
Space medicine
Encyclopedia
Medicine
Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness....
on astronauts in outer space
Outer space
Outer space is the void that exists between celestial bodies, including the Earth. It is not completely empty, but consists of a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles: predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium, as well as electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, and neutrinos....
whereas astronautical hygiene
Astronautical hygiene
Astronautical hygiene is the application of science and technology to the recognition and evaluation of hazards, and the prevention or control of risks to health, while working in low-gravity environments....
is the application of science and technology to the prevention or control of exposure to the hazards that may cause astronaut ill health. Both these sciences work together to ensure that astronauts work in a safe environment. The main thing is to discover how well and for how long people can survive the extreme conditions in space, and how fast they can adapt to the Earth's environment after coming back from space.
History
Hubertus StrugholdHubertus Strughold
Dr. Hubertus Strughold was a German doctor and prominent medical researcher during the early twentieth century. An emigre to the United States after World War II, he is also known as "The Father of Space Medicine". He was the author of over 180 papers in the field of space medicine...
(1898–1987), a former Nazi physician and physiologist, was brought to the United States after World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
as part of Operation Paperclip
Operation Paperclip
Operation Paperclip was the Office of Strategic Services program used to recruit the scientists of Nazi Germany for employment by the United States in the aftermath of World War II...
. He first coined the term "space medicine" in 1948 and was the first and only Professor of Space Medicine at the School of Aviation Medicine (SAM) at Randolph Air Force Base
Randolph Air Force Base
Randolph Air Force Base is a United States Air Force base located east-northeast of San Antonio, Texas. The base is under the jurisdiction of the 902d Mission Support Group, Air Education and Training Command ....
, Texas
Texas
Texas is the second largest U.S. state by both area and population, and the largest state by area in the contiguous United States.The name, based on the Caddo word "Tejas" meaning "friends" or "allies", was applied by the Spanish to the Caddo themselves and to the region of their settlement in...
. In 1949 Strughold was made director of the Department of Space Medicine at the SAM (which is now the U.S. Air Force School of Aerospace Medicine [USAFSAM] at Brooks Air Force Base, Texas). He played an important role in developing the pressure suit
Pressure suit
A pressure suit is a protective suit worn by high-altitude pilots who may fly at altitudes where the air pressure is too low for an unprotected person to survive, even breathing pure oxygen at positive pressure. Such suits may be either full-pressure or partial-pressure...
worn by early American astronauts. He was a co-founder of the Space Medicine Branch of the Aerospace Medical Association
Aerospace Medical Association
The Aerospace Medical Association is the largest professional organization in the fields of aviation, space, and environmental medicine. The AsMA membership includes aerospace and hyperbaric medicine specialists, scientists, flight nurses, physiologists, and researchers from all over the world.-...
in 1950. The aeromedical library at Brooks AFB was named after him in 1977, but later renamed because documents from the Nuremberg War Crimes Tribunal
Nuremberg Trials
The Nuremberg Trials were a series of military tribunals, held by the victorious Allied forces of World War II, most notable for the prosecution of prominent members of the political, military, and economic leadership of the defeated Nazi Germany....
linked Strughold to medical experiments in which inmates of the Dachau concentration camp were tortured and killed.
Who benefits from space medicine research?
Astronauts are not the only ones who benefit from space medicine research. Several medical products have been developed that are space spinoffs, that is practical applications for the field of medicine arising out of the space program. Because of joint research efforts between NASA, the National Institutes on Aging (a part of the National Institutes of Health), and other aging-related organizations, space exploration has benefitted a particular segment of society, seniors. Evidence of aging related medical research conducted in space was most publicly noticeable during STS-95 (See below).Medical space spinoffs (pre-Mercury through Apollo)
- Radiation therapy for the treatment of cancer. In conjunction with Cleveland Clinic, the cyclotron at NASA’s center in Cleveland, Ohio—which had been utilized for testing nuclear propulsion systems for air and space craft—was used in the first clinical trials for the treatment and evaluation of neutron radiation therapy for cancer patients.
- Foldable walkers. Made from a lightweight metal material developed by NASA for aircraft and spacecraft, foldable walkers are portable and easy to manage.
