during the simulation.
The Space Shuttle vehicle hardware and related GSE hardware is simulated by mathematical models (written in Shuttle Ground Operations Simulator (SGOS) modeling language ) that behave and react like real hardware. During the Shuttle Final Countdown Phase Simulation, engineers command and control hardware via real application software executing in the control consoles – just as if they were commanding real vehicle hardware. However, these real software applications do not interface with real Shuttle hardware during simulations. Instead, the applications interface with mathematical model representations of the vehicle and GSE hardware. Consequently, the simulations bypass sensitive and even dangerous mechanisms while providing engineering measurements detailing how the hardware would have reacted. Since these math models interact with the command and control application software, models and simulations are also used to debug and verify the functionality of application software.
Satellite Navigation Simulators
The only true way to test GNSS receivers (commonly known as Sat-Nav's in the commercial world)is by using an RF Constellation Simulator. A receiver that may for example be used on an aircraft, can be tested under dynamic conditions without the need to take it on a real flight. The test conditions can be repeated exactly, and there is full control over all the test parameters. this is not possible in the 'real-world' using the actual signals. For testing receivers that will use the new Galileo (satellite navigation) there is no alternative, as the real signals do not yet exist.Weather Simulation
Predicting weather conditions by extrapolating/interpolating previous data is one of the real use of simulation. Most of the weather forecats use this information published by Weather buereaus. This kind of simulations help in predicting and forwarning about extreme weather conditions like the path of an active hurricane/cyclone.Numerical weather prediction
Numerical weather prediction
Numerical weather prediction uses mathematical models of the atmosphere and oceans to predict the weather based on current weather conditions. Though first attempted in the 1920s, it was not until the advent of computer simulation in the 1950s that numerical weather predictions produced realistic...
for forecasting involves complicated numeric computer models to predict weather accurately by taking many parameters in to account.
Simulation and games
Strategy gameStrategy game
A strategy game or strategic game is a game in which the players' uncoerced, and often autonomous decision-making skills have a high significance in determining the outcome...
s — both traditional and modern — may be viewed as simulations of abstracted decision-making for the purpose of training military and political leaders (see History of Go
History of Go
The game of Go originated in China in ancient times; by the 4th century BC it was a worthy pastime for a gentleman, as described in the Analects of Confucius. It reached Korea by the 5th century, in the 7th century it had reached Japan...
for an example of such a tradition, or Kriegsspiel for a more recent example).
Many other video games are simulators of some kind. Such games can simulate various aspects of reality, from business, to government
Government simulation
A government simulation or political simulation is a game that attempts to simulate the government and politics of all or part of a nation. These games may include geopolitical situations , the creation of domestic political policies, or the simulation of political campaigns...
, to construction, to piloting vehicles
Vehicle simulation game
Vehicle simulation games are a genre of video games which attempt to provide the player with a realistic interpretation of operating various kinds of vehicles. This includes automobiles, aircraft, watercraft, spacecraft, military vehicles, and a variety of other vehicles...
(see above).
Historical usage
Historically, the word had negative connotations:However, the connection between simulation and dissembling later faded out and is now only of linguistic interest.
See also
- DissimulationDissimulationDissimulation is a form of deception in which one conceals the truth. It consists of concealing the truth, or in the case of half-truths, concealing parts of the truth, like inconvenient or secret information. Dissimulation differs from simulation, in which one exhibits false information...
- EmulatorEmulatorIn computing, an emulator is hardware or software or both that duplicates the functions of a first computer system in a different second computer system, so that the behavior of the second system closely resembles the behavior of the first system...
- in silicoIn silicoIn silico is an expression used to mean "performed on computer or via computer simulation." The phrase was coined in 1989 as an analogy to the Latin phrases in vivo and in vitro which are commonly used in biology and refer to experiments done in living organisms and outside of living organisms,...
- Futures studies
- High-level emulationHigh-level emulationHigh-level emulation is an approach for construction of emulators, especially for video game consoles, which attempts to simulate the response of the system rather than accurately recreating its internal design....