- Personal alert systems. These are emergency alert devices that can be worn by individuals who may require emergency medical or safety assistance. When a button is pushed, the device sends a signal to a remote location for help. To send the signal, the device relies on telemetry technology developed at NASA.
- CAT scans and MRIs. These devices are used by hospitals to see inside the human bodyHuman bodyThe human body is the entire structure of a human organism, and consists of a head, neck, torso, two arms and two legs.By the time the human reaches adulthood, the body consists of close to 100 trillion cells, the basic unit of life...
. Their development would not have been possible without the technology provided by NASA after it found a way to take better pictures of the Earth’s moon. - Muscle stimulator device. This device is used for ½ hour per day to prevent muscle atrophy in paralyzed individuals. It provides electrical stimulation to muscles which is equal to jogging three miles per week. Christopher Reeve used these in his therapy.
- Orthopedic evaluation tools. Equipment to evaluate posture, gait and and and balance disturbances was developed at NASA, along with a radiation-free way to measure bone flexibility using vibration.
- Diabetic foot mapping. This technique was developed at NASA’s center in Cleveland, Ohio to help monitor the effects of diabetes in feet. These efforts helped
- Foam cushioning. Special foam used for cushioning astronauts during liftoff is used in pillows and mattresses at many nursing homes and hospitals to help prevent ulcers, relieve pressure, and provide a better night’s sleep.
- Kidney dialysis machines. These machines rely on technology developed by NASA in order to process and remove toxic waste from used dialysis fluid.
- Talking wheelchairs. Paralyzed individuals who have difficulty speaking may use a talking feature on their wheelchairs which was developed by NASA to create synthesized speech for aircraft.
- Collapsible, lightweight wheelchairs. These wheelchairs are designed for portability and can be folded and put into trunks of cars. They rely on synthetic materials that NASA developed for its air and space craft
- Surgically implantable heart pacemaker. These devices depend on technologies developed by NASA for use with satellites. They communicate information about the activity of the pacemaker, such as how much time remains before the batteries need to be replaced.
- Implantable heart defibrillator. This tool continuously monitors heart activity and can deliver an electric shock to restore heartbeat regularity.
- EMS Communications. Technology used to communicate telemetry between Earth and space was developed by NASA to monitor the health of astronauts in space from the ground. Ambulances use this same technology to send information—like EKG readings—from patients in transport to hospitals. This allows faster and better treatment.
- Weightlessness. While not an invention per se, the weightlessness of space one day may allow individuals with limited mobility on Earth—even those normally confined to wheelchairs—the freedom to move about with ease. A notable individual to take advantage of weightlessness in the "Vomit Comet" during 2007 was physicist Stephen HawkingStephen HawkingStephen William Hawking, CH, CBE, FRS, FRSA is an English theoretical physicist and cosmologist, whose scientific books and public appearances have made him an academic celebrity...
.
Medical investigations in space during the Space Shuttle era
John GlennJohn Glenn
John Herschel Glenn, Jr. is a former United States Marine Corps pilot, astronaut, and United States senator who was the first American to orbit the Earth and the third American in space. Glenn was a Marine Corps fighter pilot before joining NASA's Mercury program as a member of NASA's original...
, the first American astronaut to orbit the Earth, returned with much fanfare to space once again on STS-95
STS-95
STS-95 was a Space Shuttle Discovery mission launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida on 29 October 1998. It was the 25th flight of Discovery and the 92nd mission flown since the start of the Space Shuttle program in April 1981. It was a highly publicized mission due to former Project Mercury...
at 77 years of age to confront the physiological challenges preventing long-term space travel for astronauts—loss of bone density, loss of muscle mass, balance disorders, sleep disturbances, cardiovascular changes, and immune system depression—all of which are problems confronting aging people as well as astronauts. Once again Glenn stepped forward to play an historic role in the future of space exploration, but this time he would provide new medical research in the field of gerontology as well.
Decompression illness in spaceflight
In space, astronauts use a space suitSpace suit
A space suit is a garment worn to keep an astronaut alive in the harsh environment of outer space. Space suits are often worn inside spacecraft as a safety precaution in case of loss of cabin pressure, and are necessary for extra-vehicular activity , work done outside spacecraft...
, essentially a self-contained individual spacecraft, to do spacewalks, or extra-vehicular activities
Extra-vehicular activity
Extra-vehicular activity is work done by an astronaut away from the Earth, and outside of a spacecraft. The term most commonly applies to an EVA made outside a craft orbiting Earth , but also applies to an EVA made on the surface of the Moon...
(EVAs). Spacesuits are generally inflated with 100% oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
at a total pressure that is less than a third of normal atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure is the force per unit area exerted into a surface by the weight of air above that surface in the atmosphere of Earth . In most circumstances atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point...
. Eliminating inert atmospheric components such as nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
allows the astronaut to breathe comfortably, but also have the mobility to use their hands, arms, and legs to complete required work, which would be more difficult in a higher pressure suit.
After the astronaut dons the spacesuit, air is replaced by 100% oxygen in a process called a "nitrogen purge". In order to reduce the risk of decompression sickness
Decompression sickness
Decompression sickness describes a condition arising from dissolved gases coming out of solution into bubbles inside the body on depressurization...
, the astronaut must spend several hours "pre-breathing" at an intermediate nitrogen partial pressure
Partial pressure
In a mixture of ideal gases, each gas has a partial pressure which is the pressure which the gas would have if it alone occupied the volume. The total pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas in the mixture....
, in order to let their body tissues outgas
Outgassing
Outgassing is the release of a gas that was dissolved, trapped, frozen or absorbed in some material. As an example, research has shown how the concentration of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere has sometimes been linked to ocean outgassing...
nitrogen slowly enough that bubbles are not formed. When the astronaut returns to the "shirt sleeve" environment of the spacecraft after an EVA, pressure is restored to whatever the operating pressure of that spacecraft may be, generally normal atmospheric pressure. Decompression illness
Decompression illness
Decompression Illness describes a collection of symptoms arising from decompression of the body.DCI is caused by two different mechanisms, which result in overlapping sets of symptoms. The two mechanisms are:...
in spaceflight consists of decompression sickness (DCS) and other injuries due to uncompensated changes in pressure, or barotrauma
Barotrauma
Barotrauma is physical damage to body tissues caused by a difference in pressure between an air space inside or beside the body and the surrounding fluid...
.
Decompression sickness
Decompression sicknessDecompression sickness
Decompression sickness describes a condition arising from dissolved gases coming out of solution into bubbles inside the body on depressurization...
is the injury to the tissues of the body resulting from the presence of nitrogen bubbles in the tissues and blood. This occurs due to a rapid reduction in ambient pressure causing the dissolved nitrogen to come out of solution as gas bubbles. In space the risk of DCS is significantly reduced by using a technique to wash out the nitrogen in the body’s tissues. This is achieved by breathing 100% oxygen for a specified period of time before donning the spacesuit, and is continued after a nitrogen purge. DCS may result from inadequate or interrupted pre-oxygenation time, or other factors including the astronaut’s level of hydration, physical conditioning, prior injuries and age. Other risks of DCS include inadequate nitrogen purge in the EMU, a strenuous or excessively prolonged EVA, or a loss of suit pressure. Non-EVA crewmembers may also be at risk for DCS if there is a loss of spacecraft cabin pressure.
Symptoms of DCS in space may include chest pain, shortness of breath, cough or pain with a deep breath, unusual fatigue, lightheadedness, dizziness, headache, unexplained musculoskeletal pain, tingling or numbness, extremities weakness, or visual abnormalities.
Primary treatment principles consist of in-suit repressurization to re-dissolve nitrogen bubbles, 100% oxygen to re-oxygenate tissues, and hydration to improve the circulation to injured tissues.
To date there have been no reported cases of DCS in the NASA space program.