- Lifelike experienceLifelike experienceLifelike is an adjective that relates to anything that simulates real life, in accordance with its laws. Its goal is to immerse individuals into what is called a lifelike experience. It gets as close as possible to real life behavior, appearance, senses, etc. therefore enabling its subject to...
- List of discrete event simulation software
- List of computer simulation software
- Mathematical modelMathematical modelA mathematical model is a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed mathematical modeling. Mathematical models are used not only in the natural sciences and engineering disciplines A mathematical model is a...
- Merger simulationMerger simulationMerger simulation is a commonly used technique when analyzing potential welfare costs and benefits of mergers between firms. Merger simulation models typically assume Differentiated Bertrand competition within a market ....
- Project Management Simulation
- Mining simulationMining SimulationA mining simulator is a system used to replicate elements of mining operations, for training or efficiency analysis. Mining simulation application can range from pure statistical analysis, to scale models, all the way to replica cabins of mining machinery mounted on pneumatic actuators surrounded...
- Molecular dynamicsMolecular dynamicsMolecular dynamics is a computer simulation of physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a period of time, giving a view of the motion of the atoms...
- Network SimulatorNetwork simulatorA network simulator is a piece of software or hardware that predicts the behavior of a network, without an actual network being present.-Uses of network simulators:Network simulators serve a variety of needs...
- Pharmacokinetics simulationPharmacokinetics SimulationPharmacokinetics simulation is a simulation method used in determining the safety levels of a drug during its development. It gives an insight to drug efficacy and safety before exposure of individuals to the new drug that might help to improve the design of a clinical trial...
- PlaceboPlaceboA placebo is a simulated or otherwise medically ineffectual treatment for a disease or other medical condition intended to deceive the recipient...
- Roleplay simulation
- Simulation languageSimulation languageA computer simulation language describes the operation of a simulation on a computer. There are two major types of simulation: continuous and discrete event though more modern languages can handle combinations. Most languages also have a graphical interface and at least simple statistical gathering...
- Similitude (model)Similitude (model)Similitude is a concept applicable to the testing of engineering models. A model is said to have similitude with the real application if the two share geometric similarity, kinematic similarity and dynamic similarity...
- Simulated realitySimulated realitySimulated reality is the proposition that reality could be simulated—perhaps by computer simulation—to a degree indistinguishable from "true" reality. It could contain conscious minds which may or may not be fully aware that they are living inside a simulation....
- Training SimulationTraining simulationA training simulation is a virtual medium through which various types of skills can be acquired. Training simulations can be used in a wide variety of genres; however they are most commonly used in corporate situations to improve business awareness and management skills...
- Web based simulationWeb based simulationThe term web-based simulation emerged in 1996, and is typically used to denote the invocation of computer simulation services over the internet, specifically through a web browser....
Further reading
- James J. Nutaro, Building Software for Simulation: Theory and Algorithms, with Applications in C++. Wiley, 2010.
- Roger D. Smith: Simulation Article, Encyclopedia of Computer Science, Nature Publishing Group, ISBN 978-0-333-77879-1.
- Roger D. Smith: "Simulation: The Engine Behind the Virtual World", eMatter, December, 1999.
- R. South (1688). "A Sermon Delivered at Christ-Church, Oxon., Before the University, Octob. 14. 1688: Prov. XII.22 Lying Lips are abomination to the Lord", pp. 519–657 in South, R., Twelve Sermons Preached Upon Several Occasions (Second Edition), Volume I, Printed by S.D. for Thomas Bennet, (London), 1697.
- Gabriel A. Wainer (2009) Discrete-Event Modeling and Simulation: a practitioner's approach. CRC Press, 2009.
- Eric Winsberg (1999) Sanctioning Models: The epistemology of simulation, in Sismondo, Sergio and Snait Gissis (eds.) (1999), Modeling and Simulation. Special Issue of Science in Context 12.
External links
- Bibliographies containing more references to be found on the website of the journal Simulation & Gaming.
- What are simulations good for? A Focalworks Q&A.