Barotrauma
Barotrauma is the injury to the tissues of air filled spaces in the body as a result of differences in pressure between the body spaces and the ambient atmospheric pressure. Air filled spaces include the middle ears, paranasal sinuses, lungs and gastrointestinal tract. One would be predisposed by a pre-existing upper respiratory infection, nasal allergies, recurrent changing pressures, dehydration, or a poor equalizing technique.Positive pressure in the air filled spaces results from reduced barometric pressure during the depressurization phase of an EVA. It can cause abdominal distension, ear or sinus pain, decreased hearing, and dental or jaw pain. Abdominal distension can be treated with extending the abdomen, gentle massage and encourage passing flatus. Ear and sinus pressure can be relieved with passive release of positive pressure. Pretreatment for susceptible individuals can include oral and nasal decongestants, or oral and nasal steroids.
Negative pressure in air fill spaces results from increased barometric pressure during repressurization after an EVA or following a planned restoration of a reduced cabin pressure. Common symptoms include ear or sinus pain, decreased hearing, and tooth or jaw pain.
Treatment may include active positive pressure equalization of ears and sinuses, oral and nasal decongestants, or oral and nasal steroids, and appropriate pain medication if needed.
Medicine in space
The Advanced Diagnostic Ultrasound in MicrogravityAdvanced Diagnostic Ultrasound in Microgravity
The Advanced Diagnostic Ultrasound in Microgravity Project is a US Government funded study investigating strategies for applying diagnostic telemedicine to space. The Principal Investigator is Scott Dulchavsky, Chairman of Surgery at the Henry Ford Health System...
Study is funded by the National Space and Biomedical Research Institute and involves the use of ultrasound among Astronauts including former ISS Commanders Leroy Chiao
Leroy Chiao
Dr. Leroy Chiao , is an American engineer, former NASA astronaut, entrepreneur, motivational speaker and engineering consultant. Chiao flew on three shuttle flights, and was the commander of Expedition 10, where he lived on board the International Space Station from October 13, 2004 to April 24,...
and Gennady Padalka
Gennady Padalka
Gennady Ivanovich Padalka is a Russian Air Force officer and an RSA cosmonaut. As of June 2010, Gennady ranks sixth for career time in space due to his time on both Mir and the International Space Station....
who are guided by remote experts to diagnose and potentially treat hundreds of medical conditions in space. This study has a widespread impact and has been extended to cover professional and Olympic sports injuries as well as medical students. It is anticipated that remote guided ultrasound will have application on Earth in emergency and rural care situations. Findings from this study were submitted for publication to the journal Radiology
Radiology
Radiology is a medical specialty that employs the use of imaging to both diagnose and treat disease visualized within the human body. Radiologists use an array of imaging technologies to diagnose or treat diseases...
aboard the International Space Station; the first article submitted in space.
Decreased immune system functioning
Astronauts in space have weakened immune systems, which means that in addition to increased vulnerability to new exposures, viruses already present in the body—which would normally be suppressed—become active. In space, T-cells (a part of white blood cells) do not reproduce properly. T-cells that do exist are less able tofight off infection. NASA research is measuring the change in the immune systems of its astronauts as well as performing experiments with T-cells in space.
Loss of balance
Leaving and returning to Earth’s gravity causes “space sickness,” dizziness, and loss of balance in astronauts. By studying how changes can affect balance in the human body—involving the senses, the brain, the inner ear, and blood pressure—NASA hopes to develop treatments that can be used on Earth and in space to correct balance disorders. Until then, NASA’s astronauts must rely on a medication called Midodrine (an “anti-dizzy” pill that temporarily increases blood pressure) to help carry out the tasks they need to do to return home safely.Loss of bone density
Unlike people with osteoporosis, astronauts eventually regain their bone density. After a 3-4 month trip into space, it takes about 2–3 years to regain lost bone density. New techniques are being developed to help astronauts recover faster. Research in the following areas holds the potential to aid the process of growing new bone:- Diet and Exercise changes may reduce osteoporosis.
- Vibration Therapy may stimulate bone growth.
- Medication could trigger the body to produce more of the protein responsible for bone growth and formation.
Loss of muscle mass
In space, muscles in the legs, back, spine, and heart weaken and waste away because they no longer are needed to overcome gravity, just as people lose muscle when they age due to reduced physical activity. Astronauts rely on research in the following areas to build muscle and maintain body mass:- Exercise may build muscle if at least two hours a day is spent doing resistance training routines.
- Hormone supplements (hGH) may be a way to tap into the body’s natural growth signals.
- Medication may trigger the body into producing muscle growth proteins.
Orthostatic intolerance
In space, astronauts lose fluid volume—including up to 22% of their blood volume. Because it hasless blood to pump, the heart will atrophy. A weakened heart results in low blood pressure
and can produce a problem with “orthostatic tolerance,” or the body’s ability to send enough
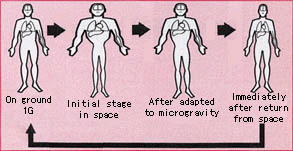
oxygen to the brain without fainting or becoming dizzy. "Under the effects of the earth's gravity, blood and other body fluids are pulled towards the lower body. When gravity is taken away or reduced during space exploration, the blood tends to collect in the upper body instead, resulting in facial edema
Edema
Edema or oedema ; both words from the Greek , oídēma "swelling"), formerly known as dropsy or hydropsy, is an abnormal accumulation of fluid beneath the skin or in one or more cavities of the body that produces swelling...
and other unwelcome side effects. Upon return to earth, the blood begins to pool in the lower extremities again, resulting in orthostatic hypotension
Orthostatic hypotension
Orthostatic hypotension, also known as postural hypotension, orthostasis, and colloquially as head rush or dizzy spell, is a form of hypotension in which a person's blood pressure suddenly falls when the person stands up or stretches. The decrease is typically greater than 20/10 mm Hg, and may be...
."
Radiation effects
Soviet cosmonaut Valentin LebedevValentin Lebedev
Valentin Vitaljevich Lebedev was a Soviet cosmonaut who made two flights into space. His stay aboard the Space Station Salyut 7 with Anatoly Berezovoy in 1982, which lasted 211 days, was recorded in the Guinness Book of Records....
, who spent 221 days in the orbit in 1982 (an absolute record for stay in Earth’s orbit), lost his eyesight to progressive cataract
Cataract
A cataract is a clouding that develops in the crystalline lens of the eye or in its envelope, varying in degree from slight to complete opacity and obstructing the passage of light...
. Lebedev stated: “I suffered from a lot of radiation in space. It was all concealed back then, during the Soviet years, but now I can say that I caused damage to my health because of that flight.”
Sleep disorders
Fifty percent of space shuttle astronauts take sleeping pills and still get two hours or less of sleep. NASA is researching two areas which may provide the keys to a better night’s sleep, asimproved sleep decreases fatigue and increases daytime productivity. A variety of methods for combating this phenomenon are constantly under discussion. A partial list of remedies would include:
- Go to sleep at the same time each night. With practice, you will (almost) always be tired and ready to hit the hay.
- MelatoninMelatoninMelatonin , also known chemically as N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine, is a naturally occurring compound found in animals, plants, and microbes...
, once thought to be an anti-aging wonder drug (this was due to the well-documented observation that as people age they gradually produce less and less of the hormone naturally). The amount of melatonin the body produces decreases linearly over a lifetime. Although the melatonin anti-aging fad was thoroughly debunked following a large number of randomized trials, it was soon in the spotlight once more due to the observation that a healthy person's normal melatonin levels varies widely throughout each day: usually, levels rise in the evening and fall in the morning. Ever since the discovery that melatonin levels are highest at bedtime, melatonin has been purported by some to be an effective sleep-aid - it is especially popular for jet-lag. Melatonin's efficacy in treating insomnia is hotly debated and therefore in the US it is sold as a dietary supplement. "These statements have not been evaluated by the FDA" is printed on the packaging even though melatonin has been studied very extensively. - RamelteonRamelteonRamelteon, marketed as Rozerem by Takeda Pharmaceuticals North America, is the first in a new class of sleep agents that selectively binds to the MT1 and MT2 receptors in the suprachiasmatic nucleus , instead of binding to GABA A receptors, such as with drugs like zolpidem, eszopiclone, and...
, a melatonin receptor agonistAgonistAn agonist is a chemical that binds to a receptor of a cell and triggers a response by that cell. Agonists often mimic the action of a naturally occurring substance...
, is a relatively new drug designed by using the melatonin molecule and the shapes of melatonin receptors as starting points. Ramelteon binds to the same M1 and M2 receptors in the suprachiasmatic nucleusSuprachiasmatic nucleusThe suprachiasmatic nucleus or nuclei, abbreviated SCN, is a tiny region on the brain's midline, situated directly above the optic chiasm. It is responsible for controlling circadian rhythms...
(the "biological clock" in the brain) as melatonin (M1 and M2 get their names from melatonin). It also may derive some of its properties from its three-times greater elimination half-life. Ramelteon is not without detractors who claim that it is no more effective than melatonin, and melatonin is less expensive by orders of magnitude. It is unclear whether Ramelteon causes its receptors to behave differently than they do when bound to melatonin, and Ramelteon may have a significantly greater affinityAffinityAffinity is a word used in a variety of fields, usually to indicate some kind of preference, relationship, or a potential or actual closeness between two entities.Articles dealing with various usages of the word: affinity include:-Commerce and law:...
for these receptors. Better information on Ramelteon's effectiveness should be available soon, and despite questions of its efficacy, the general lack of side effects makes Ramelteon one of the very few sleep medications that could potentially be safely used by astronauts. - Barbiturates and Benzodiazepines are both very strong sedatives. While they certainly would work (at least short term) in helping astronauts sleep, they have side effects that could affect the astronaut's ability to perform his/her job, especially in the "morning." This side effect renders barbiturates and benzodiazepines likely unfit as treatments for space insomnia. Narcotics and most tranquilizers also fall into this category.
- ZolpidemZolpidemZolpidem is a prescription medication used for the short-term treatment of insomnia, as well as some brain disorders. It is a short-acting nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic of the imidazopyridine class that potentiates gamma-aminobutyric acid , an inhibitory neurotransmitter, by binding to GABAA...
and ZopicloneZopicloneZopiclone is a non-benzodiazepine hypnotic agent used in the treatment of insomnia. In the United States, zopiclone is not commercially available, although its active stereoisomer, eszopiclone, is sold under the name Lunesta...
are sedative-hypnotics, best known by their trade names "Ambien" and "Lunesta". These are extremely popular sleep-aids, due in large part to their effectiveness and significantly reduced side-effect profiles vis-a-vis benzodiazepines and barbiturates. Although other drugs may be more effective in inducing sleep Zolpidem and Zopiclone essentially lack the sorts of side effects that disqualify other insomnia drugs for astronauts, for whom being able to wake up easily and quickly can be of paramount importance; astronauts who are not thinking clearly, are groggy, and are disoriented when a sudden emergency wakes thm could end up trading their grogginess for the indifference of death in seconds. Zolpidem, Zopiclone, and the like - in most people - are significantly less likely to cause drug-related daytime sleepiness, nor excessive drowsiness if woken abruptly. - Practice good sleep hygieneSleep hygieneSleep hygiene can be defined as the controlling of "all behavioural and environmental factors that precede sleep and may interfere with sleep." It is the practice of following guidelines in an attempt to ensure more restful, effective sleep which can promote daytime alertness and help treat or...
. In other words, the bed is for sleeping only; get out of bed within a few moments of waking up. Do not sit in bed watching TV or using a laptop. When one is acclimated to spending many hours awake in bed (with a laptop , ipad, your TV, etc.), it can disrupt the body's natural set of daily cycles, called the circadian rhythmCircadian rhythmA circadian rhythm, popularly referred to as body clock, is an endogenously driven , roughly 24-hour cycle in biochemical, physiological, or behavioural processes. Circadian rhythms have been widely observed in plants, animals, fungi and cyanobacteria...
. While this is less of an issue for astronauts who have very limited entertainment options in their sleeping areas, another aspect of sleep hygiene is adhering to a specific pre-sleep routine (shower, brush teeth, fold up clothing, spend 20 minutes with a trashy novel, for example); observing this sort of routine regularly can significantly improve one's sleep quality. Of course, sleep hygiene studies have all been conducted at 1G, but it seems possible (if not likely) that observing sleep hygiene would retain at least some efficacy in micro-gravity. - ModafinilModafinilModafinil is an analeptic drug manufactured by Cephalon, and is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of narcolepsy, shift work sleep disorder, and excessive daytime sleepiness associated with obstructive sleep apnea...
is a drug that is prescribed for narcolepsy and other disorders that involve excessive daytime exhaustion. It has been approved in various military situations and for astronauts thanks to its ability to stave off fatigue. It is unclear weather astronauts sometimes use the drug because they are sleep-deprived - it might only be used on spacewalks and in other high-risk situations. - Dexedrine used to be the gold-standard for fighter pilots flying long and multiple sorties in a row, and therefore may have at some point been available if astronauts were in need of a wakefulness-promoting agent stronger than coffee. Dexedrine is an amphetamine, and amphetamines can have a whole host of undesireable side effects and is addictive. Today, Modafinil has largely - if not entirely - replaced Dexedrine; reaction time and reasoning among pilots who are sleep-deprived and on dexedrine suffer, and get worse the longer the pilot stays awake. In one study, helicopter pilots that were given six-hundred milligrams of modafinil every three hours were able to perform with the same accuracy as they did at pre-deprivation levels for 40 hours without sleep; significant impairment would have been evident had the pilots been given dexedrine instead.
Spaceflight Analogues
Biomedical research in space is expensive and logistically and technically complicated, and thus limited. Conducting medical research in space alone will not provide humans with the depth of knowledge needed to ensure the safety of inter-planetary travellers. Complimentary to research in space is the use of spaceflight analogues. Analogues are particularly useful for the study of immunity, sleep, psychological factors, human performance, habitability, and telemedicine. Examples of spaceflight analogues include confinement chambers (Mars-500MARS-500
Mars-500 was an international multi-part isolation experiment simulating a manned flight to Mars. The experiment's facility was located at the Russian Academy of Sciences' Institute of Biomedical Problems in Moscow, Russia. A total of 640 experiment days were scheduled between 2007 and 2011,...
), sub-aqua habitats (NEEMO
NEEMO
NEEMO, an acronym for NASA Extreme Environment Mission Operations, is a NASA program for studying human survival in the Aquarius underwater laboratory in preparation for future space exploration....
), and Antarctic (Concordia Station
Concordia Station
Concordia Research Station, which opened in 2005, is a research facility that was built 3,233 m above sea level at a location called Dome C on the Antarctic Plateau, Antarctica...
) and Arctic (Haughton–Mars Project) stations.
Medical interventions
- Exercise to maintain muscle strength and function
- Sleep cap
- MedicationMedicationA pharmaceutical drug, also referred to as medicine, medication or medicament, can be loosely defined as any chemical substance intended for use in the medical diagnosis, cure, treatment, or prevention of disease.- Classification :...
, including hormone replacement therapyHormone replacement therapyHormone replacement therapy may refer to:*Hormone replacement therapy *Hormone replacement therapy *Hormone replacement therapy *Androgen replacement therapy -See also:...
Related degrees, areas of specialization, and certifications
- Aeromedical certification
- Aerospace medicine
- Aerospace studies
- Emergency medicine
- Internal medicine
- Occupational and preventive medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology
See also
- Artificial gravityArtificial gravityArtificial gravity is the varying of apparent gravity via artificial means, particularly in space, but also on the Earth...
- Microgravity UniversityMicrogravity UniversityMicrogravity University, also known as the Reduced Gravity Student Flight Opportunities Program is a program run by NASA which enables undergraduate university students to perform microgravity experiments aboard NASA's DC-9 aircraft at Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas.Acceptance into the...
- Spaceflight osteopeniaSpaceflight osteopeniaSpaceflight osteopenia refers to the characteristic bone loss that occurs during spaceflight. Astronauts lose an average of more than 1% bone mass per month spent in space...
- Vomit CometVomit CometA Reduced Gravity Aircraft is a type of fixed-wing aircraft that briefly provides a nearly weightless environment in which to train astronauts, conduct research and film motion pictures....
External links
- Description of space medicine
- NASA History Series Publications (many of which are online)

